| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 146727 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2015 | 6 Pages |
•Successive cultures: solid (electric field pretreatment; EFP) and liquid are proposed.•EFP increased the biocatalyst (BC) surface activity.•Enhanced surface activity was detected in BC with biomass, but not in perlite alone.•EFP caused metabolic modifications which persist in subsequent liquid culture.•This is the first study devoted to enhance microbial hydrocarbon degradation by EFP.
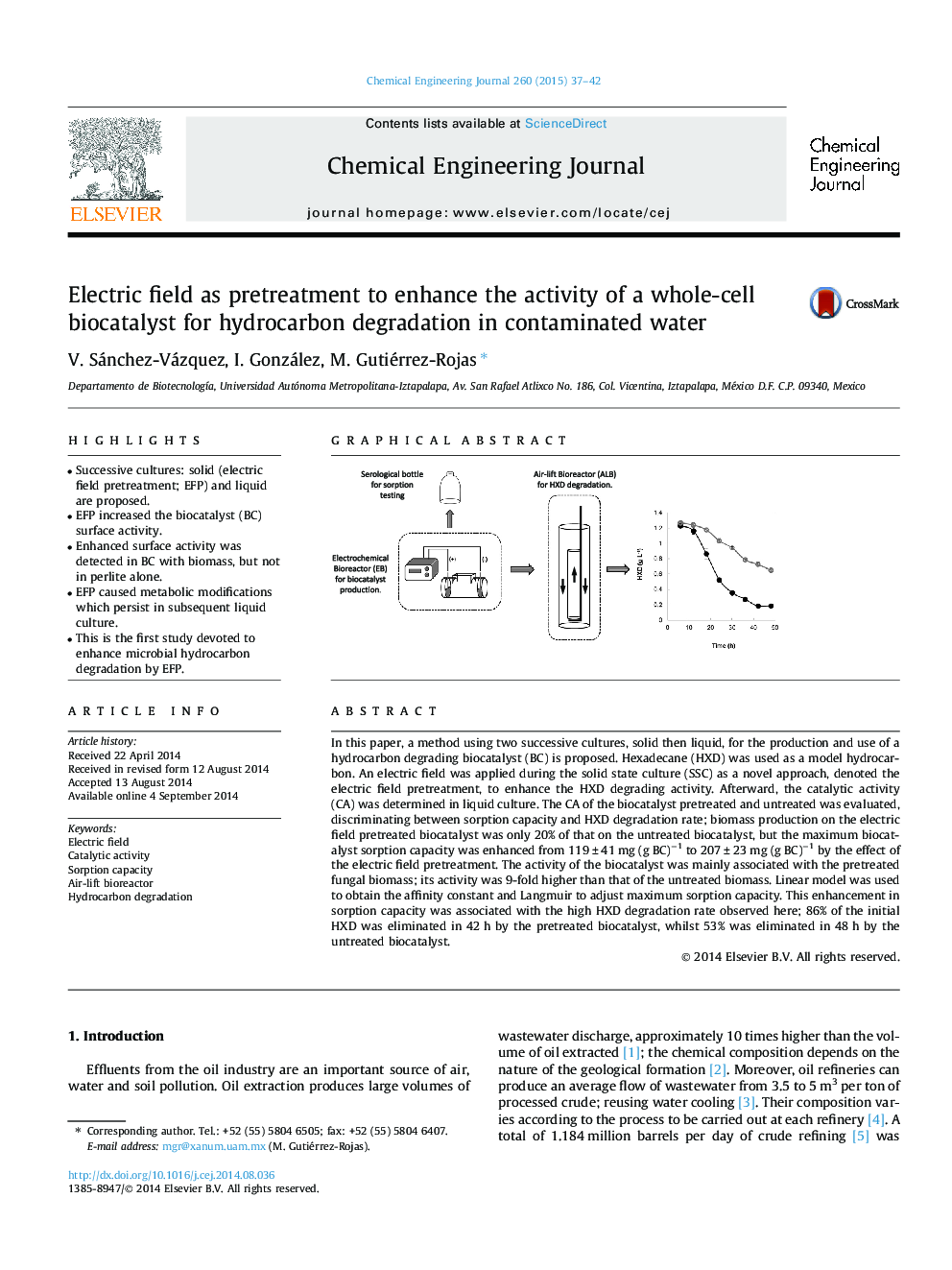
In this paper, a method using two successive cultures, solid then liquid, for the production and use of a hydrocarbon degrading biocatalyst (BC) is proposed. Hexadecane (HXD) was used as a model hydrocarbon. An electric field was applied during the solid state culture (SSC) as a novel approach, denoted the electric field pretreatment, to enhance the HXD degrading activity. Afterward, the catalytic activity (CA) was determined in liquid culture. The CA of the biocatalyst pretreated and untreated was evaluated, discriminating between sorption capacity and HXD degradation rate; biomass production on the electric field pretreated biocatalyst was only 20% of that on the untreated biocatalyst, but the maximum biocatalyst sorption capacity was enhanced from 119 ± 41 mg (g BC)−1 to 207 ± 23 mg (g BC)−1 by the effect of the electric field pretreatment. The activity of the biocatalyst was mainly associated with the pretreated fungal biomass; its activity was 9-fold higher than that of the untreated biomass. Linear model was used to obtain the affinity constant and Langmuir to adjust maximum sorption capacity. This enhancement in sorption capacity was associated with the high HXD degradation rate observed here; 86% of the initial HXD was eliminated in 42 h by the pretreated biocatalyst, whilst 53% was eliminated in 48 h by the untreated biocatalyst.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide