| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 145521 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2016 | 6 Pages |
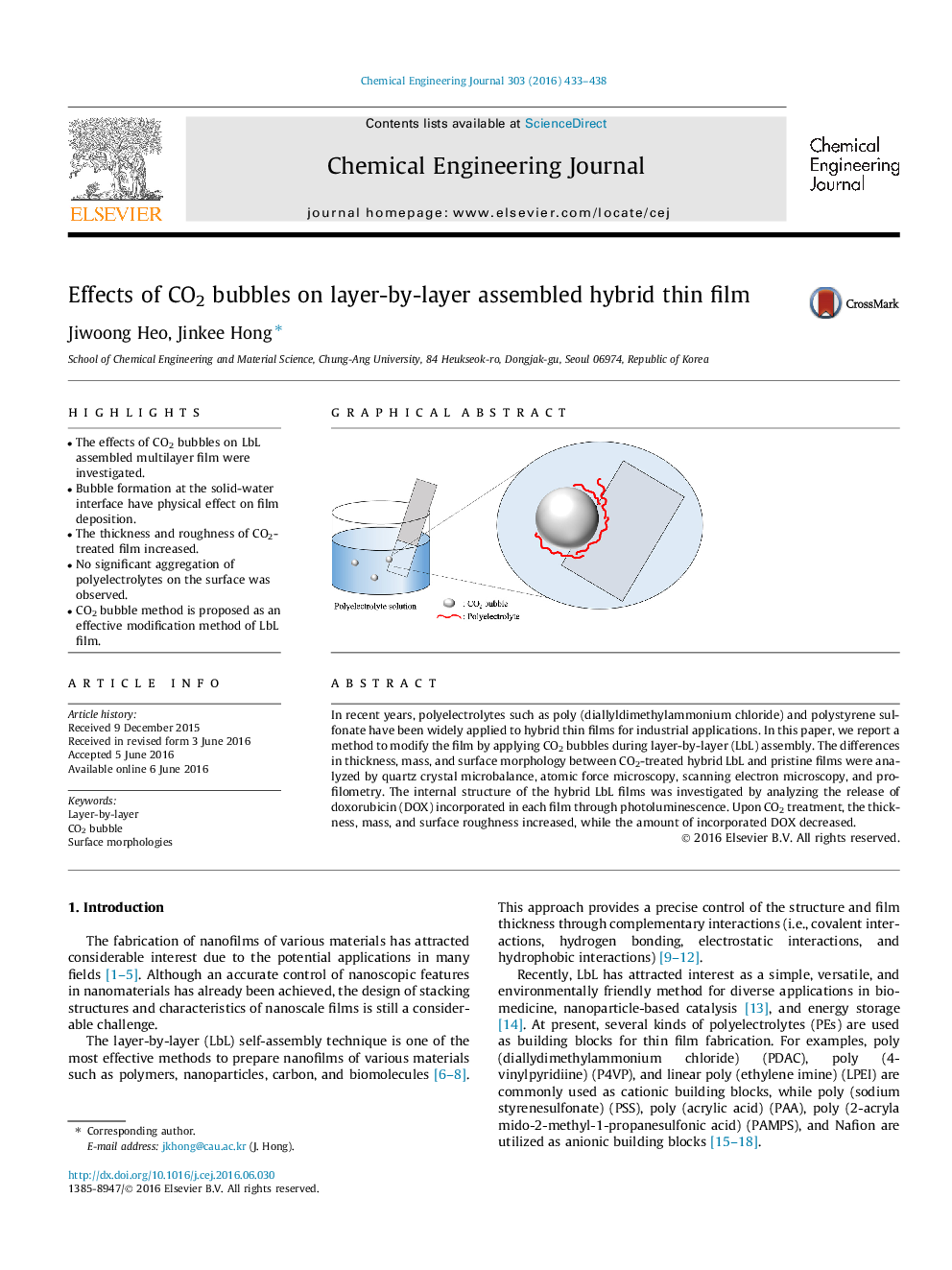
•The effects of CO2 bubbles on LbL assembled multilayer film were investigated.•Bubble formation at the solid-water interface have physical effect on film deposition.•The thickness and roughness of CO2-treated film increased.•No significant aggregation of polyelectrolytes on the surface was observed.•CO2 bubble method is proposed as an effective modification method of LbL film.
In recent years, polyelectrolytes such as poly (diallyldimethylammonium chloride) and polystyrene sulfonate have been widely applied to hybrid thin films for industrial applications. In this paper, we report a method to modify the film by applying CO2 bubbles during layer-by-layer (LbL) assembly. The differences in thickness, mass, and surface morphology between CO2-treated hybrid LbL and pristine films were analyzed by quartz crystal microbalance, atomic force microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, and profilometry. The internal structure of the hybrid LbL films was investigated by analyzing the release of doxorubicin (DOX) incorporated in each film through photoluminescence. Upon CO2 treatment, the thickness, mass, and surface roughness increased, while the amount of incorporated DOX decreased.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide