| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 145897 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2016 | 9 Pages |
•We reported a novel porous composite adsorbent.•High adsorption capacity and fast adsorption of MB by the adsorbent are achieved.•Maximum sorption capacity for MB by the adsorbent was 272.4 mg g−1.•The adsorption of MB onto the adsorbent was exothermic and spontaneous.
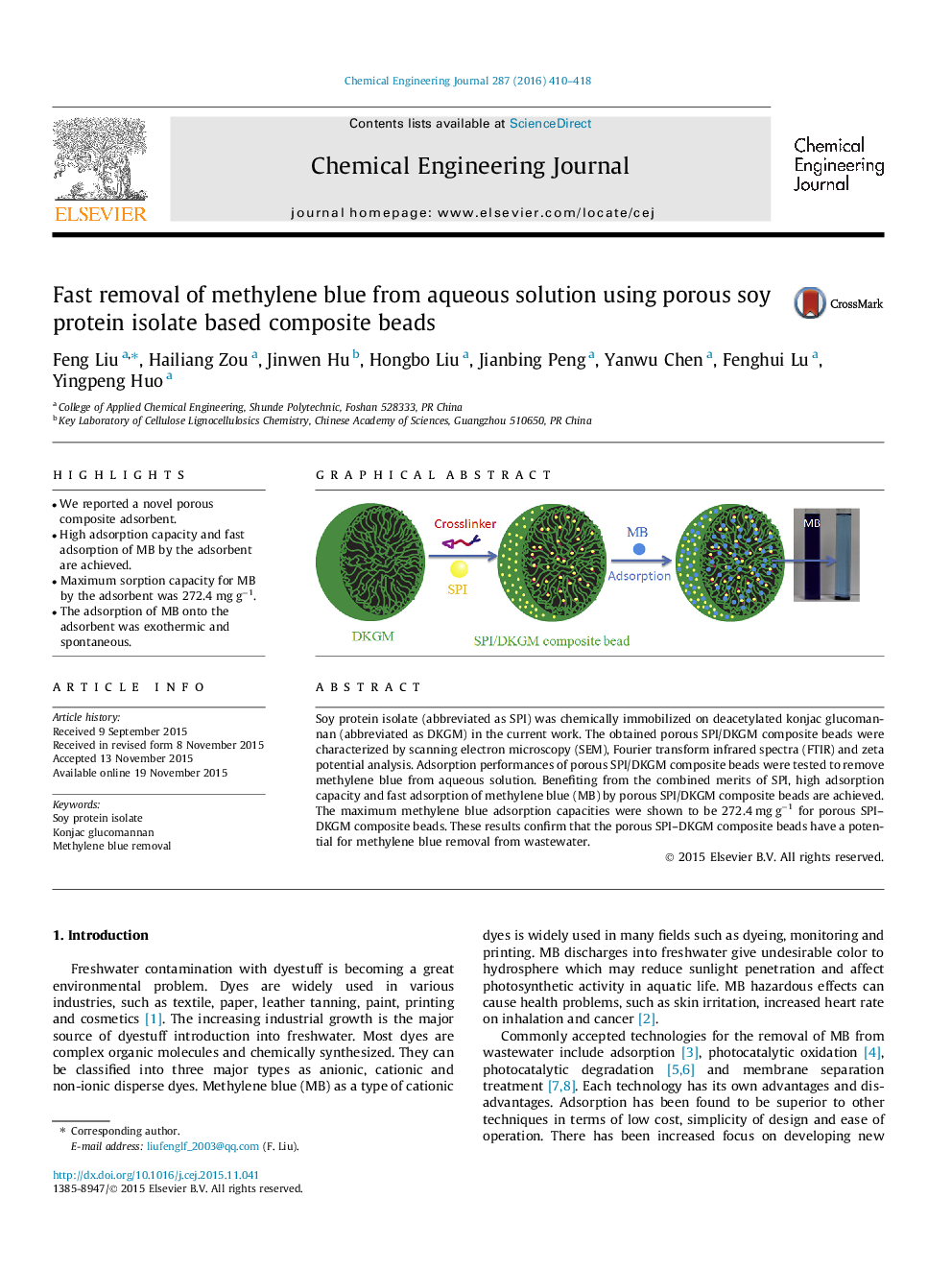
Soy protein isolate (abbreviated as SPI) was chemically immobilized on deacetylated konjac glucomannan (abbreviated as DKGM) in the current work. The obtained porous SPI/DKGM composite beads were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier transform infrared spectra (FTIR) and zeta potential analysis. Adsorption performances of porous SPI/DKGM composite beads were tested to remove methylene blue from aqueous solution. Benefiting from the combined merits of SPI, high adsorption capacity and fast adsorption of methylene blue (MB) by porous SPI/DKGM composite beads are achieved. The maximum methylene blue adsorption capacities were shown to be 272.4 mg g−1 for porous SPI–DKGM composite beads. These results confirm that the porous SPI–DKGM composite beads have a potential for methylene blue removal from wastewater.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide