| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 146726 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2015 | 9 Pages |
•This work assessed the p-chloronitrobenzene (pCNB) degradation by heterogeneous Fenton-like process in aqueous solution.•The effect of different factors on the reaction was investigated.•The intermediate products were identified and the kinetics and degradation pathway was proposed.
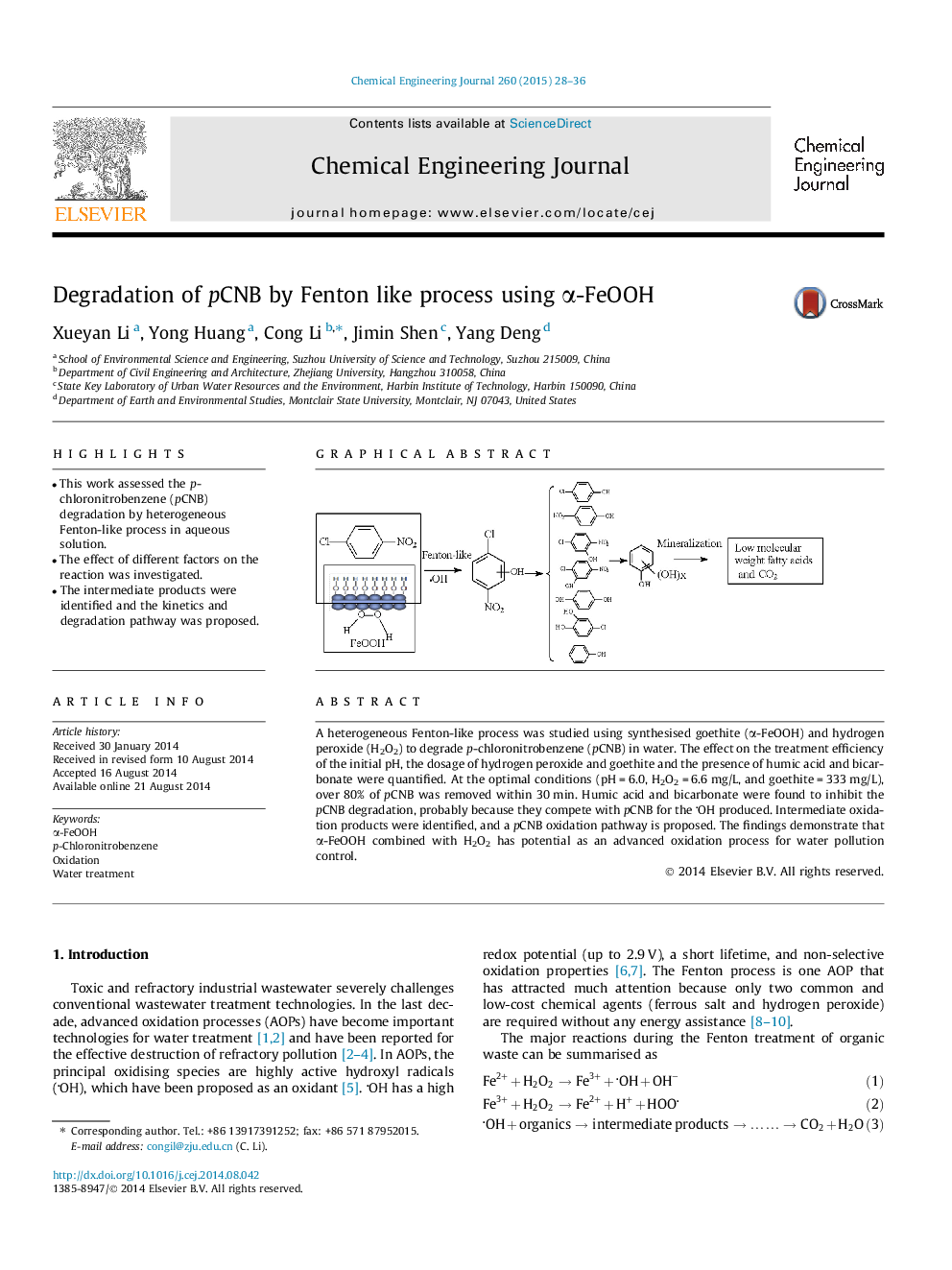
A heterogeneous Fenton-like process was studied using synthesised goethite (α-FeOOH) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) to degrade p-chloronitrobenzene (pCNB) in water. The effect on the treatment efficiency of the initial pH, the dosage of hydrogen peroxide and goethite and the presence of humic acid and bicarbonate were quantified. At the optimal conditions (pH = 6.0, H2O2 = 6.6 mg/L, and goethite = 333 mg/L), over 80% of pCNB was removed within 30 min. Humic acid and bicarbonate were found to inhibit the pCNB degradation, probably because they compete with pCNB for the OH produced. Intermediate oxidation products were identified, and a pCNB oxidation pathway is proposed. The findings demonstrate that α-FeOOH combined with H2O2 has potential as an advanced oxidation process for water pollution control.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide