| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1292361 | Journal of Power Sources | 2016 | 7 Pages |
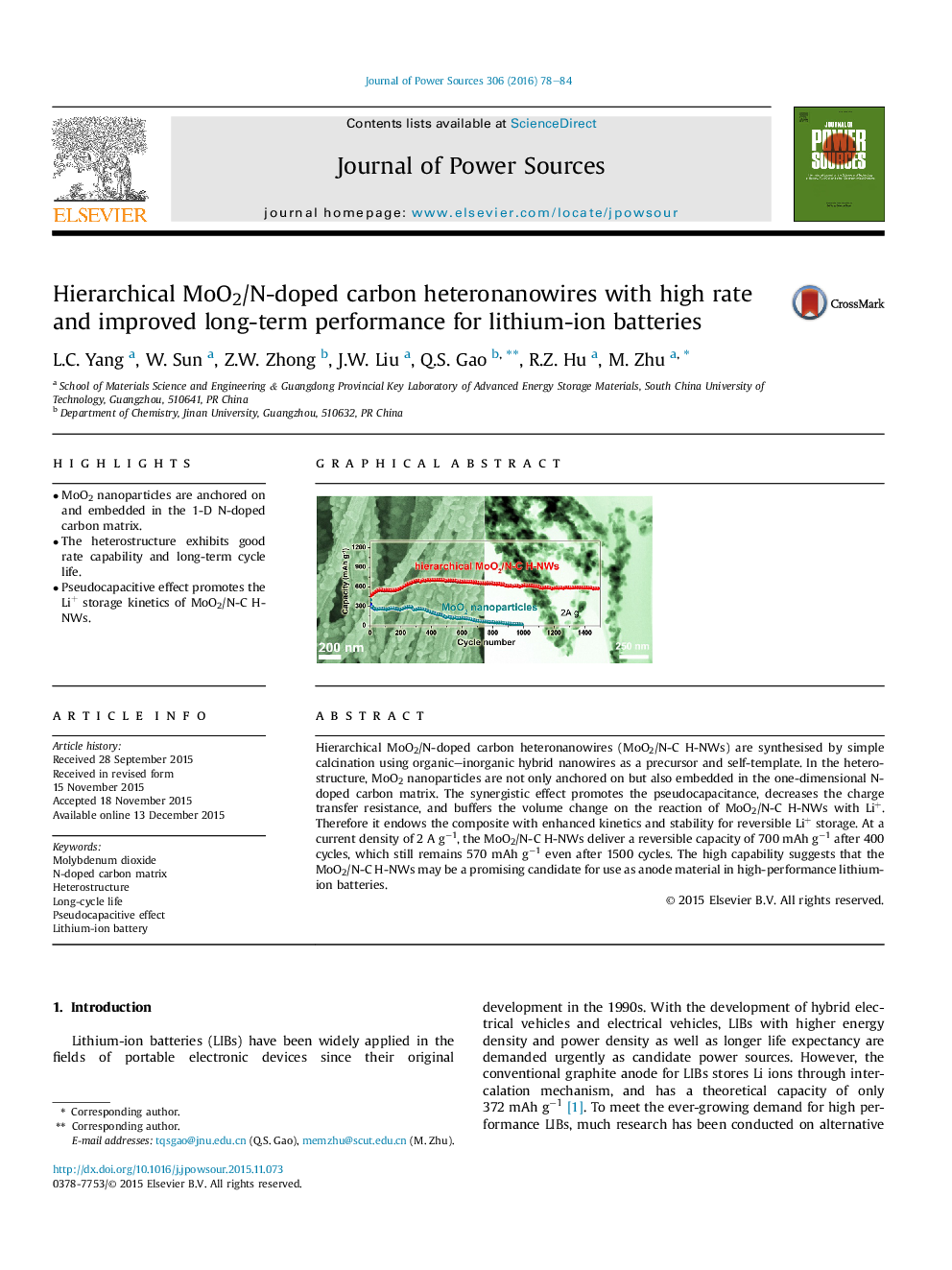
•MoO2 nanoparticles are anchored on and embedded in the 1-D N-doped carbon matrix.•The heterostructure exhibits good rate capability and long-term cycle life.•Pseudocapacitive effect promotes the Li+ storage kinetics of MoO2/N-C H-NWs.
Hierarchical MoO2/N-doped carbon heteronanowires (MoO2/N-C H-NWs) are synthesised by simple calcination using organic–inorganic hybrid nanowires as a precursor and self-template. In the heterostructure, MoO2 nanoparticles are not only anchored on but also embedded in the one-dimensional N-doped carbon matrix. The synergistic effect promotes the pseudocapacitance, decreases the charge transfer resistance, and buffers the volume change on the reaction of MoO2/N-C H-NWs with Li+. Therefore it endows the composite with enhanced kinetics and stability for reversible Li+ storage. At a current density of 2 A g−1, the MoO2/N-C H-NWs deliver a reversible capacity of 700 mAh g−1 after 400 cycles, which still remains 570 mAh g−1 even after 1500 cycles. The high capability suggests that the MoO2/N-C H-NWs may be a promising candidate for use as anode material in high-performance lithium-ion batteries.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide