| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1292333 | Journal of Power Sources | 2016 | 9 Pages |
•LiNi0.8Co0.2O2 (LNCO) shows typical layered structure by solid state reaction.•LNCO presents good ORR activity with low activation energy on BZCY electrolyte.•Proton conduction in LNCO is proven by EIS study in various moisture contents.•Fuel cell with LNCO cathode gives excellent performances, outperform typical cathodes.•A new series of cathode materials with similar structure is indicated.
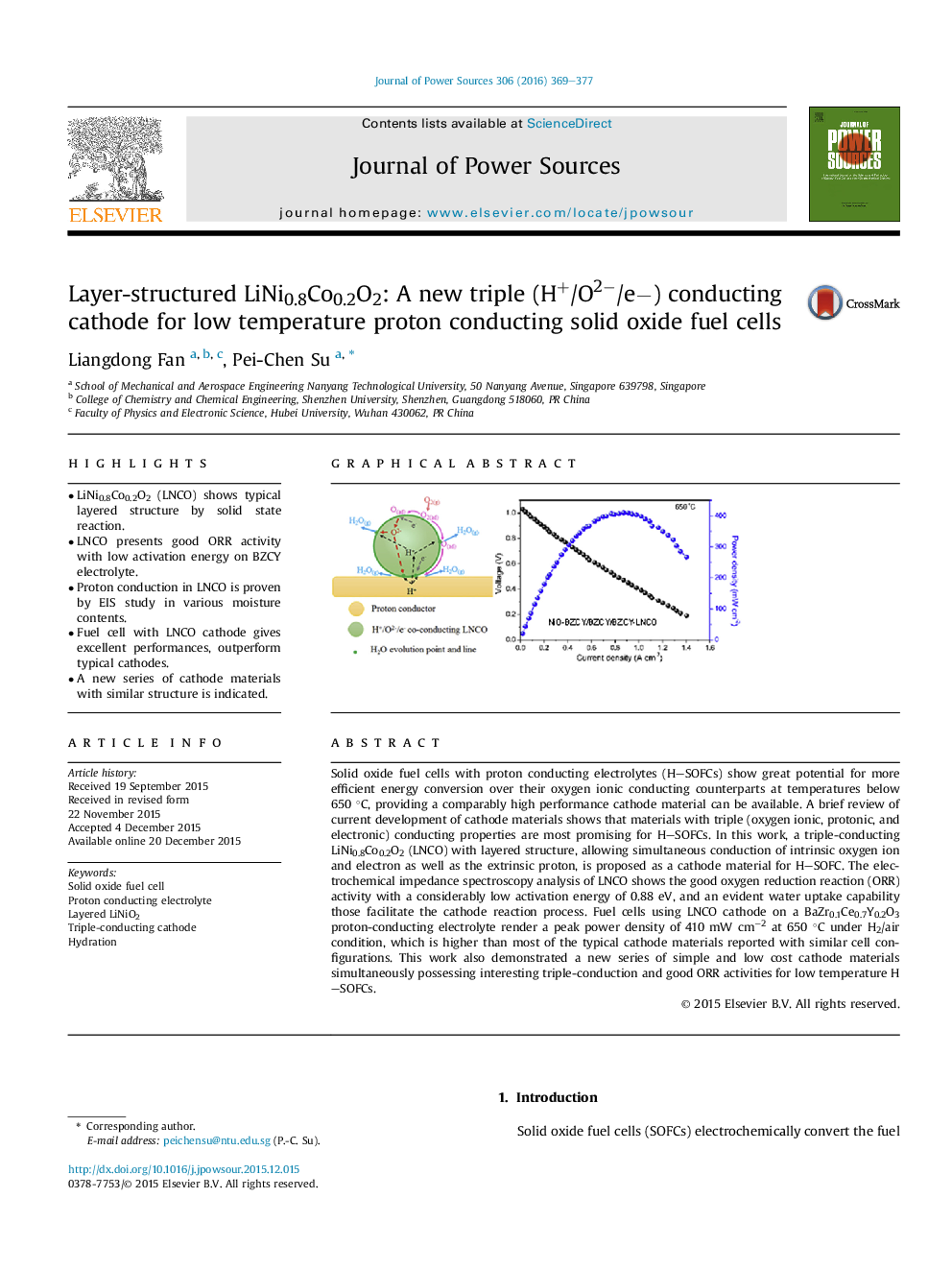
Solid oxide fuel cells with proton conducting electrolytes (H–SOFCs) show great potential for more efficient energy conversion over their oxygen ionic conducting counterparts at temperatures below 650 °C, providing a comparably high performance cathode material can be available. A brief review of current development of cathode materials shows that materials with triple (oxygen ionic, protonic, and electronic) conducting properties are most promising for H–SOFCs. In this work, a triple-conducting LiNi0.8Co0.2O2 (LNCO) with layered structure, allowing simultaneous conduction of intrinsic oxygen ion and electron as well as the extrinsic proton, is proposed as a cathode material for H–SOFC. The electrochemical impedance spectroscopy analysis of LNCO shows the good oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) activity with a considerably low activation energy of 0.88 eV, and an evident water uptake capability those facilitate the cathode reaction process. Fuel cells using LNCO cathode on a BaZr0.1Ce0.7Y0.2O3 proton-conducting electrolyte render a peak power density of 410 mW cm−2 at 650 °C under H2/air condition, which is higher than most of the typical cathode materials reported with similar cell configurations. This work also demonstrated a new series of simple and low cost cathode materials simultaneously possessing interesting triple-conduction and good ORR activities for low temperature H–SOFCs.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide