| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 145852 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2016 | 7 Pages |
•Monodisperse microspheres can be obtained by solvothermal precipitation polymerization.•The yield of PDVB microspheres can reach above 90% at a monomer loading of 20 wt%.•The microsphere size can be controlled ranging from 0.88 μm to 4.18 μm.•The microsphere uniformity can be improved by regulating reaction conditions.
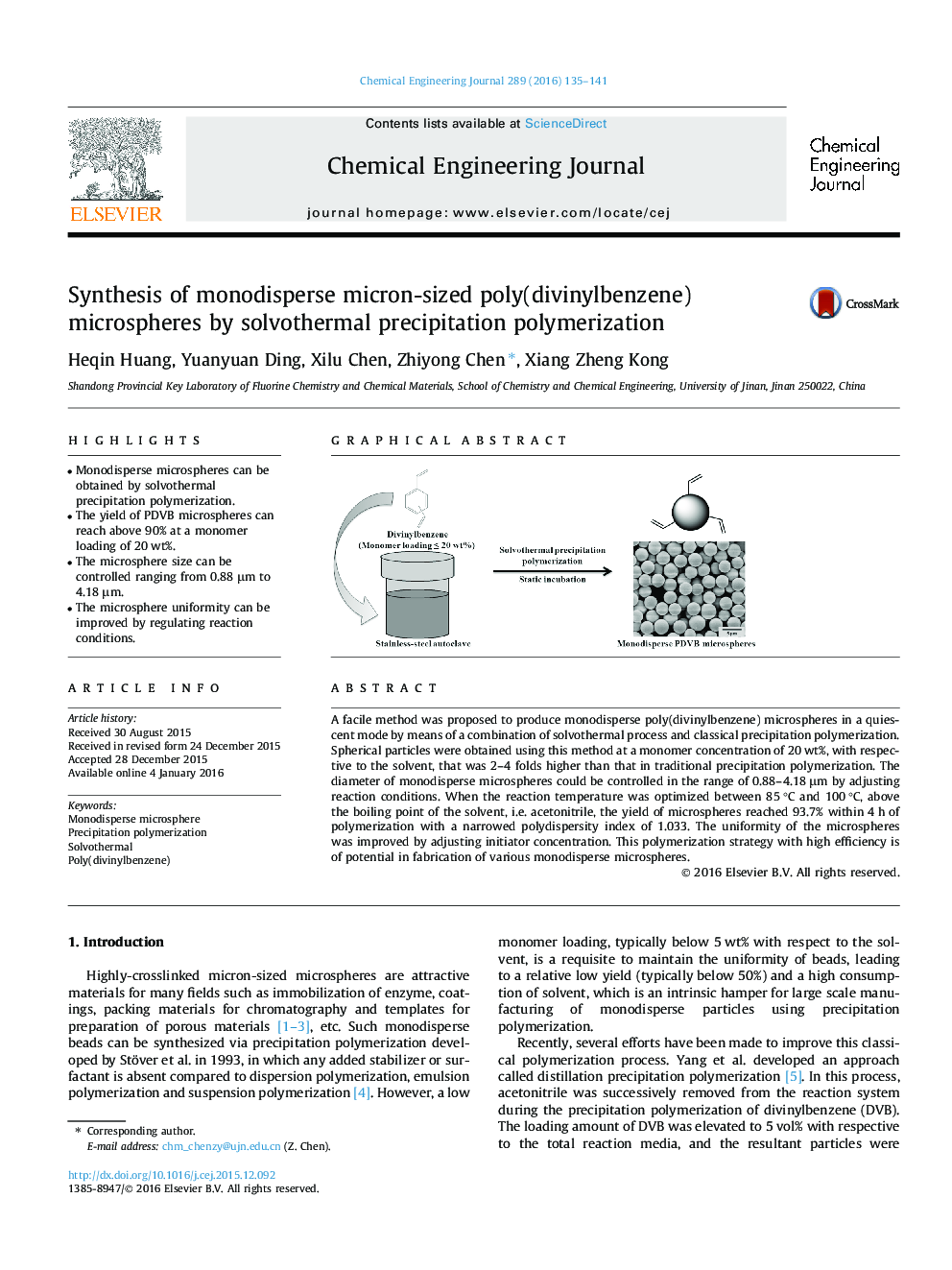
A facile method was proposed to produce monodisperse poly(divinylbenzene) microspheres in a quiescent mode by means of a combination of solvothermal process and classical precipitation polymerization. Spherical particles were obtained using this method at a monomer concentration of 20 wt%, with respective to the solvent, that was 2–4 folds higher than that in traditional precipitation polymerization. The diameter of monodisperse microspheres could be controlled in the range of 0.88–4.18 μm by adjusting reaction conditions. When the reaction temperature was optimized between 85 °C and 100 °C, above the boiling point of the solvent, i.e. acetonitrile, the yield of microspheres reached 93.7% within 4 h of polymerization with a narrowed polydispersity index of 1.033. The uniformity of the microspheres was improved by adjusting initiator concentration. This polymerization strategy with high efficiency is of potential in fabrication of various monodisperse microspheres.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide