| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 145409 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2016 | 11 Pages |
•Co-network hydrogels of covalent epoxy and crystallite PVA are synthesized.•Incorporating epoxy into PVA network greatly improves its mechanical properties.•Hysteresis is shown for PVA/epoxy hydrogels due to the structural transition.
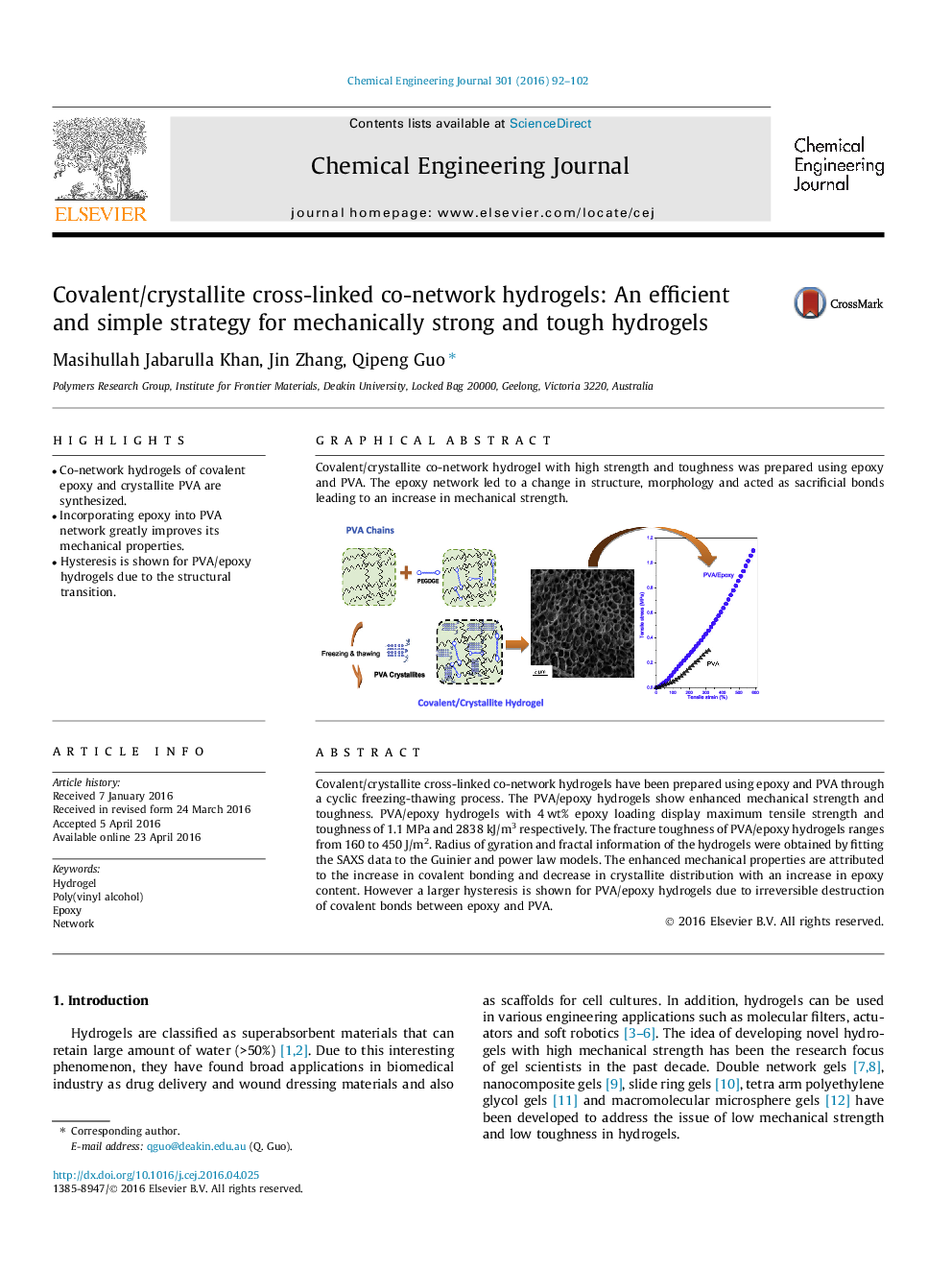
Covalent/crystallite cross-linked co-network hydrogels have been prepared using epoxy and PVA through a cyclic freezing-thawing process. The PVA/epoxy hydrogels show enhanced mechanical strength and toughness. PVA/epoxy hydrogels with 4 wt% epoxy loading display maximum tensile strength and toughness of 1.1 MPa and 2838 kJ/m3 respectively. The fracture toughness of PVA/epoxy hydrogels ranges from 160 to 450 J/m2. Radius of gyration and fractal information of the hydrogels were obtained by fitting the SAXS data to the Guinier and power law models. The enhanced mechanical properties are attributed to the increase in covalent bonding and decrease in crystallite distribution with an increase in epoxy content. However a larger hysteresis is shown for PVA/epoxy hydrogels due to irreversible destruction of covalent bonds between epoxy and PVA.
Graphical abstractCovalent/crystallite co-network hydrogel with high strength and toughness was prepared using epoxy and PVA. The epoxy network led to a change in structure, morphology and acted as sacrificial bonds leading to an increase in mechanical strength.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide