| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 145719 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2016 | 7 Pages |
•Deep eutectic solvents (DESs) are used for the first time for soil remediation.•Saponins are used to enhance DESs performances for lead (Pb) removal.•Natural DESs formed with choline chloride and fructose/sucrose examined in details.•Up to 72% Pb was removed with a combination of 40% DES-fructose and 1% saponin.•Soil corrosion by DES washing is negligible.
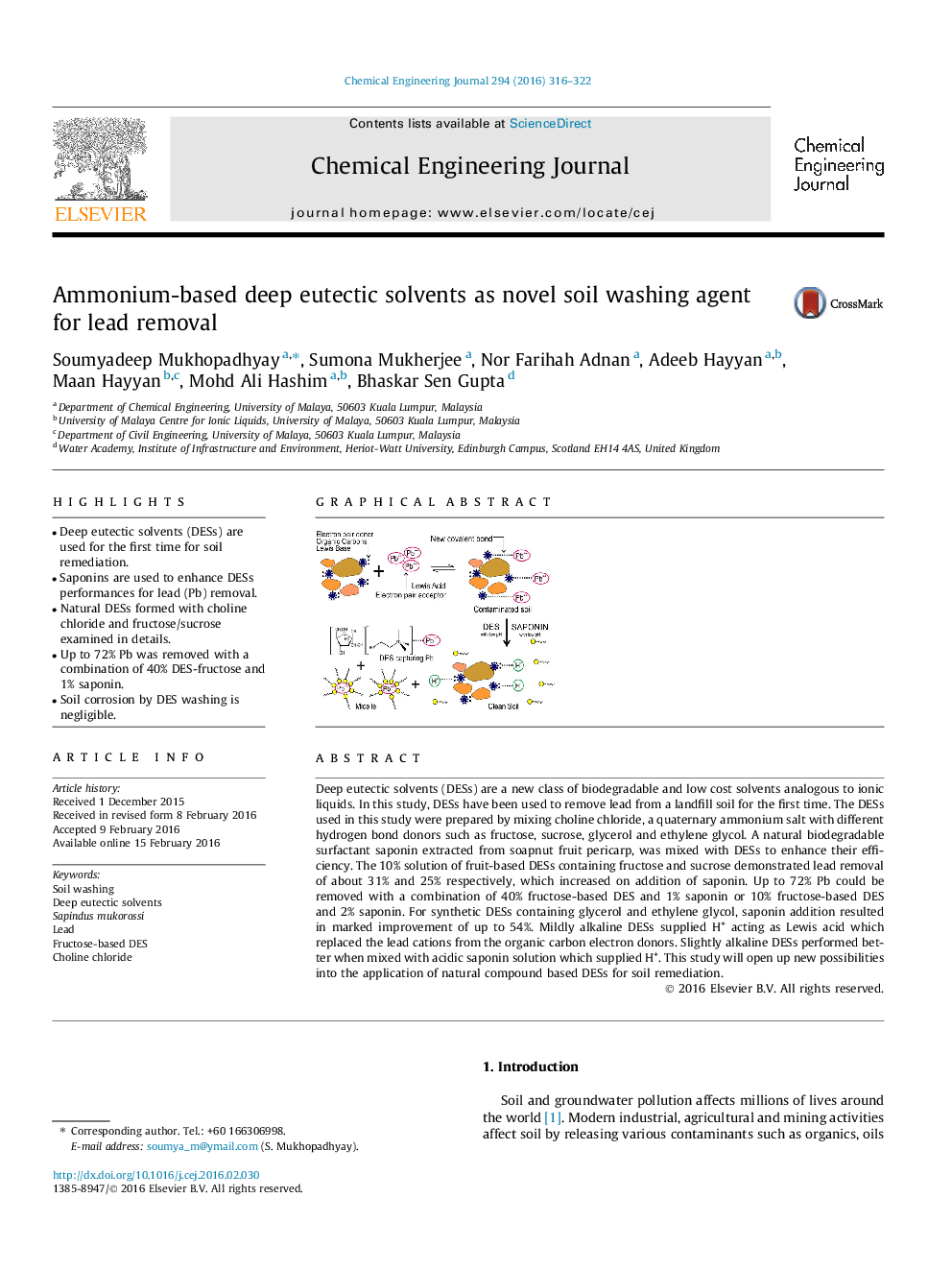
Deep eutectic solvents (DESs) are a new class of biodegradable and low cost solvents analogous to ionic liquids. In this study, DESs have been used to remove lead from a landfill soil for the first time. The DESs used in this study were prepared by mixing choline chloride, a quaternary ammonium salt with different hydrogen bond donors such as fructose, sucrose, glycerol and ethylene glycol. A natural biodegradable surfactant saponin extracted from soapnut fruit pericarp, was mixed with DESs to enhance their efficiency. The 10% solution of fruit-based DESs containing fructose and sucrose demonstrated lead removal of about 31% and 25% respectively, which increased on addition of saponin. Up to 72% Pb could be removed with a combination of 40% fructose-based DES and 1% saponin or 10% fructose-based DES and 2% saponin. For synthetic DESs containing glycerol and ethylene glycol, saponin addition resulted in marked improvement of up to 54%. Mildly alkaline DESs supplied H+ acting as Lewis acid which replaced the lead cations from the organic carbon electron donors. Slightly alkaline DESs performed better when mixed with acidic saponin solution which supplied H+. This study will open up new possibilities into the application of natural compound based DESs for soil remediation.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide