| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1365357 | Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters | 2008 | 4 Pages |
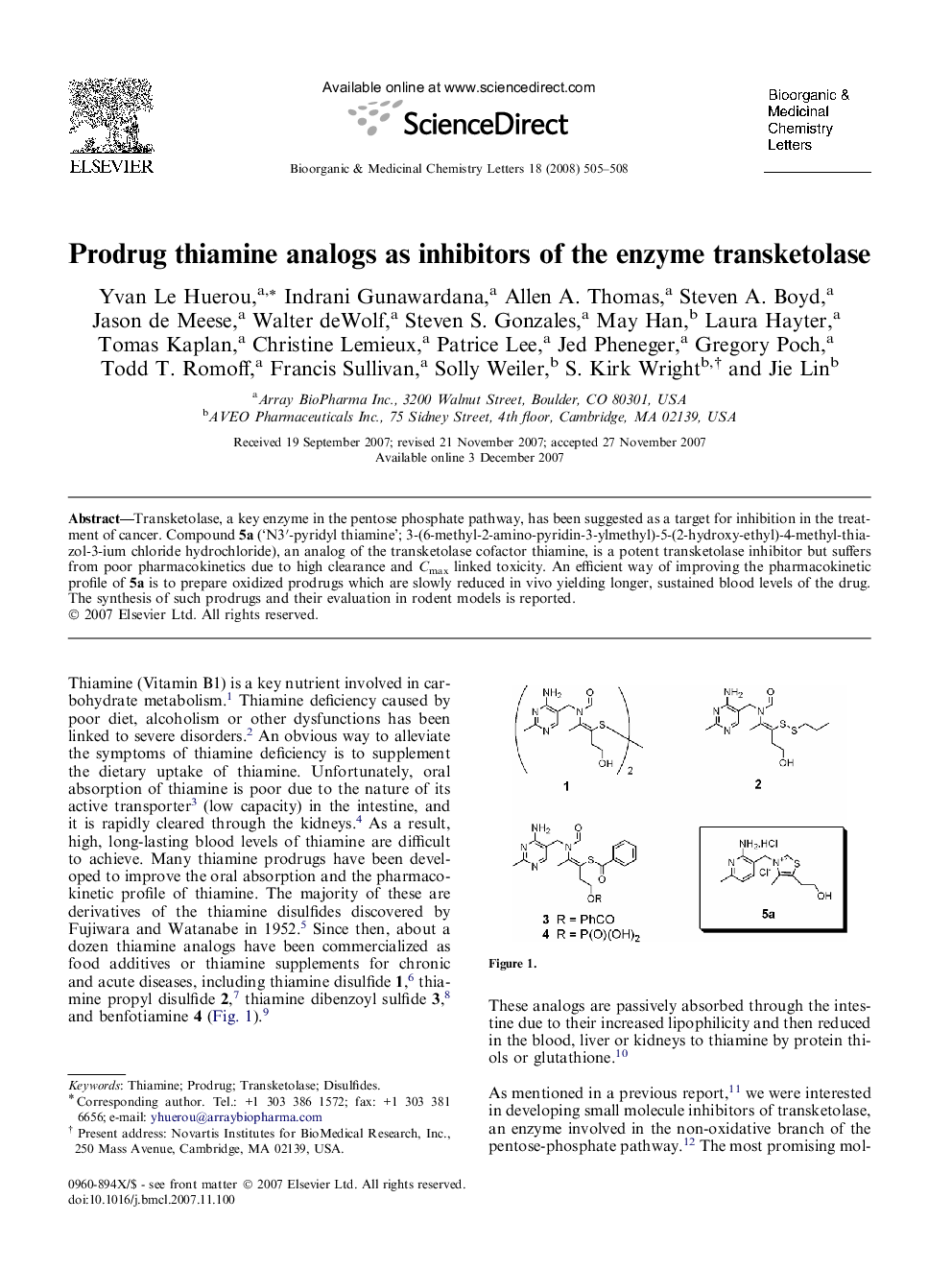
Transketolase, a key enzyme in the pentose phosphate pathway, has been suggested as a target for inhibition in the treatment of cancer. Compound 5a (‘N3′-pyridyl thiamine’; 3-(6-methyl-2-amino-pyridin-3-ylmethyl)-5-(2-hydroxy-ethyl)-4-methyl-thiazol-3-ium chloride hydrochloride), an analog of the transketolase cofactor thiamine, is a potent transketolase inhibitor but suffers from poor pharmacokinetics due to high clearance and Cmax linked toxicity. An efficient way of improving the pharmacokinetic profile of 5a is to prepare oxidized prodrugs which are slowly reduced in vivo yielding longer, sustained blood levels of the drug. The synthesis of such prodrugs and their evaluation in rodent models is reported.
Graphical abstractSynthesis of prodrugs of the transketolase inhibitor 5a and their evaluation in murine pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic models.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide