| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 146433 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2015 | 13 Pages |
•HPNC was synthesized by ring opening polymerization and sol–gel reaction.•Hydrated radius and electronegativity played significant role in metal adsorption.•Metal ions interaction with –NH active sites was a possible adsorption mechanism.•Elution was maximum (Pb(II) 94.13% > Zn(II) 93.59% > Cd(II) 84.15%) with 0.1 M HCl.•28.99% and 16.96% loss in Pb(II) adsorption and recovery after four consecutive cycles.
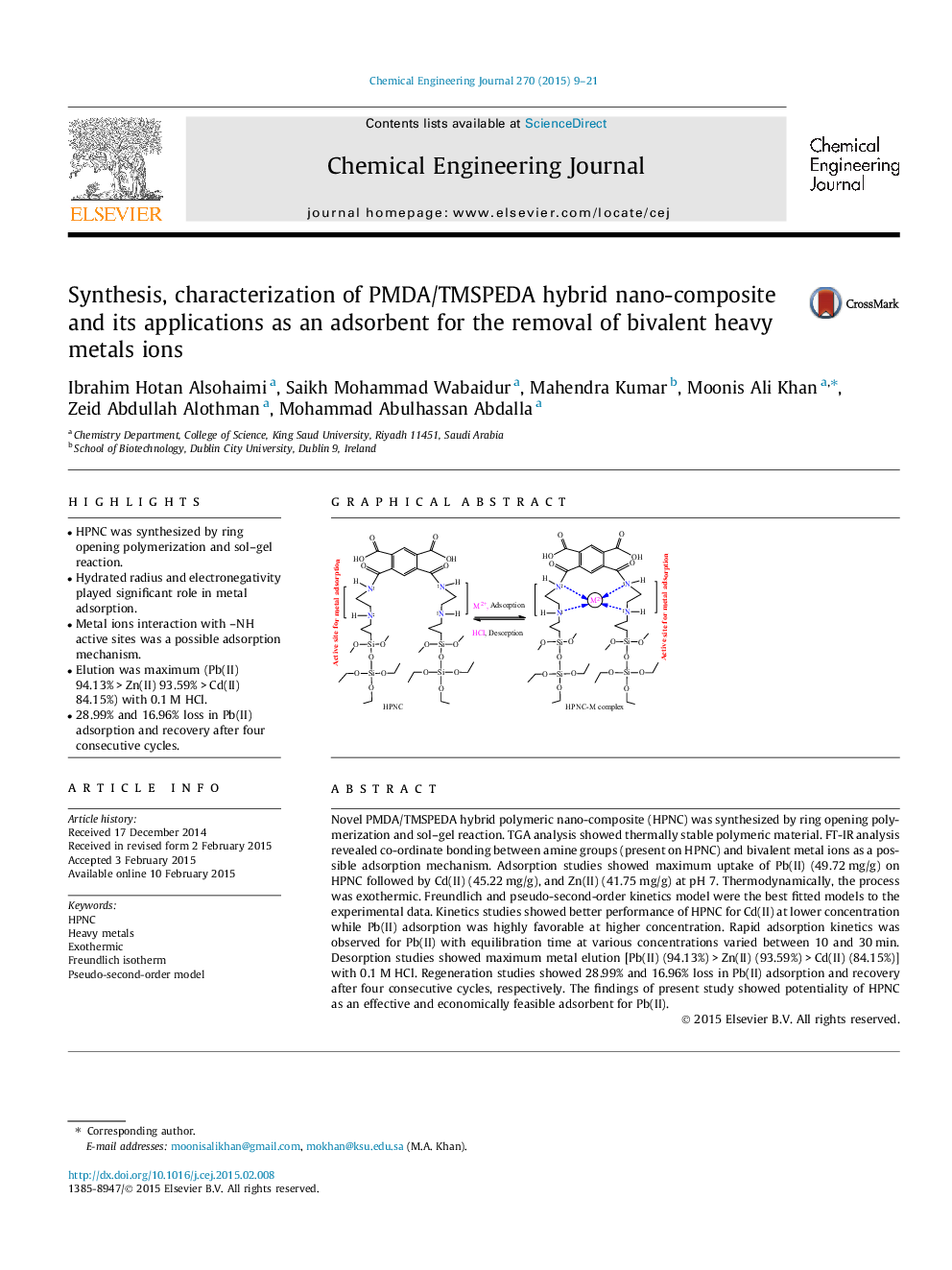
Novel PMDA/TMSPEDA hybrid polymeric nano-composite (HPNC) was synthesized by ring opening polymerization and sol–gel reaction. TGA analysis showed thermally stable polymeric material. FT-IR analysis revealed co-ordinate bonding between amine groups (present on HPNC) and bivalent metal ions as a possible adsorption mechanism. Adsorption studies showed maximum uptake of Pb(II) (49.72 mg/g) on HPNC followed by Cd(II) (45.22 mg/g), and Zn(II) (41.75 mg/g) at pH 7. Thermodynamically, the process was exothermic. Freundlich and pseudo-second-order kinetics model were the best fitted models to the experimental data. Kinetics studies showed better performance of HPNC for Cd(II) at lower concentration while Pb(II) adsorption was highly favorable at higher concentration. Rapid adsorption kinetics was observed for Pb(II) with equilibration time at various concentrations varied between 10 and 30 min. Desorption studies showed maximum metal elution [Pb(II) (94.13%) > Zn(II) (93.59%) > Cd(II) (84.15%)] with 0.1 M HCl. Regeneration studies showed 28.99% and 16.96% loss in Pb(II) adsorption and recovery after four consecutive cycles, respectively. The findings of present study showed potentiality of HPNC as an effective and economically feasible adsorbent for Pb(II).
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide