| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1292780 | Journal of Power Sources | 2015 | 7 Pages |
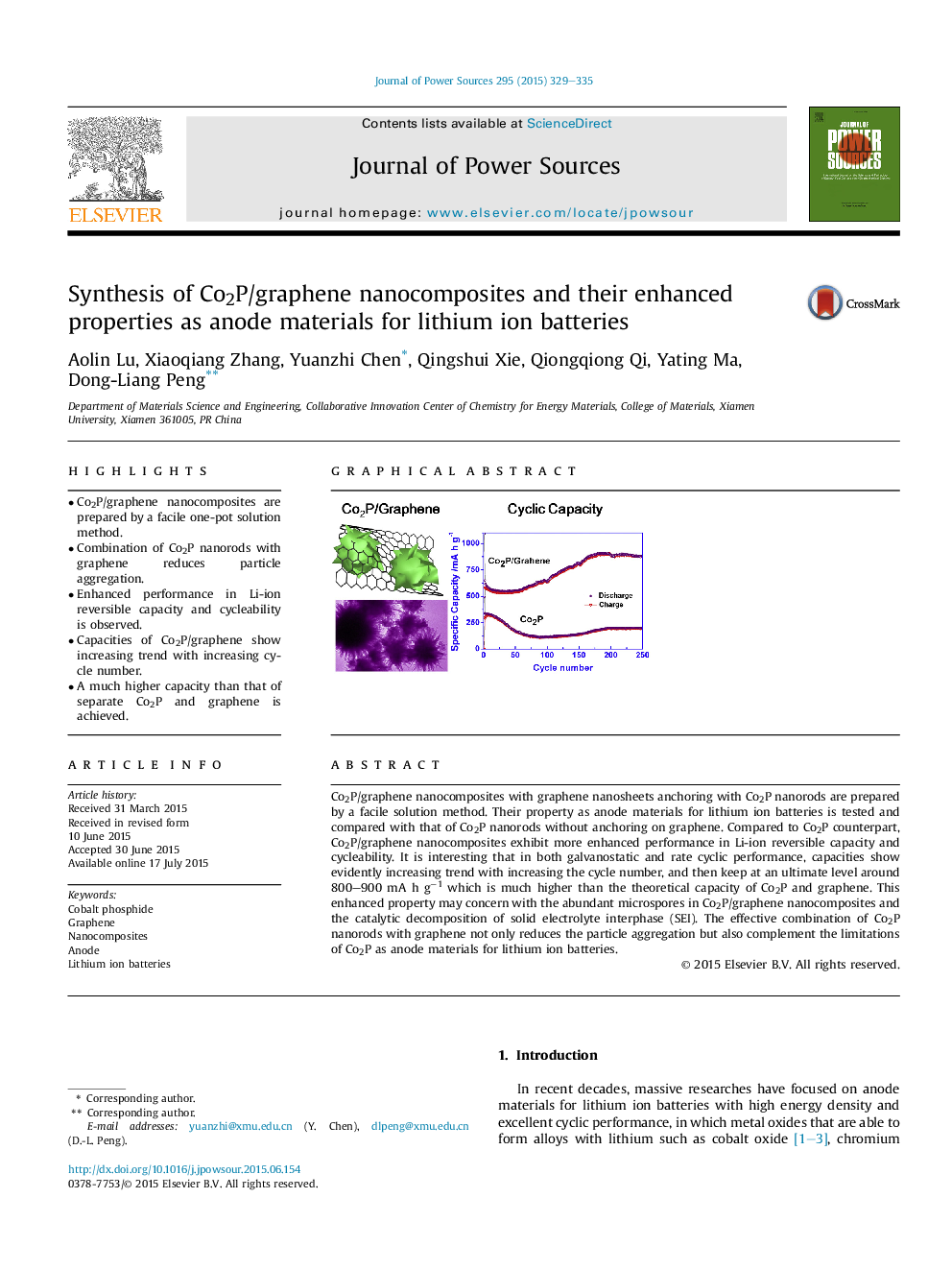
•Co2P/graphene nanocomposites are prepared by a facile one-pot solution method.•Combination of Co2P nanorods with graphene reduces particle aggregation.•Enhanced performance in Li-ion reversible capacity and cycleability is observed.•Capacities of Co2P/graphene show increasing trend with increasing cycle number.•A much higher capacity than that of separate Co2P and graphene is achieved.
Co2P/graphene nanocomposites with graphene nanosheets anchoring with Co2P nanorods are prepared by a facile solution method. Their property as anode materials for lithium ion batteries is tested and compared with that of Co2P nanorods without anchoring on graphene. Compared to Co2P counterpart, Co2P/graphene nanocomposites exhibit more enhanced performance in Li-ion reversible capacity and cycleability. It is interesting that in both galvanostatic and rate cyclic performance, capacities show evidently increasing trend with increasing the cycle number, and then keep at an ultimate level around 800–900 mA h g−1 which is much higher than the theoretical capacity of Co2P and graphene. This enhanced property may concern with the abundant microspores in Co2P/graphene nanocomposites and the catalytic decomposition of solid electrolyte interphase (SEI). The effective combination of Co2P nanorods with graphene not only reduces the particle aggregation but also complement the limitations of Co2P as anode materials for lithium ion batteries.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide