| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 145420 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2016 | 7 Pages |
•The BTMSH/TEOS hybrid aerogels were coated onto Al2O3 tubular membrane supports.•The BTMSH/TEOS aerogel membranes allow efficient carbon dioxide absorption into amines.•The BTMSH/TEOS aerogel membranes are durable and reusable for CO2 capture in power plants.•The BTMSH/TEOS aerogel membranes show promise for large-scale CO2 capture in power plants.
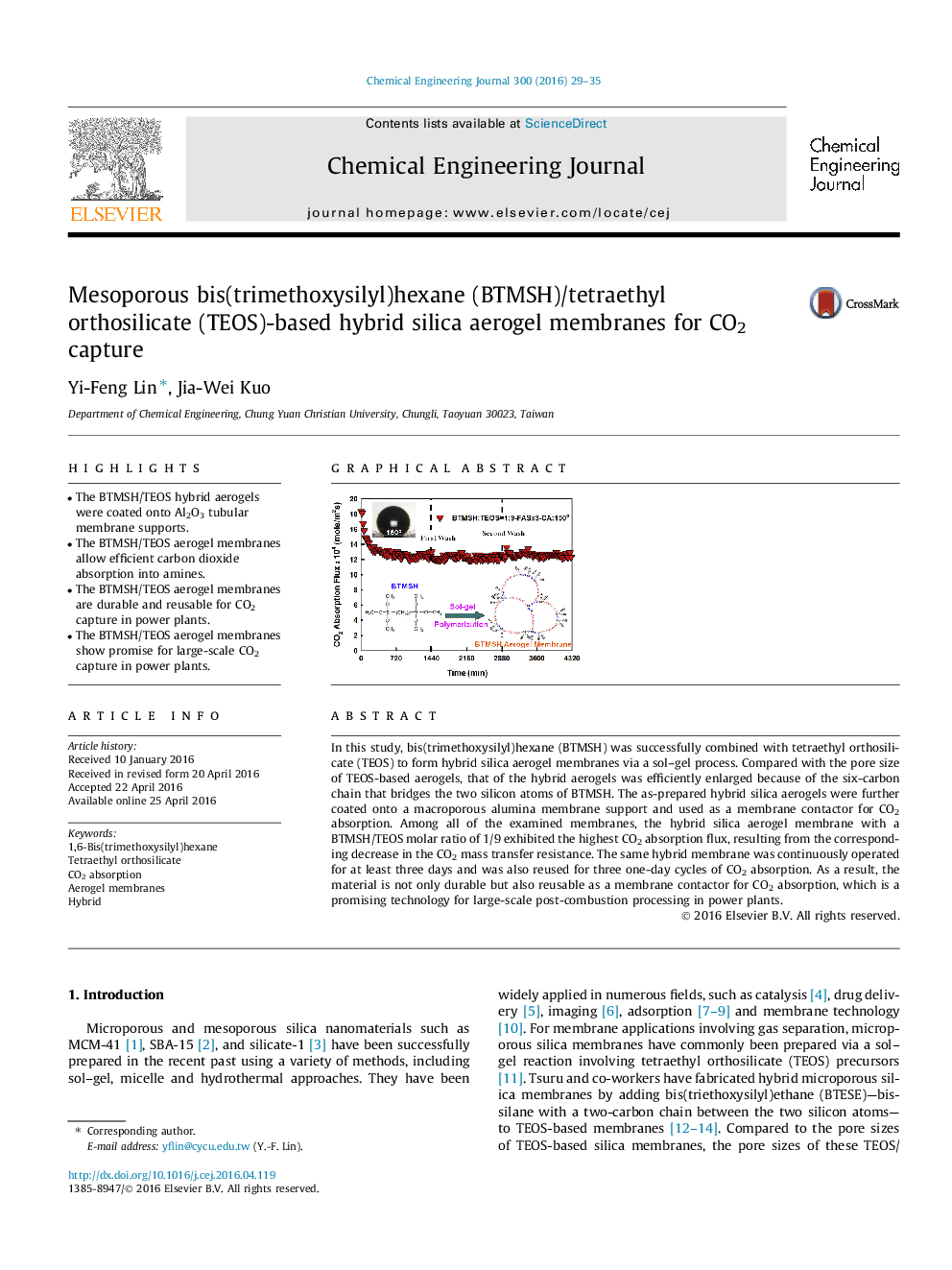
In this study, bis(trimethoxysilyl)hexane (BTMSH) was successfully combined with tetraethyl orthosilicate (TEOS) to form hybrid silica aerogel membranes via a sol–gel process. Compared with the pore size of TEOS-based aerogels, that of the hybrid aerogels was efficiently enlarged because of the six-carbon chain that bridges the two silicon atoms of BTMSH. The as-prepared hybrid silica aerogels were further coated onto a macroporous alumina membrane support and used as a membrane contactor for CO2 absorption. Among all of the examined membranes, the hybrid silica aerogel membrane with a BTMSH/TEOS molar ratio of 1/9 exhibited the highest CO2 absorption flux, resulting from the corresponding decrease in the CO2 mass transfer resistance. The same hybrid membrane was continuously operated for at least three days and was also reused for three one-day cycles of CO2 absorption. As a result, the material is not only durable but also reusable as a membrane contactor for CO2 absorption, which is a promising technology for large-scale post-combustion processing in power plants.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide