| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1378273 | Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters | 2007 | 4 Pages |
Abstract
Investigation of halogen substitution in lead compound 1 has led to the identification of analogues which combine high affinity for 5-HT1A receptors and potent serotonin reuptake inhibitory activity. Several compounds show an improved selectivity over 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D receptors and a superior pharmacokinetic profile in the rat.
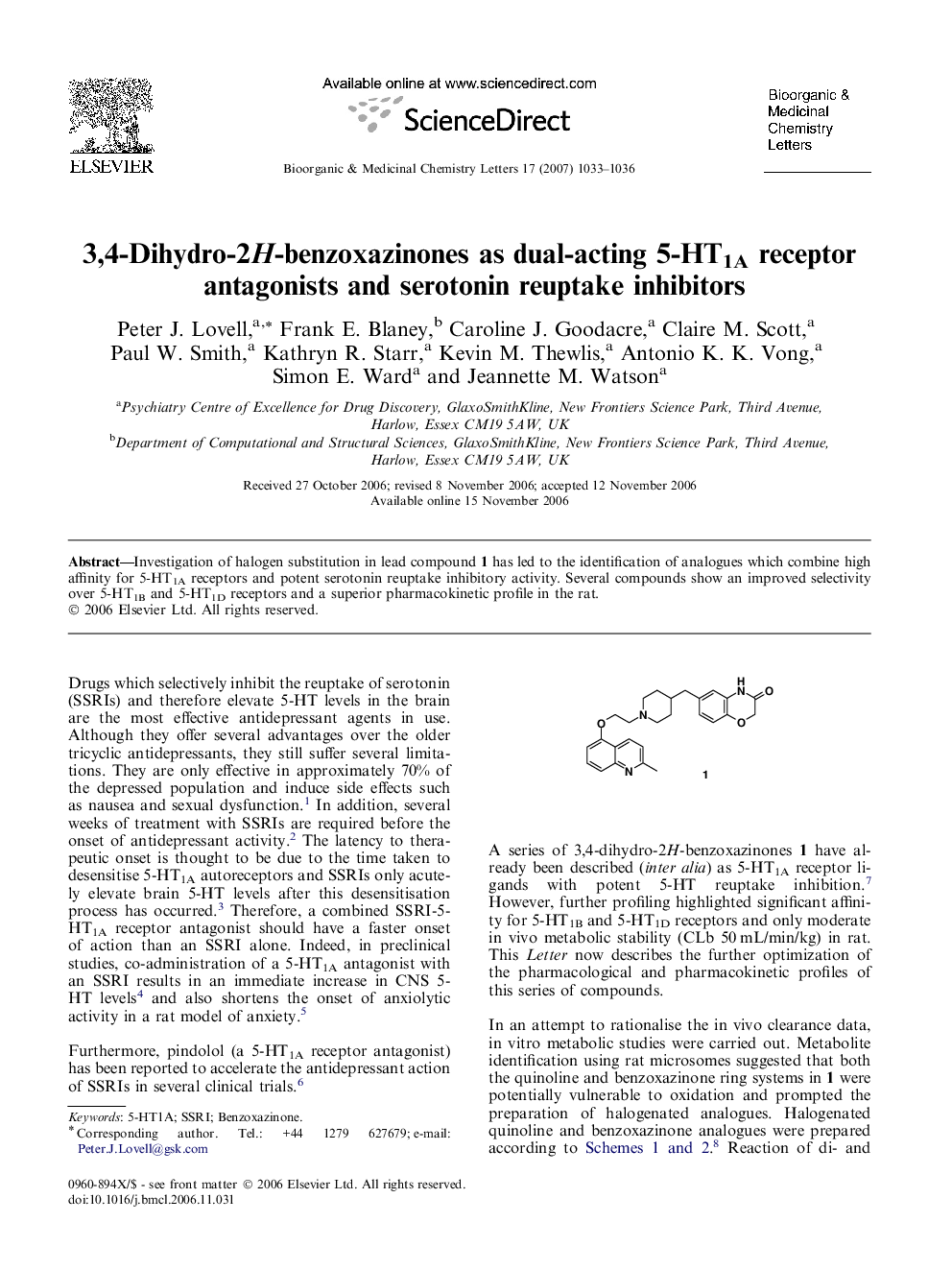
Graphical abstractInvestigation of halogen substitution in lead compound 1 has led to the identification of analogues which combine high affinity for 5-HT1A receptors and potent serotonin reuptake inhibitory activity. Several compounds show an improved selectivity over 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D receptors and a superior pharmacokinetic profile in the rat.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide
Keywords
Related Topics
Physical Sciences and Engineering
Chemistry
Organic Chemistry
Authors
Peter J. Lovell, Frank E. Blaney, Caroline J. Goodacre, Claire M. Scott, Paul W. Smith, Kathryn R. Starr, Kevin M. Thewlis, Antonio K.K. Vong, Simon E. Ward, Jeannette M. Watson,