| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 146691 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2015 | 10 Pages |
•A new porous resin with Schiff base chelating groups was synthesized.•Extraction of Cu2+, Cd2+, Cr3+, Ni2+ and Co2+ from aqueous solution was examined.•The process of metal ions adsorption generally followed the Langmuir model.•The adsorption kinetics follow the pseudo-second-order kinetic model.•The resin was effective for removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater samples.
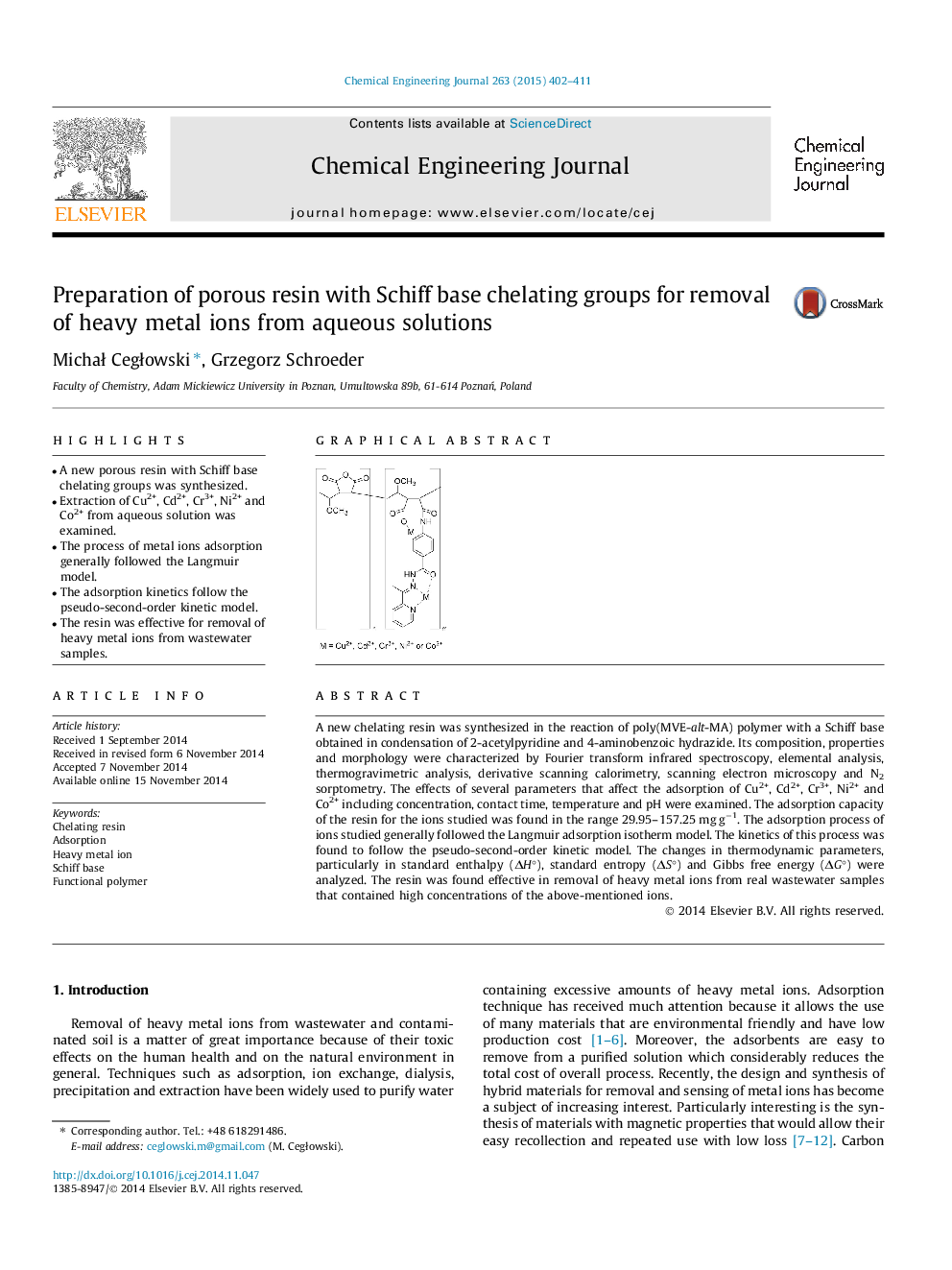
A new chelating resin was synthesized in the reaction of poly(MVE-alt-MA) polymer with a Schiff base obtained in condensation of 2-acetylpyridine and 4-aminobenzoic hydrazide. Its composition, properties and morphology were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, elemental analysis, thermogravimetric analysis, derivative scanning calorimetry, scanning electron microscopy and N2 sorptometry. The effects of several parameters that affect the adsorption of Cu2+, Cd2+, Cr3+, Ni2+ and Co2+ including concentration, contact time, temperature and pH were examined. The adsorption capacity of the resin for the ions studied was found in the range 29.95–157.25 mg g−1. The adsorption process of ions studied generally followed the Langmuir adsorption isotherm model. The kinetics of this process was found to follow the pseudo-second-order kinetic model. The changes in thermodynamic parameters, particularly in standard enthalpy (ΔH°), standard entropy (ΔS°) and Gibbs free energy (ΔG°) were analyzed. The resin was found effective in removal of heavy metal ions from real wastewater samples that contained high concentrations of the above-mentioned ions.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide