| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 145643 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2016 | 10 Pages |
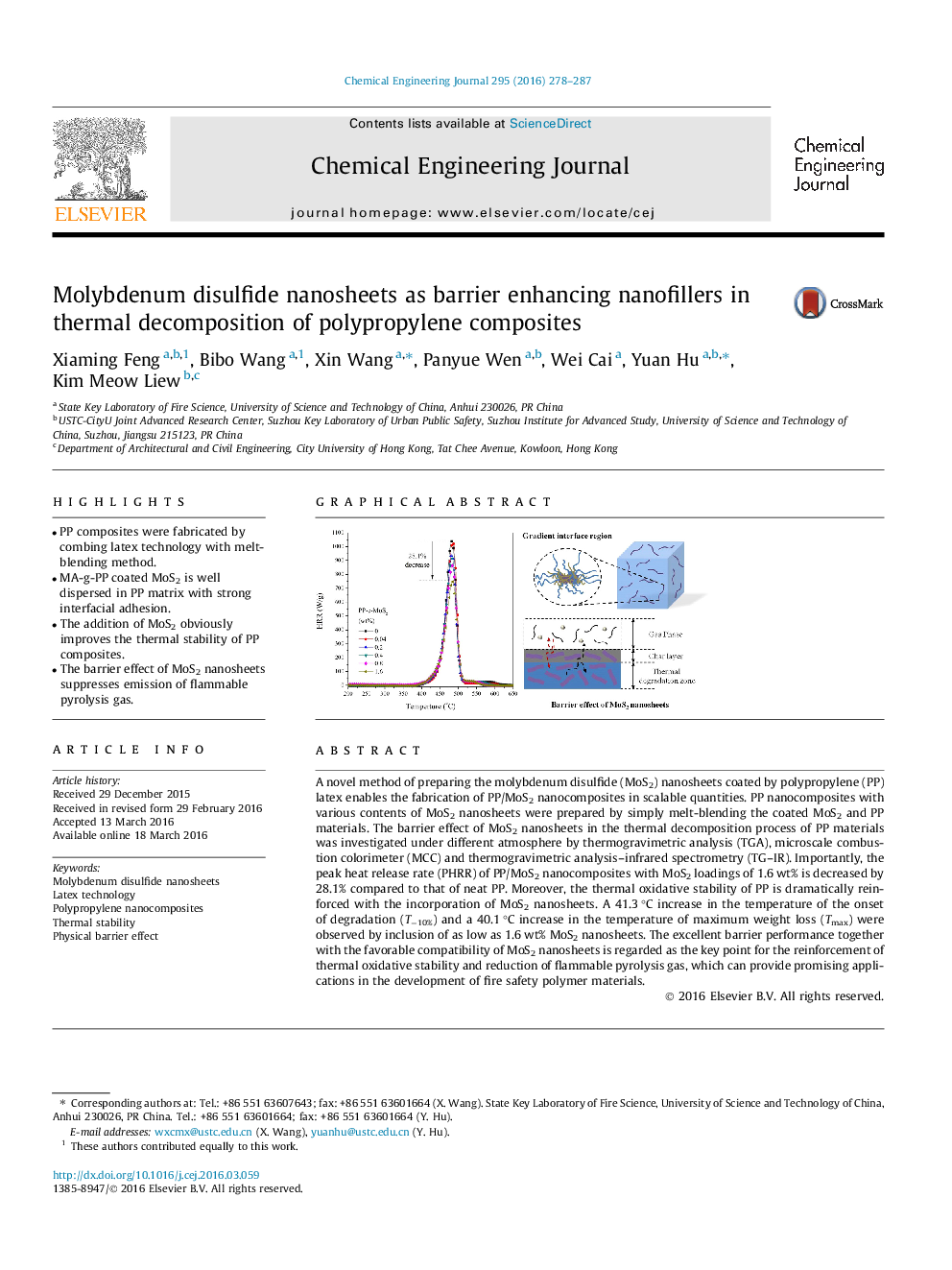
•PP composites were fabricated by combing latex technology with melt-blending method.•MA-g-PP coated MoS2 is well dispersed in PP matrix with strong interfacial adhesion.•The addition of MoS2 obviously improves the thermal stability of PP composites.•The barrier effect of MoS2 nanosheets suppresses emission of flammable pyrolysis gas.
A novel method of preparing the molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) nanosheets coated by polypropylene (PP) latex enables the fabrication of PP/MoS2 nanocomposites in scalable quantities. PP nanocomposites with various contents of MoS2 nanosheets were prepared by simply melt-blending the coated MoS2 and PP materials. The barrier effect of MoS2 nanosheets in the thermal decomposition process of PP materials was investigated under different atmosphere by thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), microscale combustion colorimeter (MCC) and thermogravimetric analysis–infrared spectrometry (TG–IR). Importantly, the peak heat release rate (PHRR) of PP/MoS2 nanocomposites with MoS2 loadings of 1.6 wt% is decreased by 28.1% compared to that of neat PP. Moreover, the thermal oxidative stability of PP is dramatically reinforced with the incorporation of MoS2 nanosheets. A 41.3 °C increase in the temperature of the onset of degradation (T−10%) and a 40.1 °C increase in the temperature of maximum weight loss (Tmax) were observed by inclusion of as low as 1.6 wt% MoS2 nanosheets. The excellent barrier performance together with the favorable compatibility of MoS2 nanosheets is regarded as the key point for the reinforcement of thermal oxidative stability and reduction of flammable pyrolysis gas, which can provide promising applications in the development of fire safety polymer materials.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide