| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1378888 | Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters | 2006 | 5 Pages |
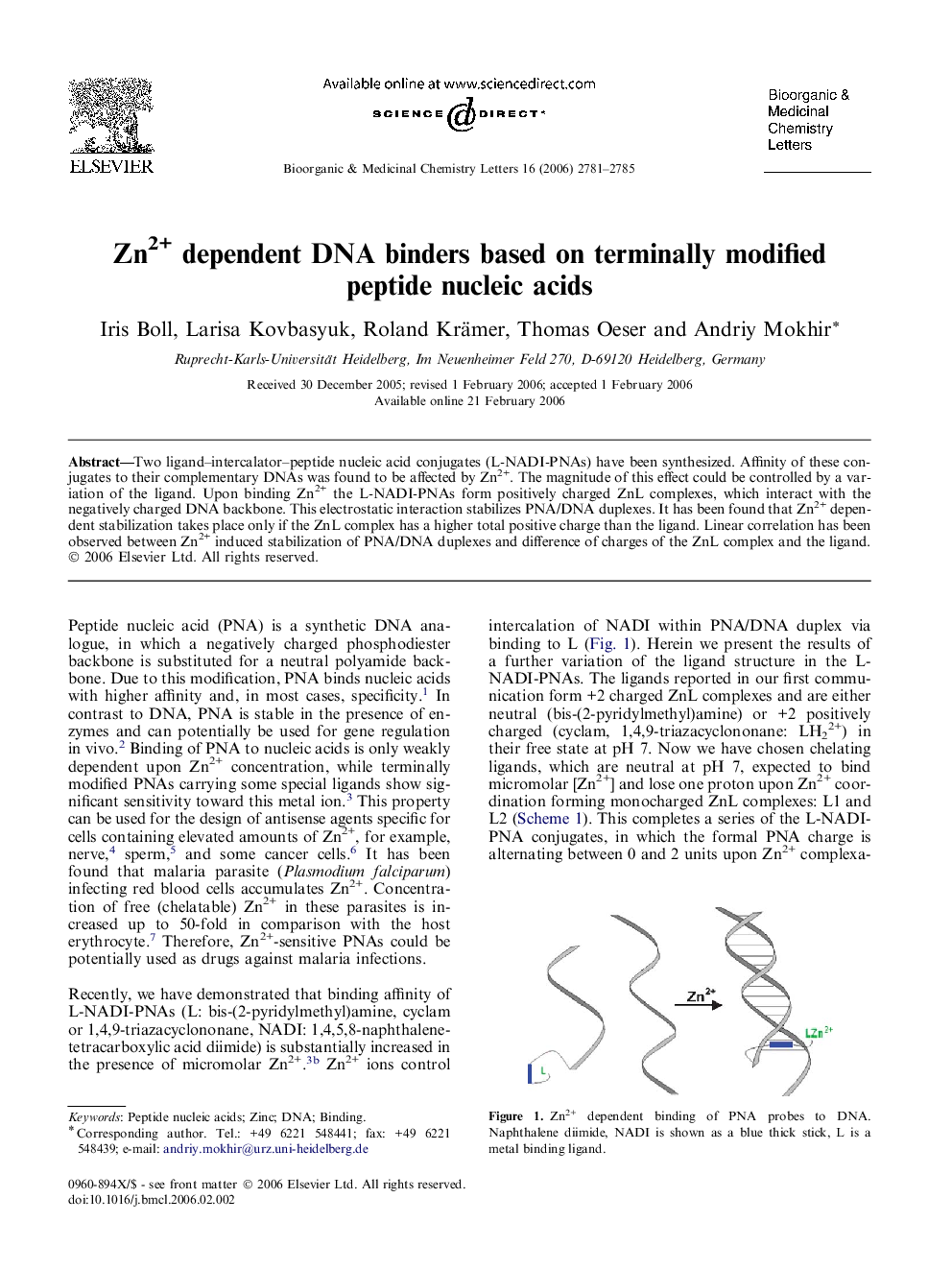
Two ligand–intercalator–peptide nucleic acid conjugates (L-NADI-PNAs) have been synthesized. Affinity of these conjugates to their complementary DNAs was found to be affected by Zn2+. The magnitude of this effect could be controlled by a variation of the ligand. Upon binding Zn2+ the L-NADI-PNAs form positively charged ZnL complexes, which interact with the negatively charged DNA backbone. This electrostatic interaction stabilizes PNA/DNA duplexes. It has been found that Zn2+ dependent stabilization takes place only if the ZnL complex has a higher total positive charge than the ligand. Linear correlation has been observed between Zn2+ induced stabilization of PNA/DNA duplexes and difference of charges of the ZnL complex and the ligand.
Graphical abstractIt has been found that affinity of a ligand–intercalator–peptide nucleic acid conjugate to its complementary DNA is affected by Zn2+ due to electrostatic interaction between the positively charged Zn(ligand) complex and the phosphodiester backbone of the DNA.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide