| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 146060 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2015 | 10 Pages |
•BPA was completely degraded by mixed metal oxides catalyzed of PMS.•The SO4− were recognized as the main species to oxidize pollutant.•The hydroxyl radicals could induce the acceleration of PMS decomposition.•The hydroxylation and cleavage of benzene-rings are major degradation pathways.
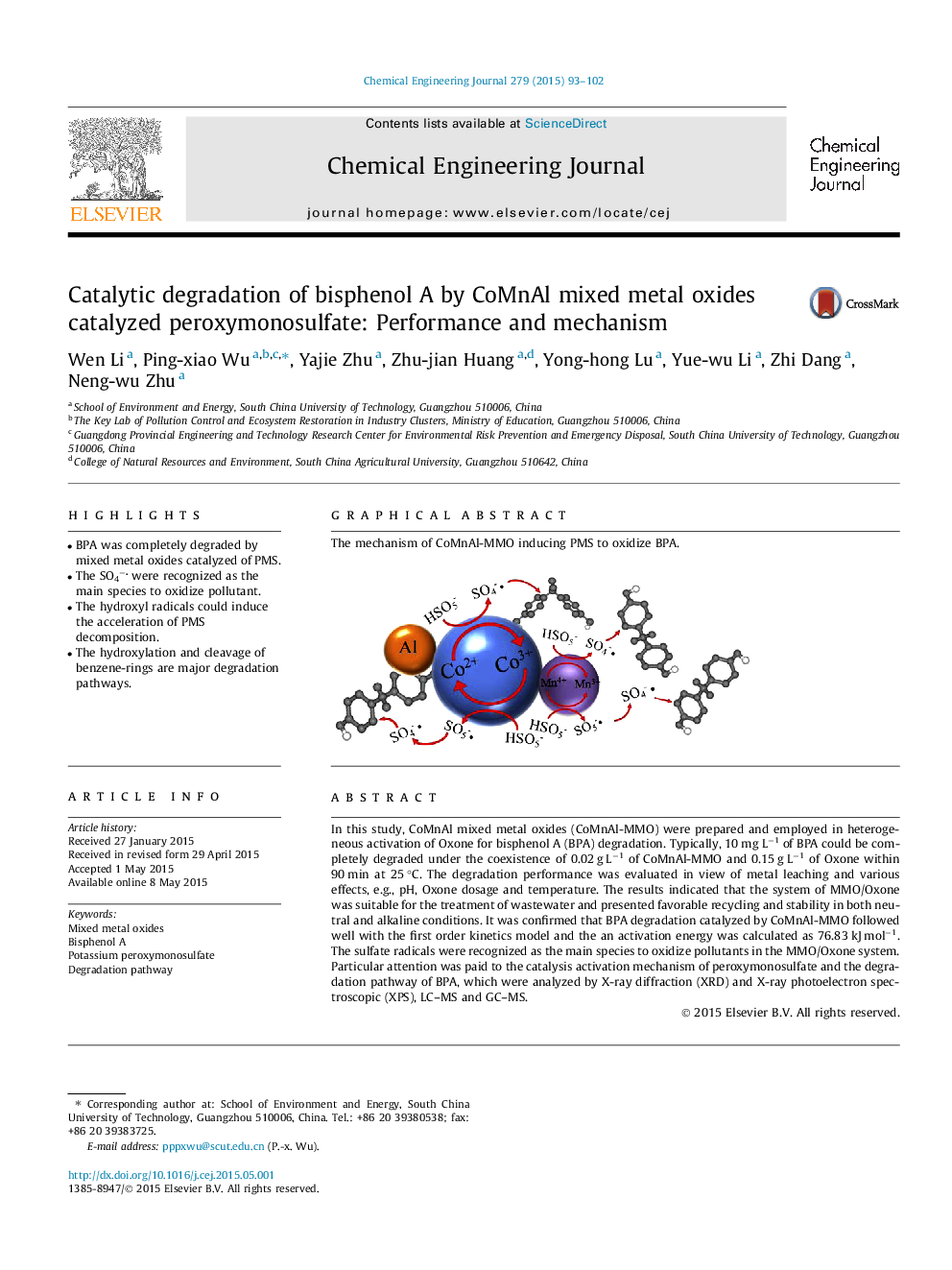
In this study, CoMnAl mixed metal oxides (CoMnAl-MMO) were prepared and employed in heterogeneous activation of Oxone for bisphenol A (BPA) degradation. Typically, 10 mg L−1 of BPA could be completely degraded under the coexistence of 0.02 g L−1 of CoMnAl-MMO and 0.15 g L−1 of Oxone within 90 min at 25 °C. The degradation performance was evaluated in view of metal leaching and various effects, e.g., pH, Oxone dosage and temperature. The results indicated that the system of MMO/Oxone was suitable for the treatment of wastewater and presented favorable recycling and stability in both neutral and alkaline conditions. It was confirmed that BPA degradation catalyzed by CoMnAl-MMO followed well with the first order kinetics model and the an activation energy was calculated as 76.83 kJ mol−1. The sulfate radicals were recognized as the main species to oxidize pollutants in the MMO/Oxone system. Particular attention was paid to the catalysis activation mechanism of peroxymonosulfate and the degradation pathway of BPA, which were analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic (XPS), LC–MS and GC–MS.
Graphical abstractThe mechanism of CoMnAl-MMO inducing PMS to oxidize BPA.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide