| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1378287 | Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters | 2007 | 5 Pages |
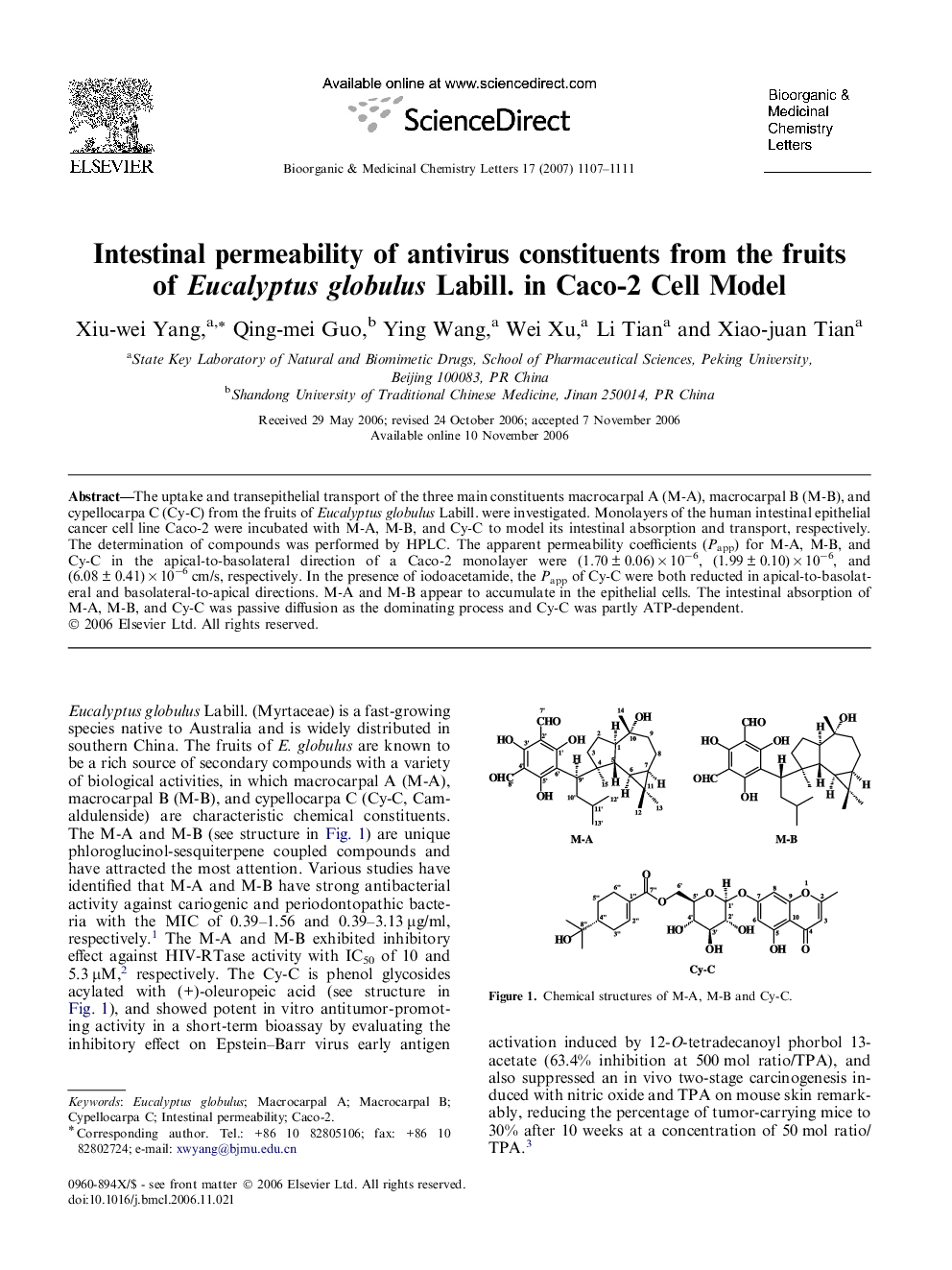
The uptake and transepithelial transport of the three main constituents macrocarpal A (M-A), macrocarpal B (M-B), and cypellocarpa C (Cy-C) from the fruits of Eucalyptus globulus Labill. were investigated. Monolayers of the human intestinal epithelial cancer cell line Caco-2 were incubated with M-A, M-B, and Cy-C to model its intestinal absorption and transport, respectively. The determination of compounds was performed by HPLC. The apparent permeability coefficients (Papp) for M-A, M-B, and Cy-C in the apical-to-basolateral direction of a Caco-2 monolayer were (1.70 ± 0.06) × 10−6, (1.99 ± 0.10) × 10−6, and (6.08 ± 0.41) × 10−6 cm/s, respectively. In the presence of iodoacetamide, the Papp of Cy-C were both reducted in apical-to-basolateral and basolateral-to-apical directions. M-A and M-B appear to accumulate in the epithelial cells. The intestinal absorption of M-A, M-B, and Cy-C was passive diffusion as the dominating process and Cy-C was partly ATP-dependent.
Graphical abstractThe intestinal absorption of M-A, M-B, and Cy-C was passive diffusion as the dominating process and Cy-C was partly ATP-dependent.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide