| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 146754 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2015 | 6 Pages |
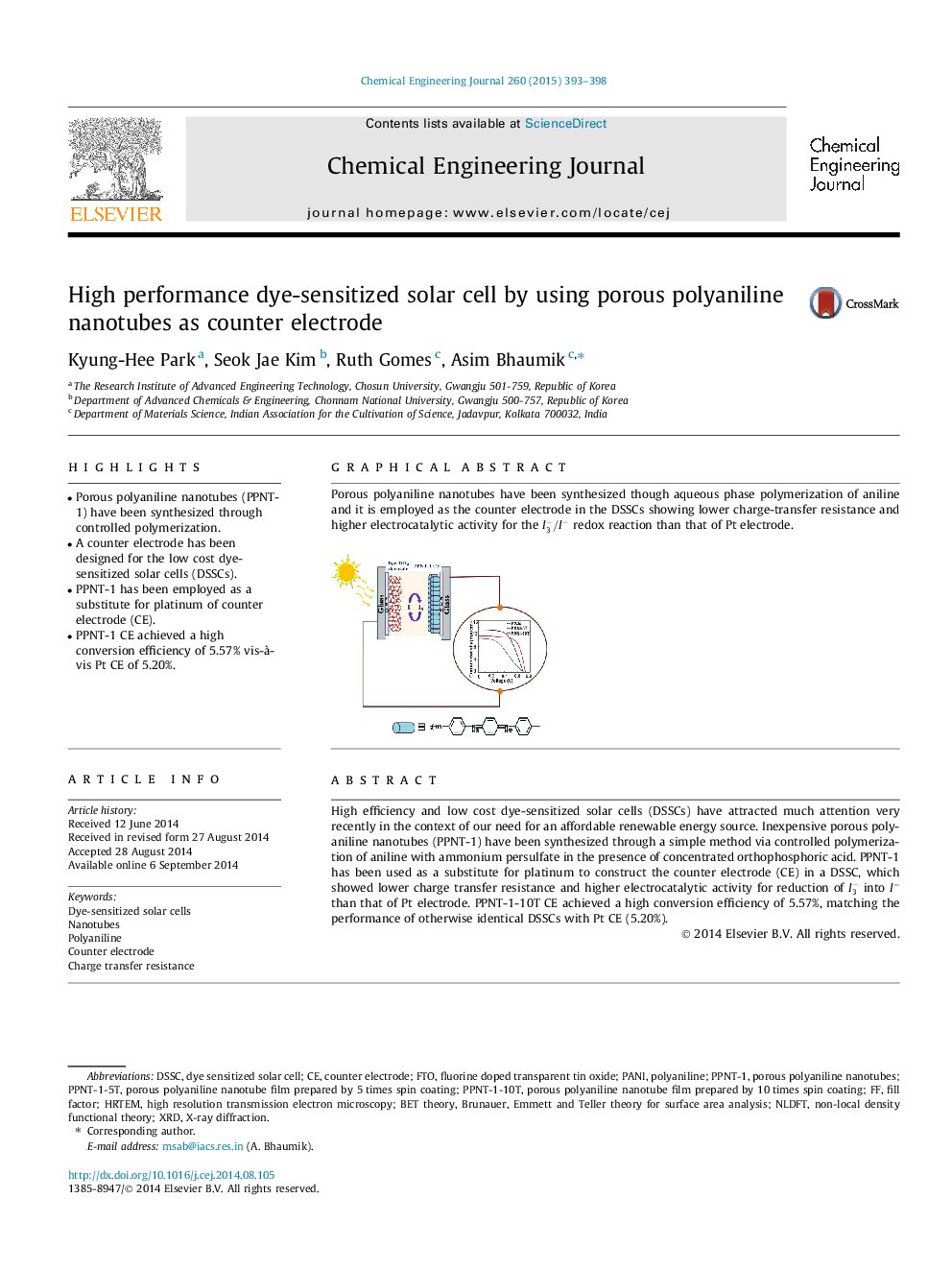
•Porous polyaniline nanotubes (PPNT-1) have been synthesized through controlled polymerization.•A counter electrode has been designed for the low cost dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs).•PPNT-1 has been employed as a substitute for platinum of counter electrode (CE).•PPNT-1 CE achieved a high conversion efficiency of 5.57% vis-à-vis Pt CE of 5.20%.
High efficiency and low cost dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) have attracted much attention very recently in the context of our need for an affordable renewable energy source. Inexpensive porous polyaniline nanotubes (PPNT-1) have been synthesized through a simple method via controlled polymerization of aniline with ammonium persulfate in the presence of concentrated orthophosphoric acid. PPNT-1 has been used as a substitute for platinum to construct the counter electrode (CE) in a DSSC, which showed lower charge transfer resistance and higher electrocatalytic activity for reduction of I3- into I− than that of Pt electrode. PPNT-1-10T CE achieved a high conversion efficiency of 5.57%, matching the performance of otherwise identical DSSCs with Pt CE (5.20%).
Graphical abstractPorous polyaniline nanotubes have been synthesized though aqueous phase polymerization of aniline and it is employed as the counter electrode in the DSSCs showing lower charge-transfer resistance and higher electrocatalytic activity for the I3-/I- redox reaction than that of Pt electrode.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide