| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1372766 | Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters | 2011 | 4 Pages |
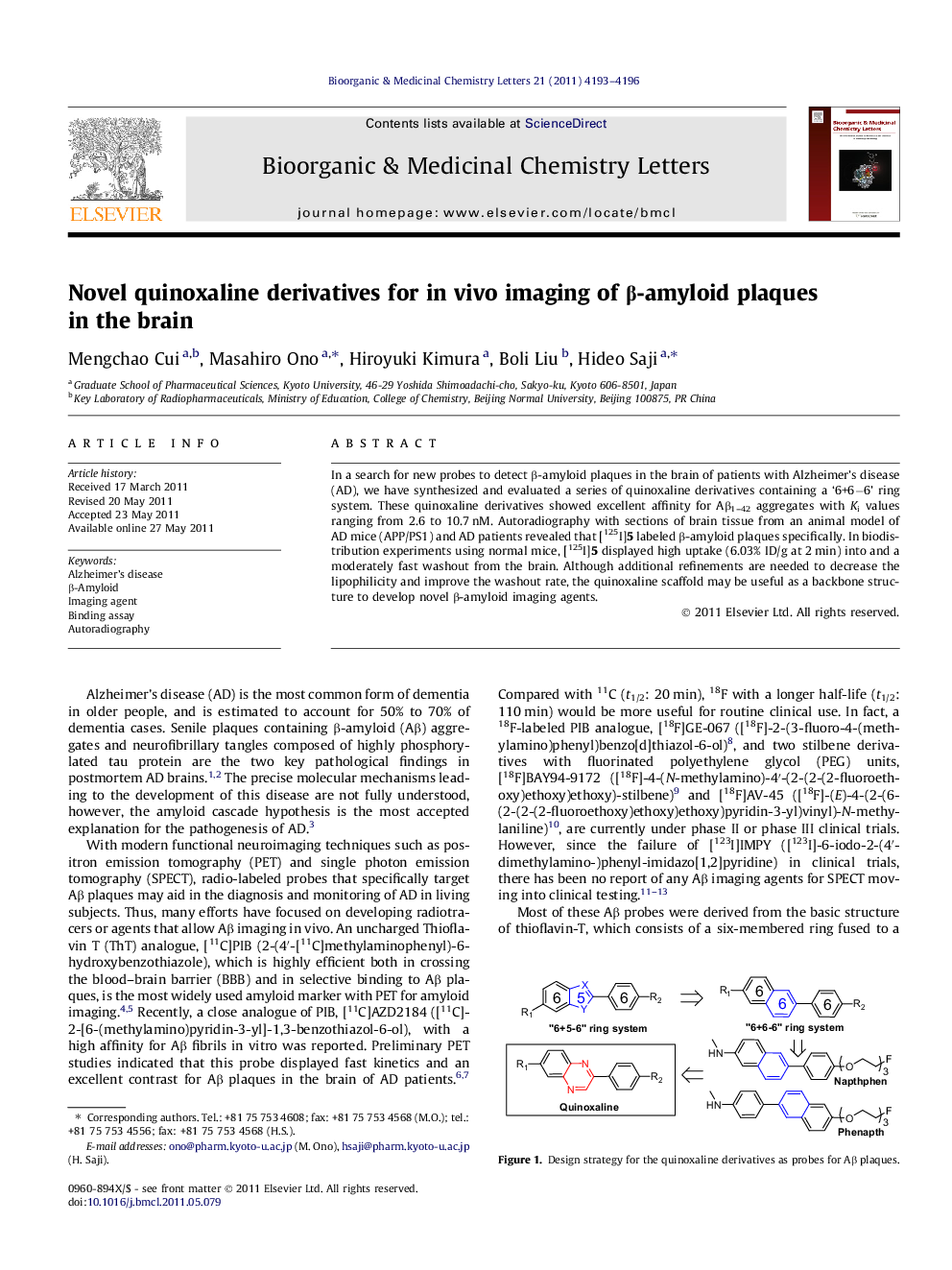
In a search for new probes to detect β-amyloid plaques in the brain of patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD), we have synthesized and evaluated a series of quinoxaline derivatives containing a ‘6+6−6’ ring system. These quinoxaline derivatives showed excellent affinity for Aβ1–42 aggregates with Ki values ranging from 2.6 to 10.7 nM. Autoradiography with sections of brain tissue from an animal model of AD mice (APP/PS1) and AD patients revealed that [125I]5 labeled β-amyloid plaques specifically. In biodistribution experiments using normal mice, [125I]5 displayed high uptake (6.03% ID/g at 2 min) into and a moderately fast washout from the brain. Although additional refinements are needed to decrease the lipophilicity and improve the washout rate, the quinoxaline scaffold may be useful as a backbone structure to develop novel β-amyloid imaging agents.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide