| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 146828 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2015 | 8 Pages |
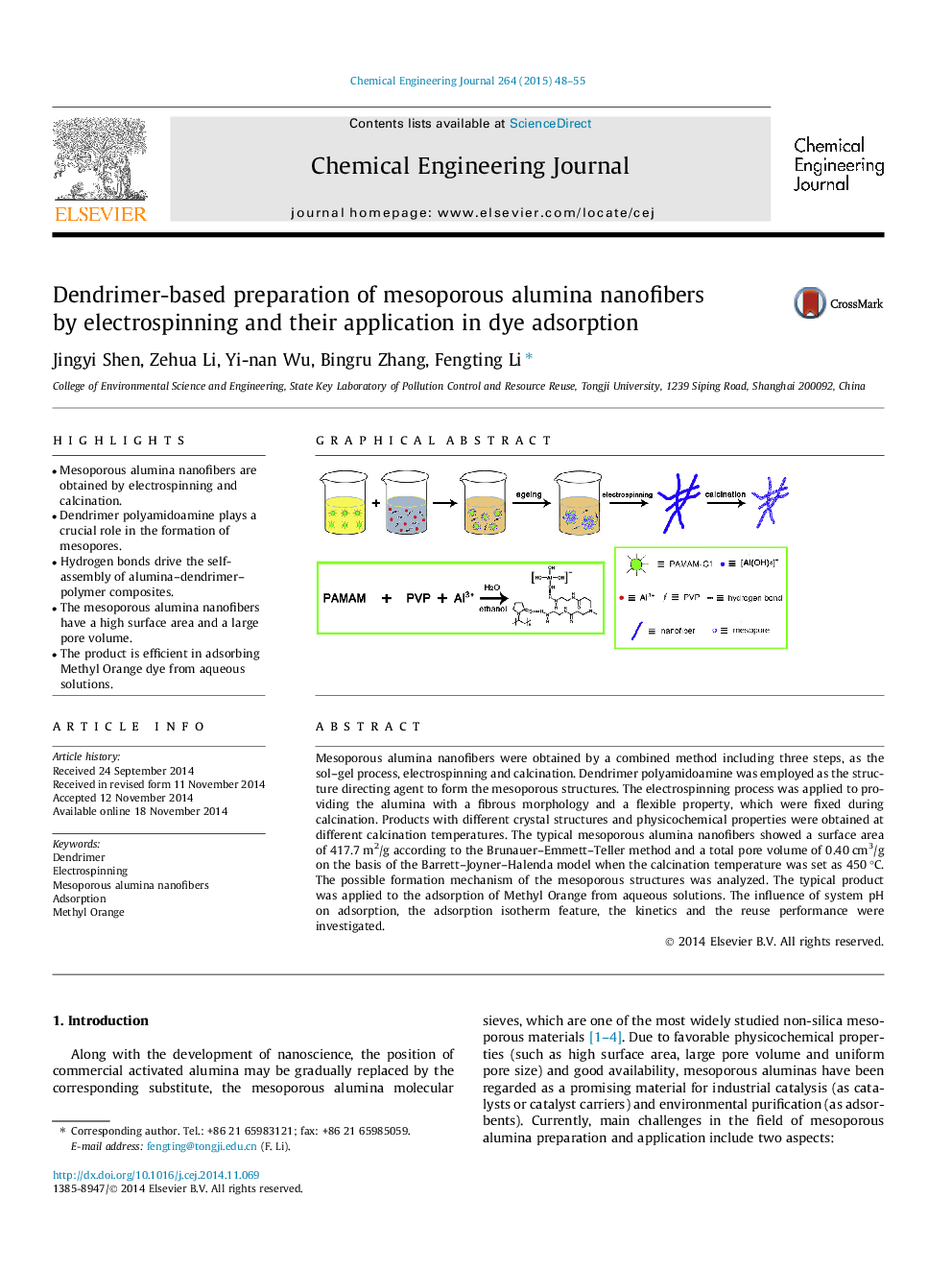
•Mesoporous alumina nanofibers are obtained by electrospinning and calcination.•Dendrimer polyamidoamine plays a crucial role in the formation of mesopores.•Hydrogen bonds drive the self-assembly of alumina–dendrimer–polymer composites.•The mesoporous alumina nanofibers have a high surface area and a large pore volume.•The product is efficient in adsorbing Methyl Orange dye from aqueous solutions.
Mesoporous alumina nanofibers were obtained by a combined method including three steps, as the sol–gel process, electrospinning and calcination. Dendrimer polyamidoamine was employed as the structure directing agent to form the mesoporous structures. The electrospinning process was applied to providing the alumina with a fibrous morphology and a flexible property, which were fixed during calcination. Products with different crystal structures and physicochemical properties were obtained at different calcination temperatures. The typical mesoporous alumina nanofibers showed a surface area of 417.7 m2/g according to the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller method and a total pore volume of 0.40 cm3/g on the basis of the Barrett–Joyner–Halenda model when the calcination temperature was set as 450 °C. The possible formation mechanism of the mesoporous structures was analyzed. The typical product was applied to the adsorption of Methyl Orange from aqueous solutions. The influence of system pH on adsorption, the adsorption isotherm feature, the kinetics and the reuse performance were investigated.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide