| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 145661 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2016 | 7 Pages |
•SnO2 was used as catalyst support for LaMnO3.•The reaction temperature window was enlarged over LaMnO3/SnO2.•The Hg0 removal efficiencies were enhanced by adding SnO2 support.•The mechanisms for Hg0 removal at low and high temperature were discussed.
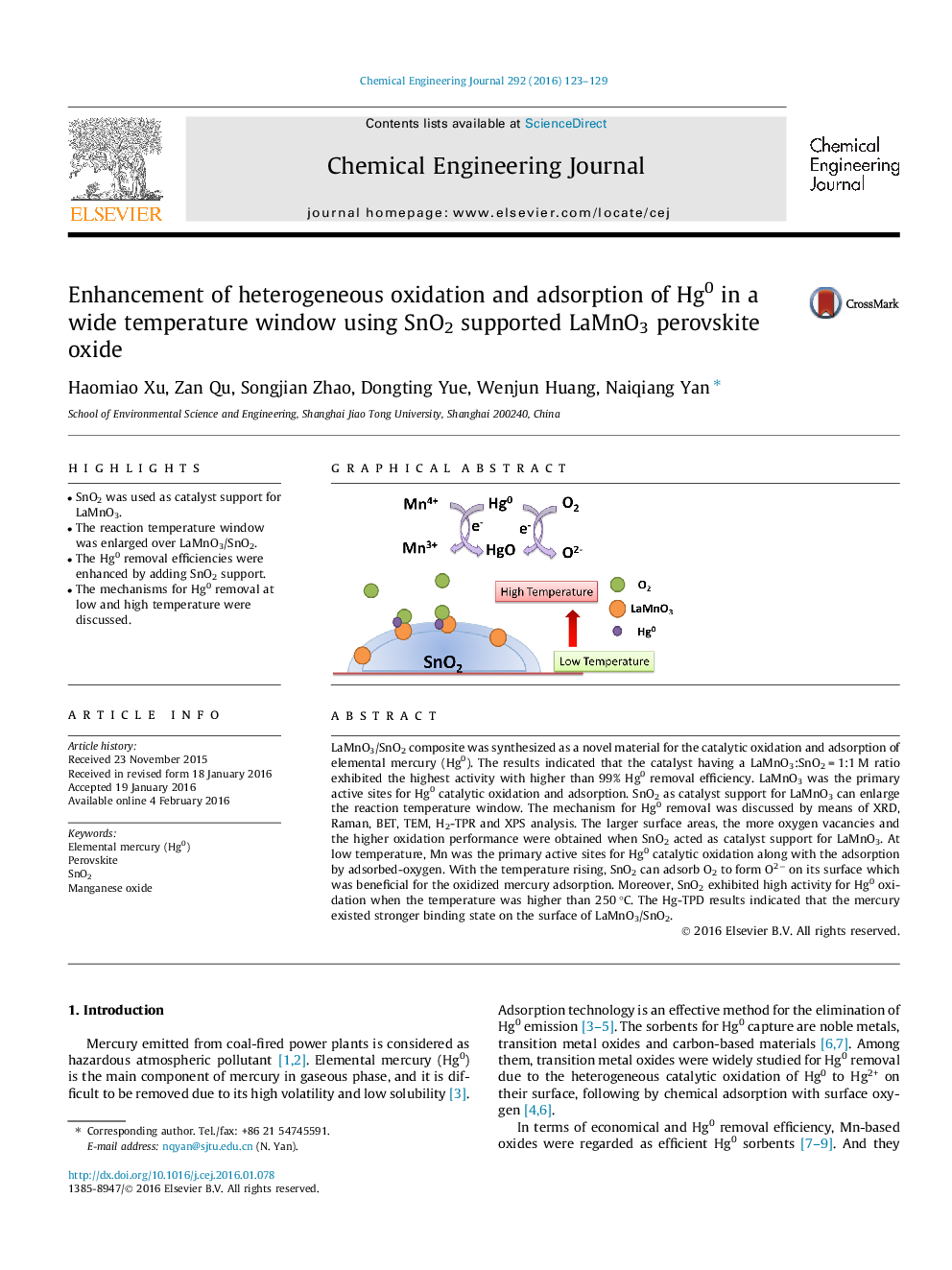
LaMnO3/SnO2 composite was synthesized as a novel material for the catalytic oxidation and adsorption of elemental mercury (Hg0). The results indicated that the catalyst having a LaMnO3:SnO2 = 1:1 M ratio exhibited the highest activity with higher than 99% Hg0 removal efficiency. LaMnO3 was the primary active sites for Hg0 catalytic oxidation and adsorption. SnO2 as catalyst support for LaMnO3 can enlarge the reaction temperature window. The mechanism for Hg0 removal was discussed by means of XRD, Raman, BET, TEM, H2-TPR and XPS analysis. The larger surface areas, the more oxygen vacancies and the higher oxidation performance were obtained when SnO2 acted as catalyst support for LaMnO3. At low temperature, Mn was the primary active sites for Hg0 catalytic oxidation along with the adsorption by adsorbed-oxygen. With the temperature rising, SnO2 can adsorb O2 to form O2− on its surface which was beneficial for the oxidized mercury adsorption. Moreover, SnO2 exhibited high activity for Hg0 oxidation when the temperature was higher than 250 °C. The Hg-TPD results indicated that the mercury existed stronger binding state on the surface of LaMnO3/SnO2.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide