| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1293001 | Journal of Power Sources | 2013 | 7 Pages |
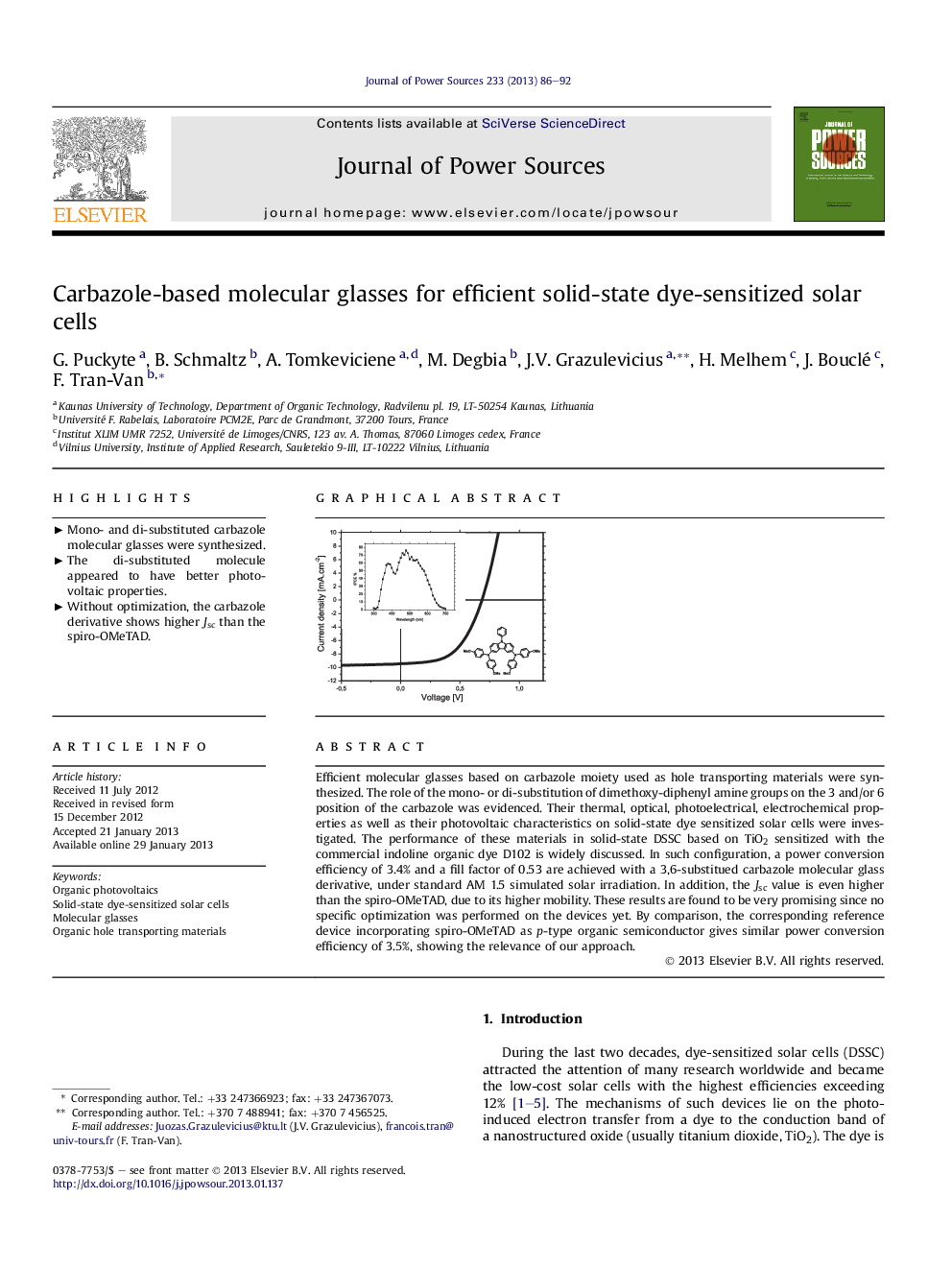
Efficient molecular glasses based on carbazole moiety used as hole transporting materials were synthesized. The role of the mono- or di-substitution of dimethoxy-diphenyl amine groups on the 3 and/or 6 position of the carbazole was evidenced. Their thermal, optical, photoelectrical, electrochemical properties as well as their photovoltaic characteristics on solid-state dye sensitized solar cells were investigated. The performance of these materials in solid-state DSSC based on TiO2 sensitized with the commercial indoline organic dye D102 is widely discussed. In such configuration, a power conversion efficiency of 3.4% and a fill factor of 0.53 are achieved with a 3,6-substitued carbazole molecular glass derivative, under standard AM 1.5 simulated solar irradiation. In addition, the Jsc value is even higher than the spiro-OMeTAD, due to its higher mobility. These results are found to be very promising since no specific optimization was performed on the devices yet. By comparison, the corresponding reference device incorporating spiro-OMeTAD as p-type organic semiconductor gives similar power conversion efficiency of 3.5%, showing the relevance of our approach.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► Mono- and di-substituted carbazole molecular glasses were synthesized. ► The di-substituted molecule appeared to have better photovoltaic properties. ► Without optimization, the carbazole derivative shows higher Jsc than the spiro-OMeTAD.