| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 146375 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2015 | 8 Pages |
•Sodium cobaltate is able to chemisorb CO2 in a wide temperature range.•Sodium cobaltate was evaluated as CO oxidant catalyst.•CO oxidation–chemisorption double reaction mechanism was studied.
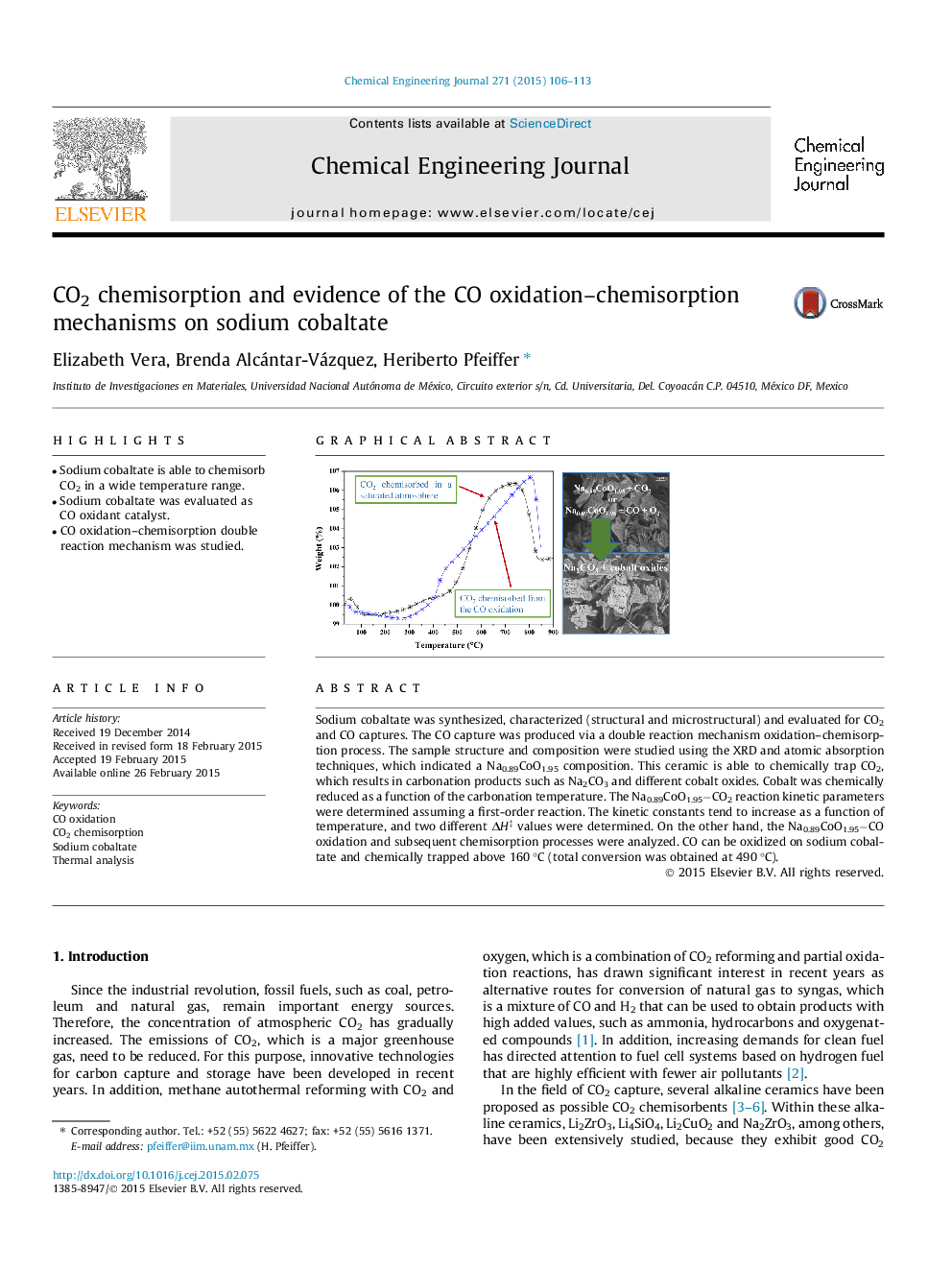
Sodium cobaltate was synthesized, characterized (structural and microstructural) and evaluated for CO2 and CO captures. The CO capture was produced via a double reaction mechanism oxidation–chemisorption process. The sample structure and composition were studied using the XRD and atomic absorption techniques, which indicated a Na0.89CoO1.95 composition. This ceramic is able to chemically trap CO2, which results in carbonation products such as Na2CO3 and different cobalt oxides. Cobalt was chemically reduced as a function of the carbonation temperature. The Na0.89CoO1.95−CO2 reaction kinetic parameters were determined assuming a first-order reaction. The kinetic constants tend to increase as a function of temperature, and two different ΔH‡ values were determined. On the other hand, the Na0.89CoO1.95−CO oxidation and subsequent chemisorption processes were analyzed. CO can be oxidized on sodium cobaltate and chemically trapped above 160 °C (total conversion was obtained at 490 °C).
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide