| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 146178 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2015 | 10 Pages |
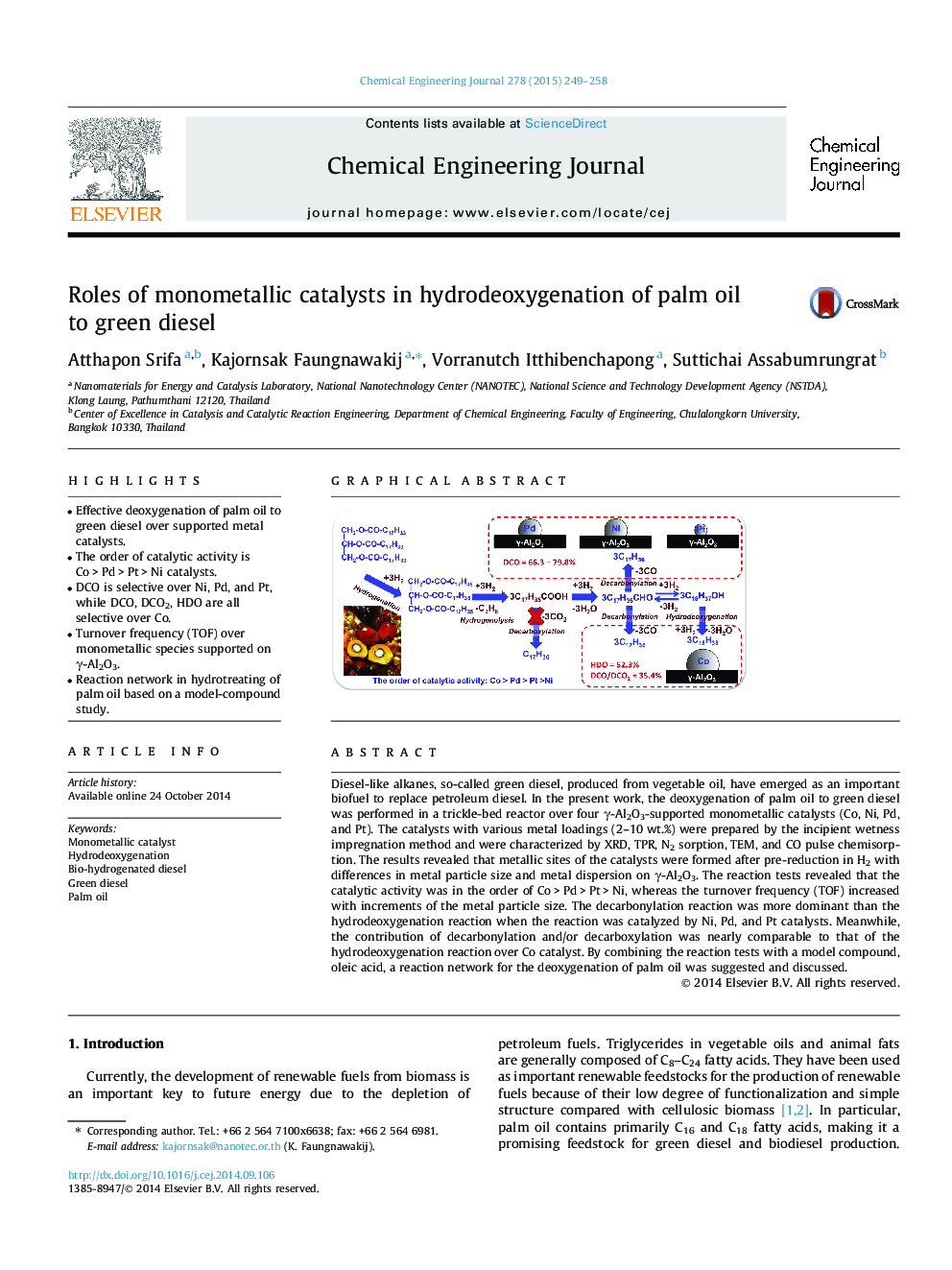
•Effective deoxygenation of palm oil to green diesel over supported metal catalysts.•The order of catalytic activity is Co > Pd > Pt > Ni catalysts.•DCO is selective over Ni, Pd, and Pt, while DCO, DCO2, HDO are all selective over Co.•Turnover frequency (TOF) over monometallic species supported on γ-Al2O3.•Reaction network in hydrotreating of palm oil based on a model-compound study.
Diesel-like alkanes, so-called green diesel, produced from vegetable oil, have emerged as an important biofuel to replace petroleum diesel. In the present work, the deoxygenation of palm oil to green diesel was performed in a trickle-bed reactor over four γ-Al2O3-supported monometallic catalysts (Co, Ni, Pd, and Pt). The catalysts with various metal loadings (2–10 wt.%) were prepared by the incipient wetness impregnation method and were characterized by XRD, TPR, N2 sorption, TEM, and CO pulse chemisorption. The results revealed that metallic sites of the catalysts were formed after pre-reduction in H2 with differences in metal particle size and metal dispersion on γ-Al2O3. The reaction tests revealed that the catalytic activity was in the order of Co > Pd > Pt > Ni, whereas the turnover frequency (TOF) increased with increments of the metal particle size. The decarbonylation reaction was more dominant than the hydrodeoxygenation reaction when the reaction was catalyzed by Ni, Pd, and Pt catalysts. Meanwhile, the contribution of decarbonylation and/or decarboxylation was nearly comparable to that of the hydrodeoxygenation reaction over Co catalyst. By combining the reaction tests with a model compound, oleic acid, a reaction network for the deoxygenation of palm oil was suggested and discussed.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide