| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1292843 | Journal of Power Sources | 2015 | 8 Pages |
•N-doped hierarchically porous carbon spheres were prepared by nanocasting method.•Methyl violet was used as carbon and nitrogen precursor with mesoporous silica as template.•The catalyst exhibited high performance in ORR.•The onset potential of the catalyst was very closer to that of Pt/C catalyst.
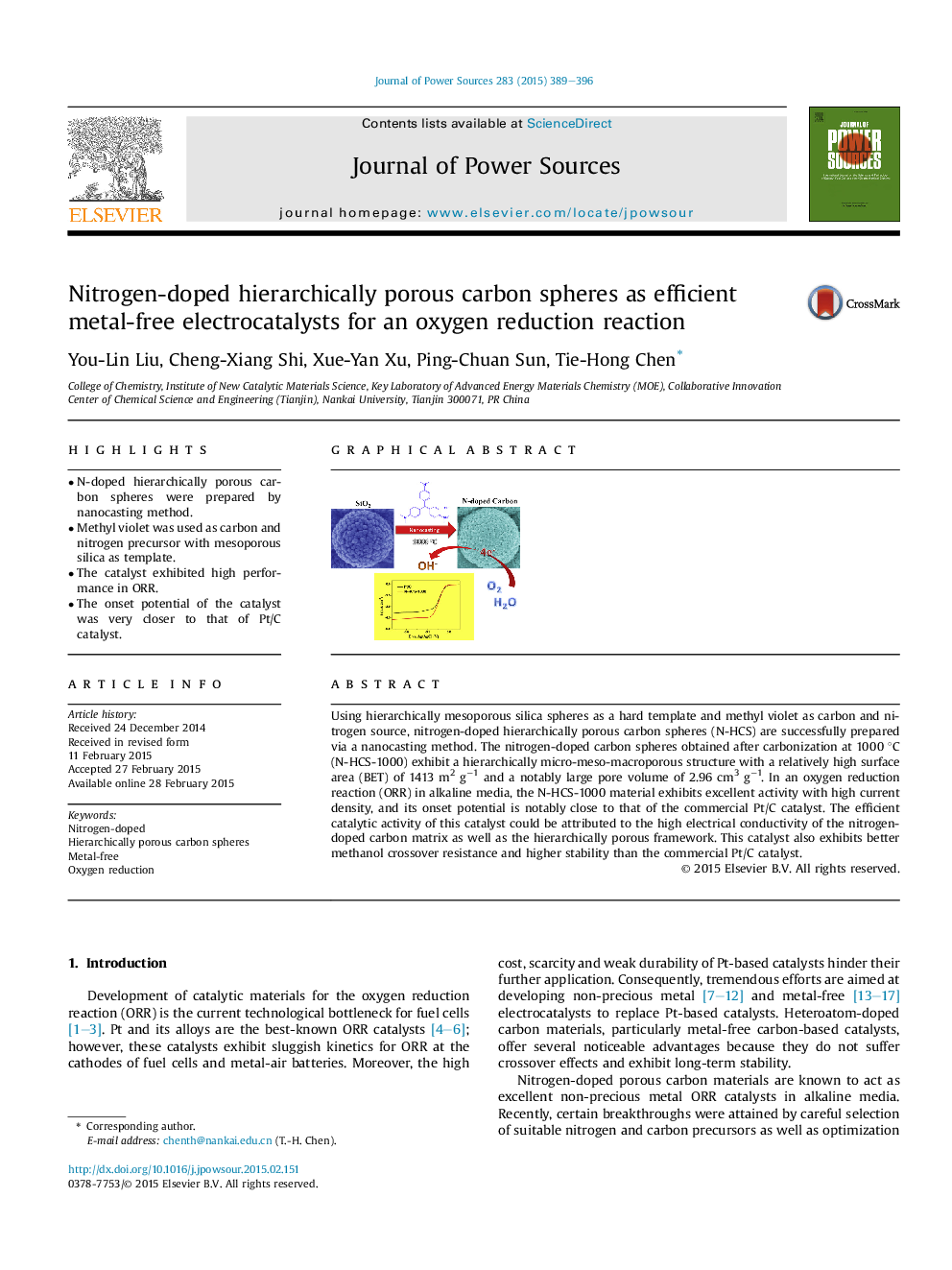
Using hierarchically mesoporous silica spheres as a hard template and methyl violet as carbon and nitrogen source, nitrogen-doped hierarchically porous carbon spheres (N-HCS) are successfully prepared via a nanocasting method. The nitrogen-doped carbon spheres obtained after carbonization at 1000 °C (N-HCS-1000) exhibit a hierarchically micro-meso-macroporous structure with a relatively high surface area (BET) of 1413 m2 g−1 and a notably large pore volume of 2.96 cm3 g−1. In an oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) in alkaline media, the N-HCS-1000 material exhibits excellent activity with high current density, and its onset potential is notably close to that of the commercial Pt/C catalyst. The efficient catalytic activity of this catalyst could be attributed to the high electrical conductivity of the nitrogen-doped carbon matrix as well as the hierarchically porous framework. This catalyst also exhibits better methanol crossover resistance and higher stability than the commercial Pt/C catalyst.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide