| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 145279 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2016 | 10 Pages |
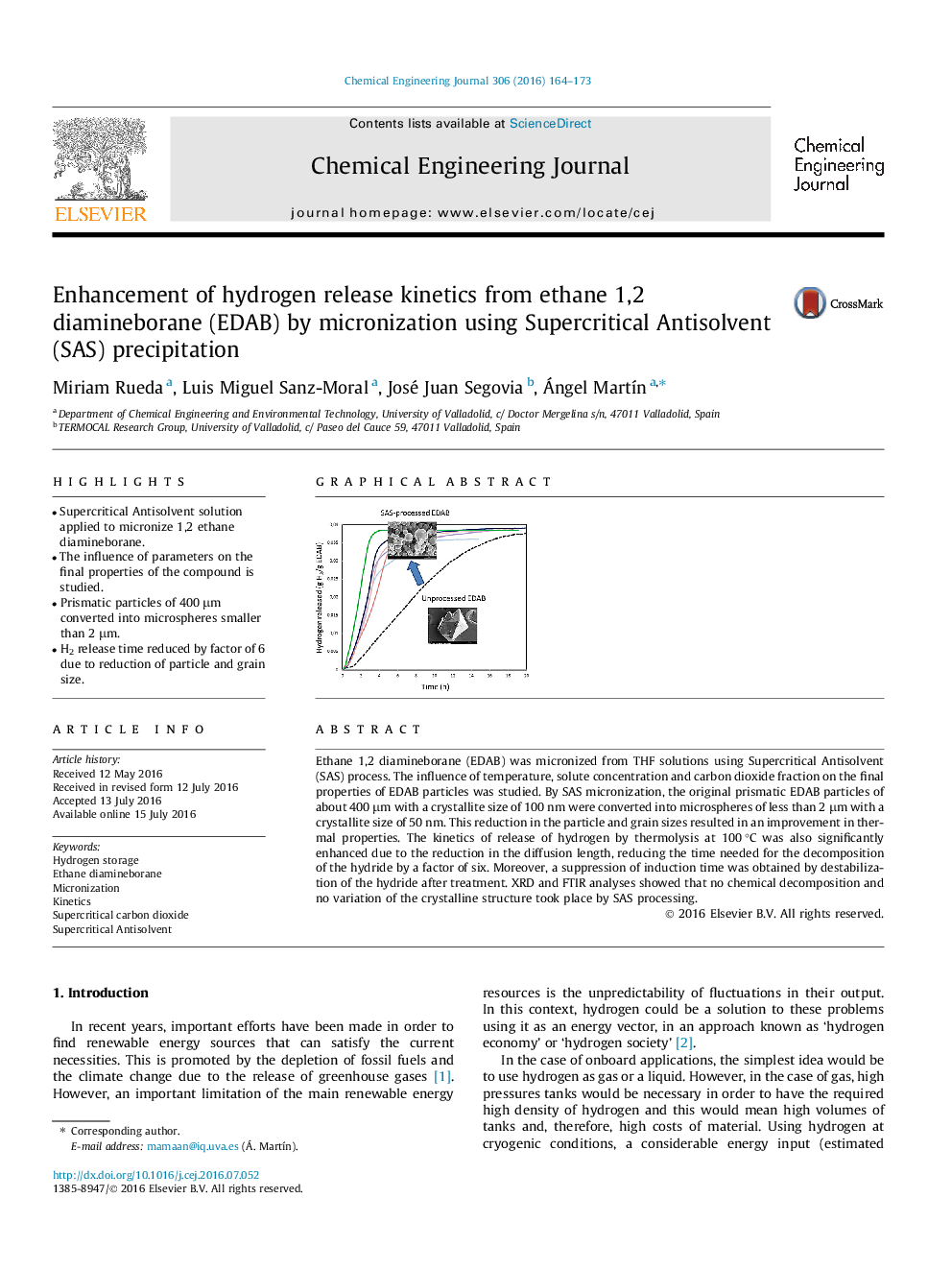
•Supercritical Antisolvent solution applied to micronize 1,2 ethane diamineborane.•The influence of parameters on the final properties of the compound is studied.•Prismatic particles of 400 μm converted into microspheres smaller than 2 μm.•H2 release time reduced by factor of 6 due to reduction of particle and grain size.
Ethane 1,2 diamineborane (EDAB) was micronized from THF solutions using Supercritical Antisolvent (SAS) process. The influence of temperature, solute concentration and carbon dioxide fraction on the final properties of EDAB particles was studied. By SAS micronization, the original prismatic EDAB particles of about 400 μm with a crystallite size of 100 nm were converted into microspheres of less than 2 μm with a crystallite size of 50 nm. This reduction in the particle and grain sizes resulted in an improvement in thermal properties. The kinetics of release of hydrogen by thermolysis at 100 °C was also significantly enhanced due to the reduction in the diffusion length, reducing the time needed for the decomposition of the hydride by a factor of six. Moreover, a suppression of induction time was obtained by destabilization of the hydride after treatment. XRD and FTIR analyses showed that no chemical decomposition and no variation of the crystalline structure took place by SAS processing.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide