| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 146295 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2015 | 8 Pages |
•Carbon/graphene composite (CGC) nanosheets are obtained by a facile method.•The CGC nanosheets consist of nitrogen-containing graphitized carbon and graphene.•The CGC nanosheets exhibit excellent lithium storage performances.
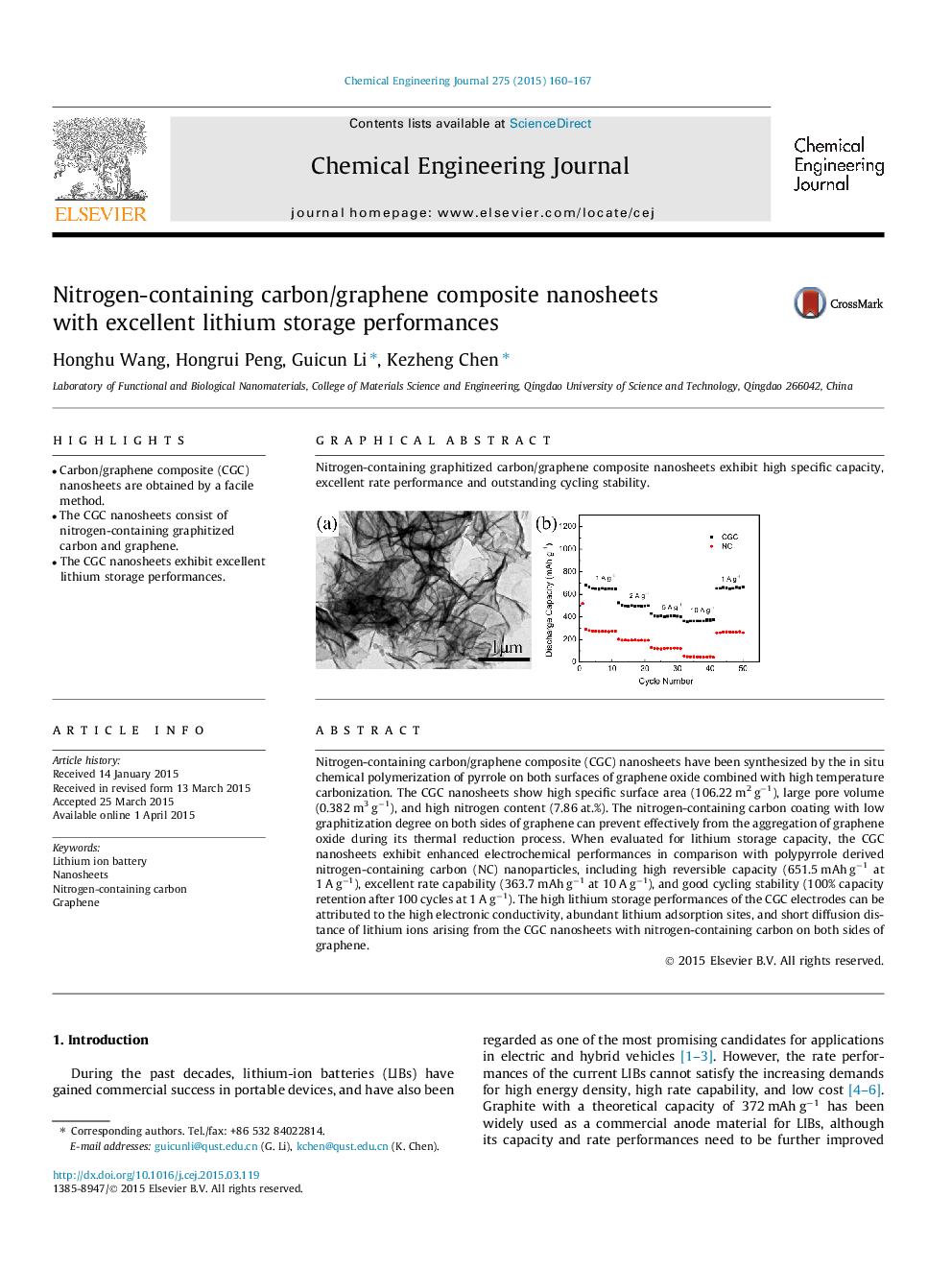
Nitrogen-containing carbon/graphene composite (CGC) nanosheets have been synthesized by the in situ chemical polymerization of pyrrole on both surfaces of graphene oxide combined with high temperature carbonization. The CGC nanosheets show high specific surface area (106.22 m2 g−1), large pore volume (0.382 m3 g−1), and high nitrogen content (7.86 at.%). The nitrogen-containing carbon coating with low graphitization degree on both sides of graphene can prevent effectively from the aggregation of graphene oxide during its thermal reduction process. When evaluated for lithium storage capacity, the CGC nanosheets exhibit enhanced electrochemical performances in comparison with polypyrrole derived nitrogen-containing carbon (NC) nanoparticles, including high reversible capacity (651.5 mAh g−1 at 1 A g−1), excellent rate capability (363.7 mAh g−1 at 10 A g−1), and good cycling stability (100% capacity retention after 100 cycles at 1 A g−1). The high lithium storage performances of the CGC electrodes can be attributed to the high electronic conductivity, abundant lithium adsorption sites, and short diffusion distance of lithium ions arising from the CGC nanosheets with nitrogen-containing carbon on both sides of graphene.
Graphical abstractNitrogen-containing graphitized carbon/graphene composite nanosheets exhibit high specific capacity, excellent rate performance and outstanding cycling stability.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide