| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1292916 | Journal of Power Sources | 2015 | 8 Pages |
•Bimetallic Pt–Au alloyed string-bead nanochain networks are prepared by a simple one-pot wet-chemical method.•Allantoin is used as a structure-directing agent, without using any template, surfactant or seed.•The as-prepared Pt–Au nanocrystals display the improved catalytic activity for ORR and MOR.•The Pt–Au nanocrystals show high resistance to poisoning CO-like intermediates.
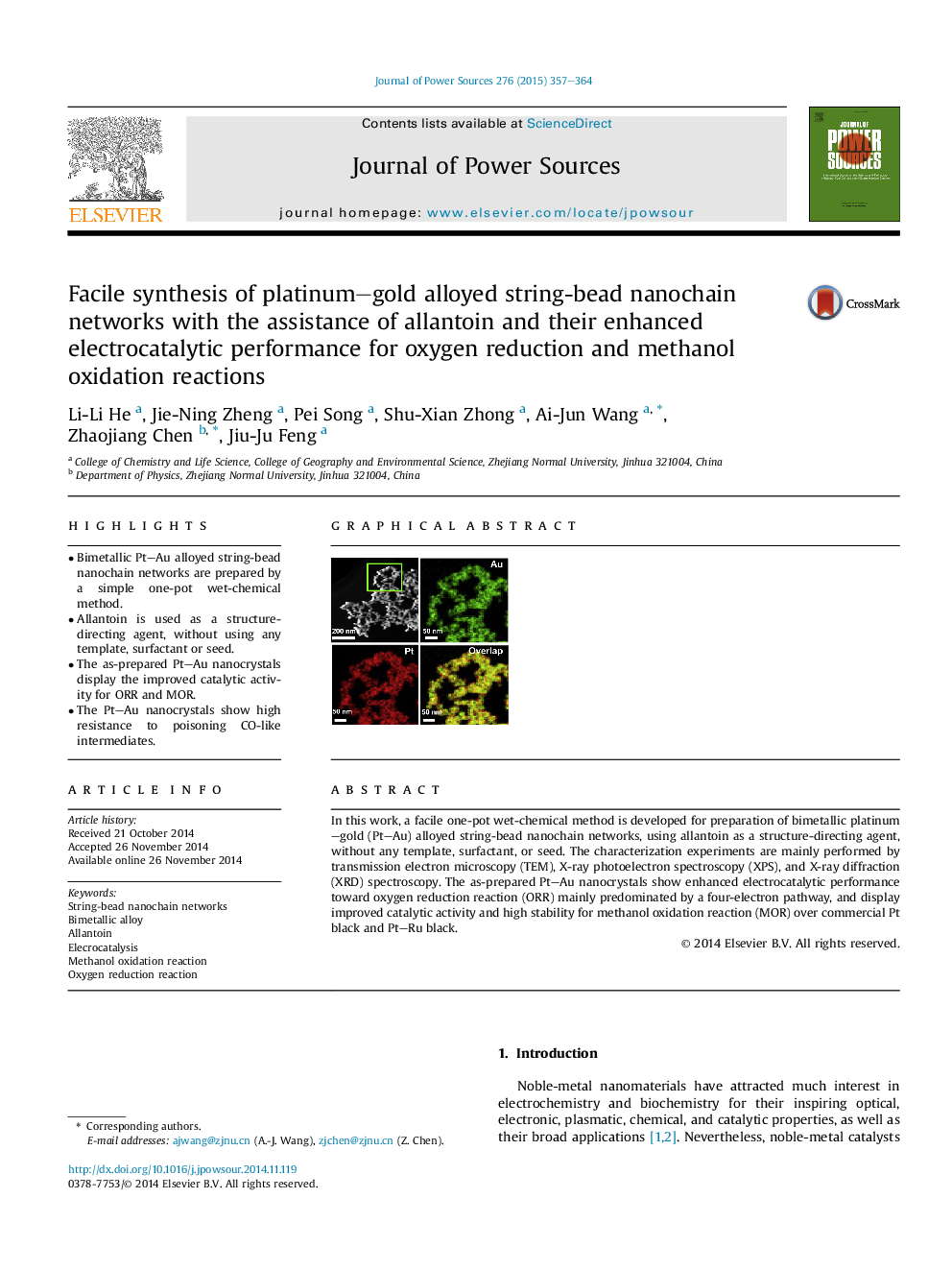
In this work, a facile one-pot wet-chemical method is developed for preparation of bimetallic platinum–gold (Pt–Au) alloyed string-bead nanochain networks, using allantoin as a structure-directing agent, without any template, surfactant, or seed. The characterization experiments are mainly performed by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and X-ray diffraction (XRD) spectroscopy. The as-prepared Pt–Au nanocrystals show enhanced electrocatalytic performance toward oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) mainly predominated by a four-electron pathway, and display improved catalytic activity and high stability for methanol oxidation reaction (MOR) over commercial Pt black and Pt–Ru black.
Graphical abstractPt–Au alloyed string-bead nanochain networks were prepared by a facile one-pot wet-chemical method using allantoin as a structure-directing agent. The as-prepared Pt–Au nanocrystals displayed improved catalytic performances for ORR and MOR, compared with commercial Pd black and Pt–Ru black.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide