| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 145759 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2016 | 8 Pages |
•Highly-active and nitrogen selective Pd–Cu/γAl2O3 catalyst was prepared.•A novel electrochemical-catalytic (ECC) nitrate reduction system was developed.•H2 was generated on cathode surface and served as reductant in catalytic reaction.•NO3− removal rate, N2 selectivity, and current efficiency were enhanced in ECC.
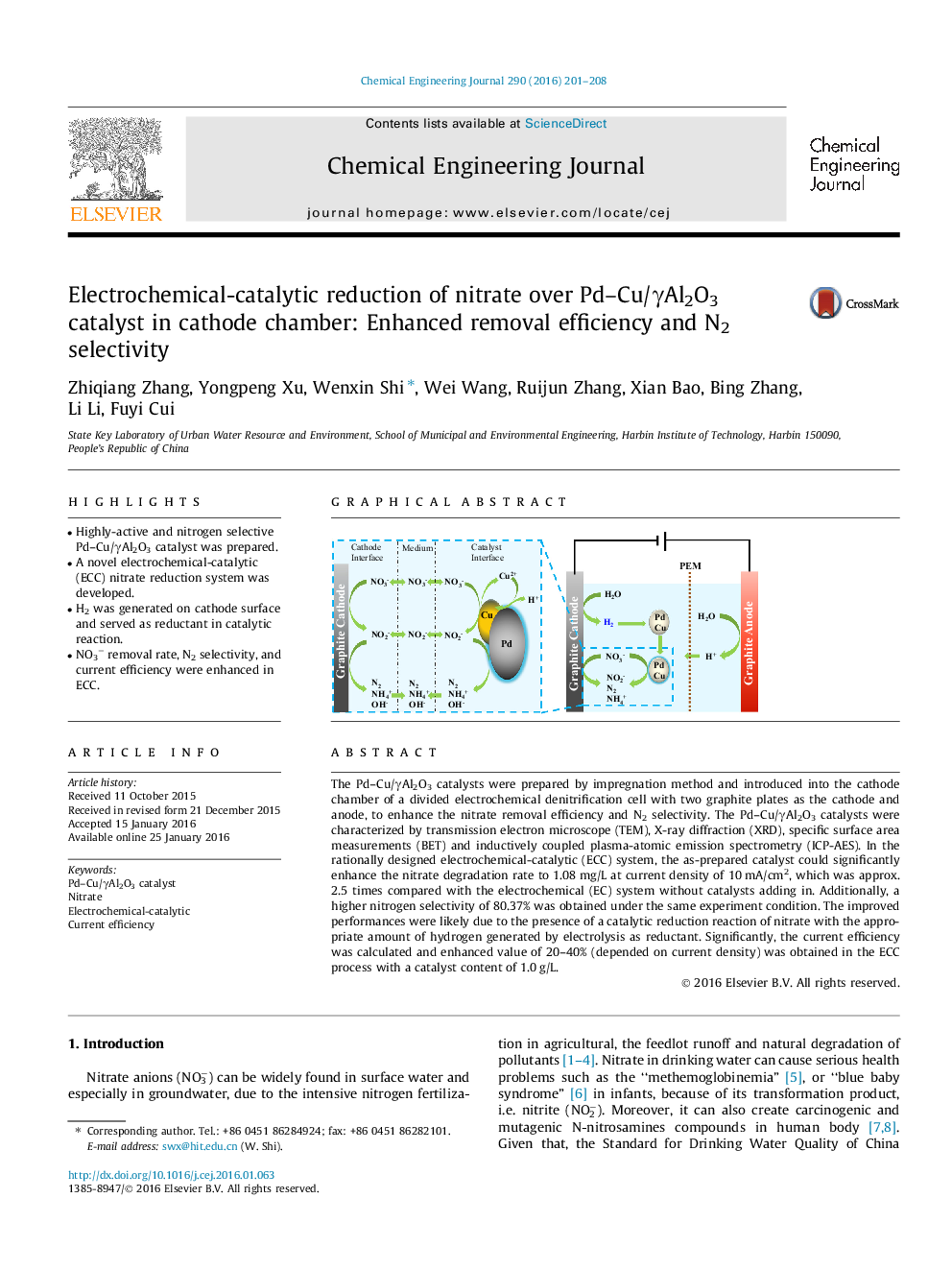
The Pd–Cu/γAl2O3 catalysts were prepared by impregnation method and introduced into the cathode chamber of a divided electrochemical denitrification cell with two graphite plates as the cathode and anode, to enhance the nitrate removal efficiency and N2 selectivity. The Pd–Cu/γAl2O3 catalysts were characterized by transmission electron microscope (TEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), specific surface area measurements (BET) and inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry (ICP-AES). In the rationally designed electrochemical-catalytic (ECC) system, the as-prepared catalyst could significantly enhance the nitrate degradation rate to 1.08 mg/L at current density of 10 mA/cm2, which was approx. 2.5 times compared with the electrochemical (EC) system without catalysts adding in. Additionally, a higher nitrogen selectivity of 80.37% was obtained under the same experiment condition. The improved performances were likely due to the presence of a catalytic reduction reaction of nitrate with the appropriate amount of hydrogen generated by electrolysis as reductant. Significantly, the current efficiency was calculated and enhanced value of 20–40% (depended on current density) was obtained in the ECC process with a catalyst content of 1.0 g/L.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide