| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 146784 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2015 | 8 Pages |
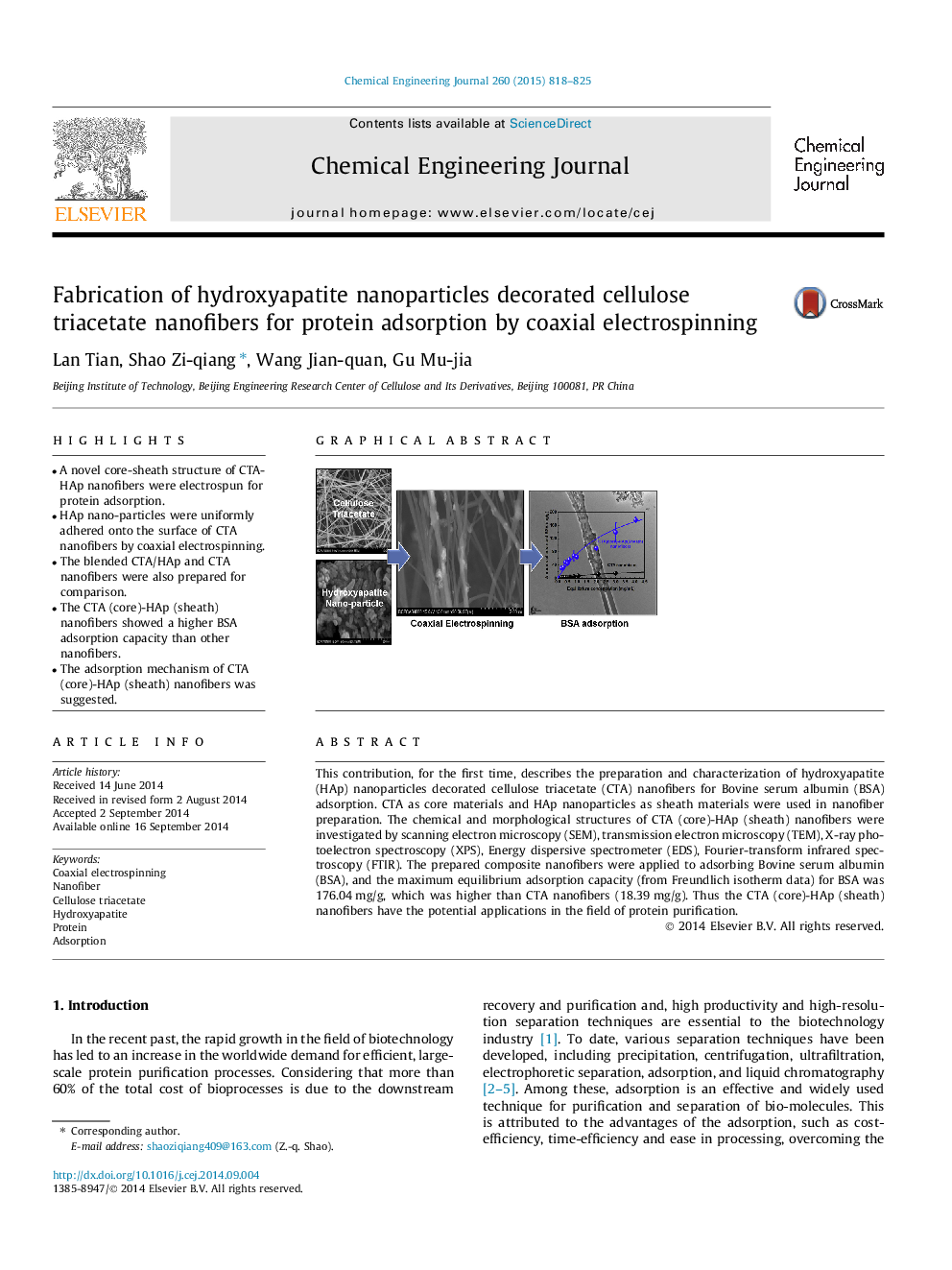
•A novel core-sheath structure of CTA-HAp nanofibers were electrospun for protein adsorption.•HAp nano-particles were uniformly adhered onto the surface of CTA nanofibers by coaxial electrospinning.•The blended CTA/HAp and CTA nanofibers were also prepared for comparison.•The CTA (core)-HAp (sheath) nanofibers showed a higher BSA adsorption capacity than other nanofibers.•The adsorption mechanism of CTA (core)-HAp (sheath) nanofibers was suggested.
This contribution, for the first time, describes the preparation and characterization of hydroxyapatite (HAp) nanoparticles decorated cellulose triacetate (CTA) nanofibers for Bovine serum albumin (BSA) adsorption. CTA as core materials and HAp nanoparticles as sheath materials were used in nanofiber preparation. The chemical and morphological structures of CTA (core)-HAp (sheath) nanofibers were investigated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), Energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). The prepared composite nanofibers were applied to adsorbing Bovine serum albumin (BSA), and the maximum equilibrium adsorption capacity (from Freundlich isotherm data) for BSA was 176.04 mg/g, which was higher than CTA nanofibers (18.39 mg/g). Thus the CTA (core)-HAp (sheath) nanofibers have the potential applications in the field of protein purification.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide