| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1371645 | Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters | 2010 | 6 Pages |
Abstract
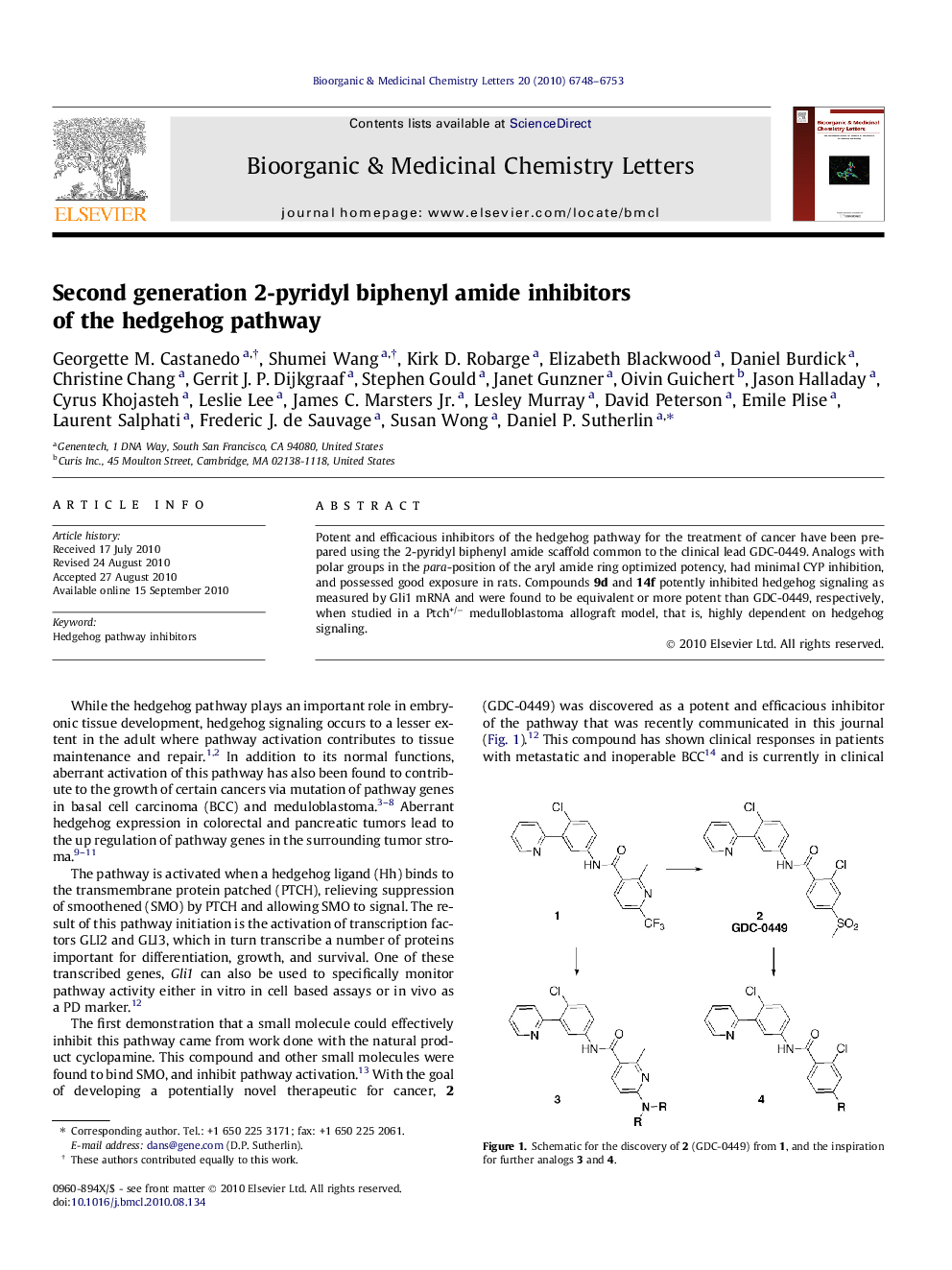
Potent and efficacious inhibitors of the hedgehog pathway for the treatment of cancer have been prepared using the 2-pyridyl biphenyl amide scaffold common to the clinical lead GDC-0449. Analogs with polar groups in the para-position of the aryl amide ring optimized potency, had minimal CYP inhibition, and possessed good exposure in rats. Compounds 9d and 14f potently inhibited hedgehog signaling as measured by Gli1 mRNA and were found to be equivalent or more potent than GDC-0449, respectively, when studied in a Ptch+/− medulloblastoma allograft model, that is, highly dependent on hedgehog signaling.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide
Related Topics
Physical Sciences and Engineering
Chemistry
Organic Chemistry
Authors
Georgette M. Castanedo, Shumei Wang, Kirk D. Robarge, Elizabeth Blackwood, Daniel Burdick, Christine Chang, Gerrit J.P. Dijkgraaf, Stephen Gould, Janet Gunzner, Oivin Guichert, Jason Halladay, Cyrus Khojasteh, Leslie Lee, James C. Marsters Jr.,