| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 146485 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2015 | 10 Pages |
•The onset of the maldistribution in fluidized beds has been studied.•A half-covered distributor plate was employed in the experiments.•Deep beds can overcome maldistribution at the bed surface.•Standard deviation of pressure signals can be used to detect maldistribution.•Online monitoring methods were successfully applied to maldistribution detection.
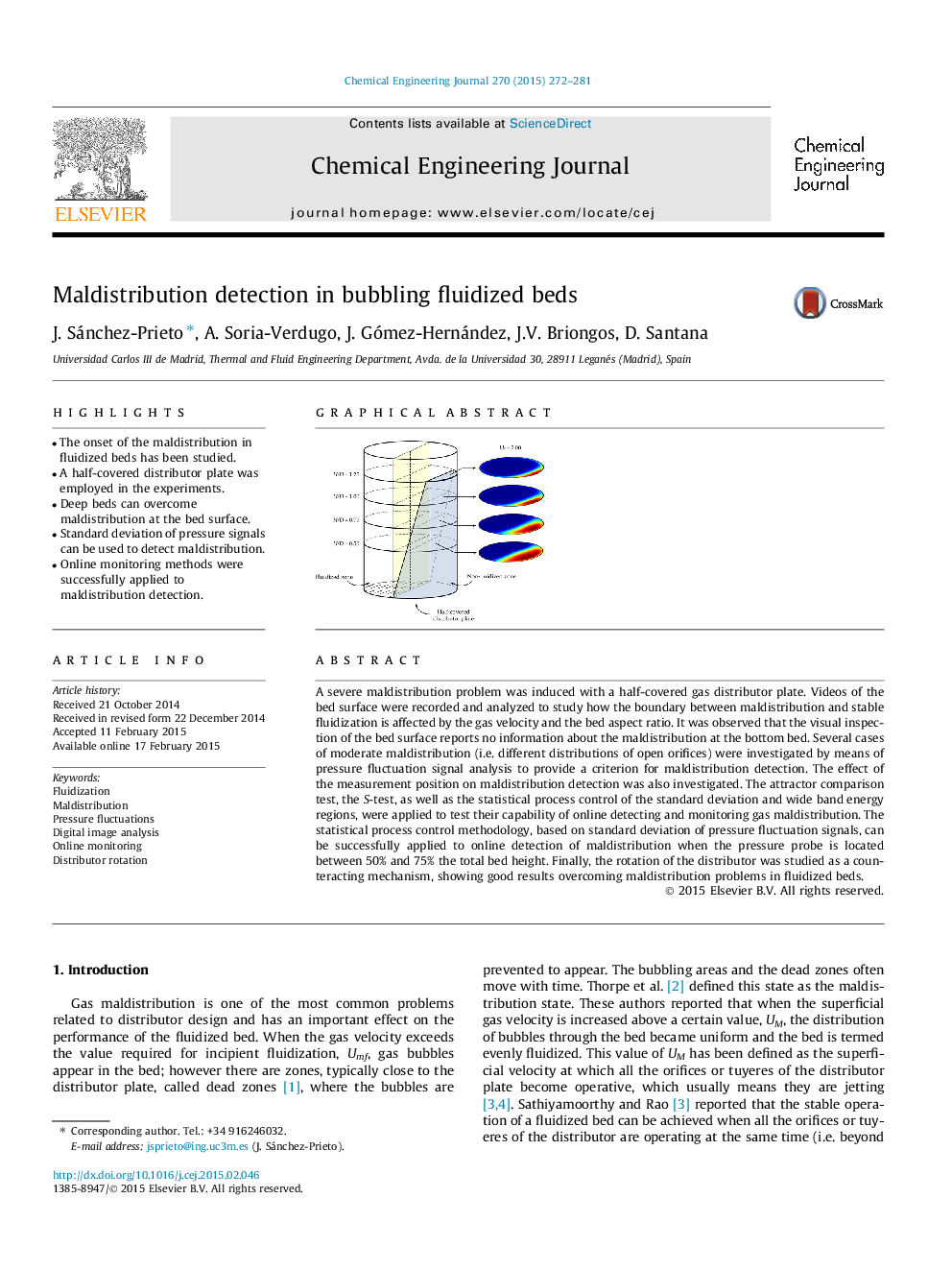
A severe maldistribution problem was induced with a half-covered gas distributor plate. Videos of the bed surface were recorded and analyzed to study how the boundary between maldistribution and stable fluidization is affected by the gas velocity and the bed aspect ratio. It was observed that the visual inspection of the bed surface reports no information about the maldistribution at the bottom bed. Several cases of moderate maldistribution (i.e. different distributions of open orifices) were investigated by means of pressure fluctuation signal analysis to provide a criterion for maldistribution detection. The effect of the measurement position on maldistribution detection was also investigated. The attractor comparison test, the S-test, as well as the statistical process control of the standard deviation and wide band energy regions, were applied to test their capability of online detecting and monitoring gas maldistribution. The statistical process control methodology, based on standard deviation of pressure fluctuation signals, can be successfully applied to online detection of maldistribution when the pressure probe is located between 50% and 75% the total bed height. Finally, the rotation of the distributor was studied as a counteracting mechanism, showing good results overcoming maldistribution problems in fluidized beds.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide