| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1375025 | Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters | 2009 | 4 Pages |
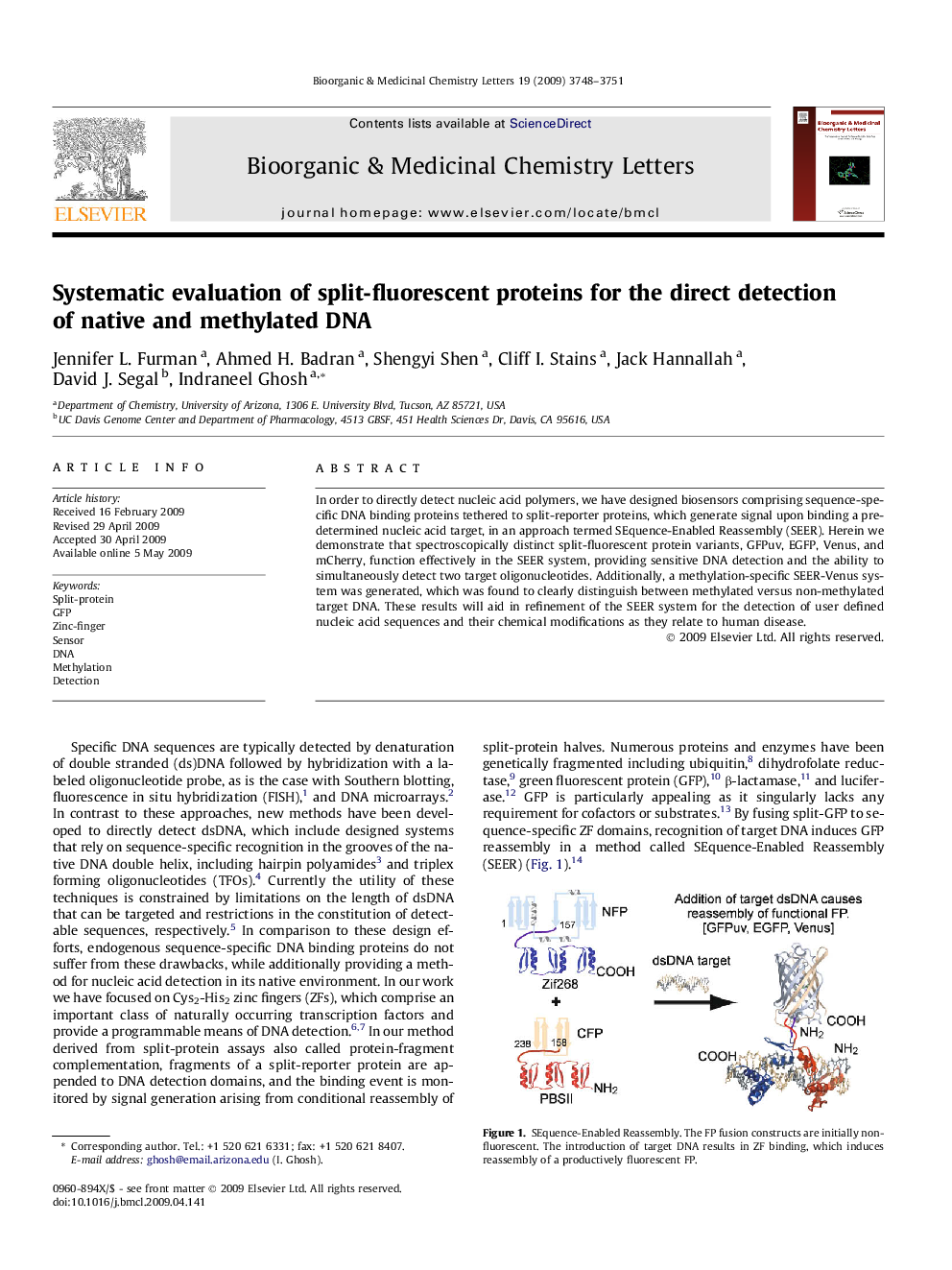
In order to directly detect nucleic acid polymers, we have designed biosensors comprising sequence-specific DNA binding proteins tethered to split-reporter proteins, which generate signal upon binding a predetermined nucleic acid target, in an approach termed SEquence-Enabled Reassembly (SEER). Herein we demonstrate that spectroscopically distinct split-fluorescent protein variants, GFPuv, EGFP, Venus, and mCherry, function effectively in the SEER system, providing sensitive DNA detection and the ability to simultaneously detect two target oligonucleotides. Additionally, a methylation-specific SEER-Venus system was generated, which was found to clearly distinguish between methylated versus non-methylated target DNA. These results will aid in refinement of the SEER system for the detection of user defined nucleic acid sequences and their chemical modifications as they relate to human disease.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide