| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 145477 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2016 | 7 Pages |
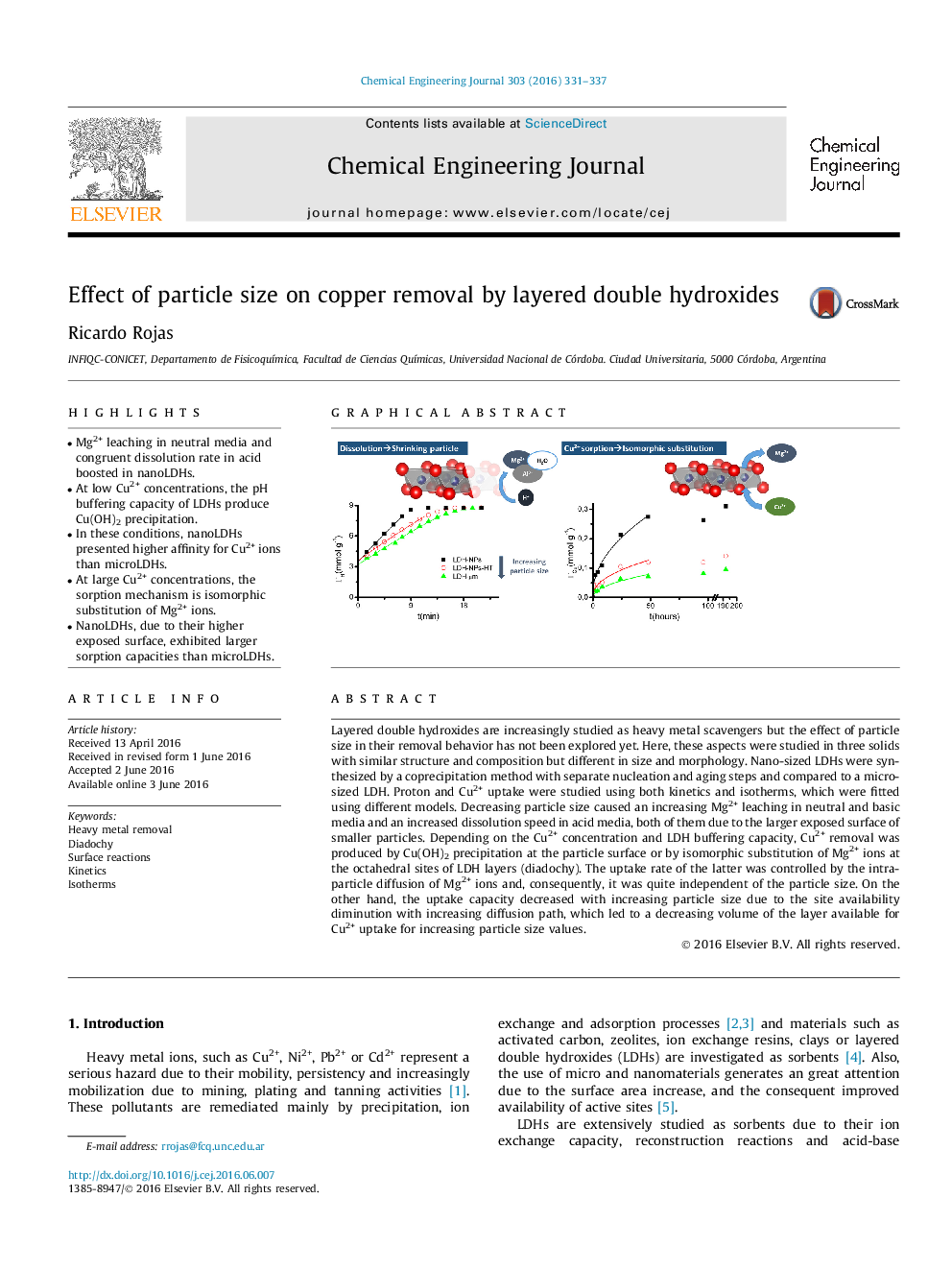
•Mg2+ leaching in neutral media and congruent dissolution rate in acid boosted in nanoLDHs.•At low Cu2+ concentrations, the pH buffering capacity of LDHs produce Cu(OH)2 precipitation.•In these conditions, nanoLDHs presented higher affinity for Cu2+ ions than microLDHs.•At large Cu2+ concentrations, the sorption mechanism is isomorphic substitution of Mg2+ ions.•NanoLDHs, due to their higher exposed surface, exhibited larger sorption capacities than microLDHs.
Layered double hydroxides are increasingly studied as heavy metal scavengers but the effect of particle size in their removal behavior has not been explored yet. Here, these aspects were studied in three solids with similar structure and composition but different in size and morphology. Nano-sized LDHs were synthesized by a coprecipitation method with separate nucleation and aging steps and compared to a micro-sized LDH. Proton and Cu2+ uptake were studied using both kinetics and isotherms, which were fitted using different models. Decreasing particle size caused an increasing Mg2+ leaching in neutral and basic media and an increased dissolution speed in acid media, both of them due to the larger exposed surface of smaller particles. Depending on the Cu2+ concentration and LDH buffering capacity, Cu2+ removal was produced by Cu(OH)2 precipitation at the particle surface or by isomorphic substitution of Mg2+ ions at the octahedral sites of LDH layers (diadochy). The uptake rate of the latter was controlled by the intraparticle diffusion of Mg2+ ions and, consequently, it was quite independent of the particle size. On the other hand, the uptake capacity decreased with increasing particle size due to the site availability diminution with increasing diffusion path, which led to a decreasing volume of the layer available for Cu2+ uptake for increasing particle size values.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide