| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 146853 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2015 | 9 Pages |
•Different air-gap lengths were used to fabricate the surface modified PSf HFMs.•The outer surface roughness of HFMs decreased slightly by increasing air-gap.•The PSf HFMs were used in contactor application for CO2 absorption.•The CO2 absorption flux increased by increasing air-gap to 15 cm then decreased.
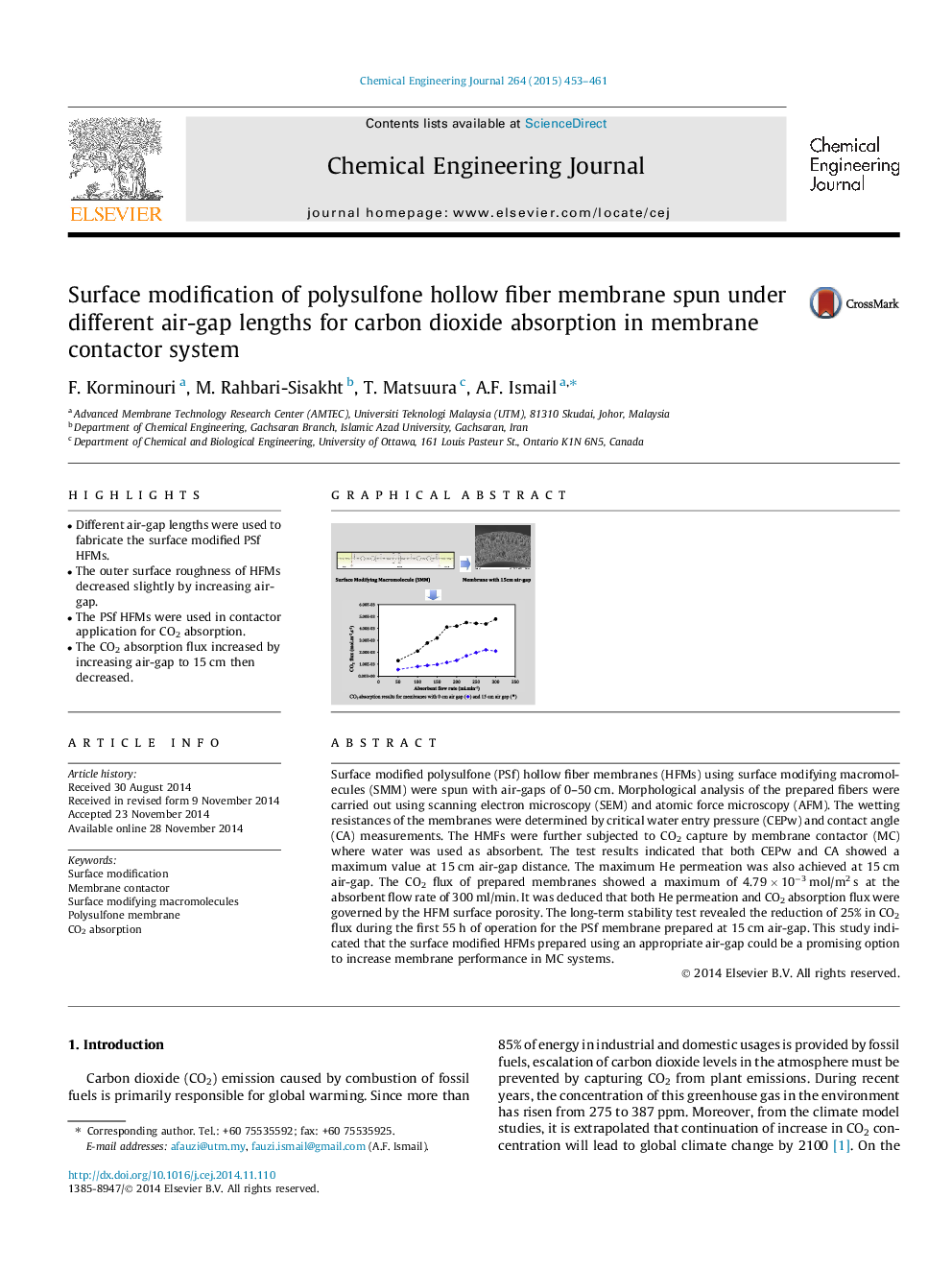
Surface modified polysulfone (PSf) hollow fiber membranes (HFMs) using surface modifying macromolecules (SMM) were spun with air-gaps of 0–50 cm. Morphological analysis of the prepared fibers were carried out using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and atomic force microscopy (AFM). The wetting resistances of the membranes were determined by critical water entry pressure (CEPw) and contact angle (CA) measurements. The HMFs were further subjected to CO2 capture by membrane contactor (MC) where water was used as absorbent. The test results indicated that both CEPw and CA showed a maximum value at 15 cm air-gap distance. The maximum He permeation was also achieved at 15 cm air-gap. The CO2 flux of prepared membranes showed a maximum of 4.79 × 10−3 mol/m2 s at the absorbent flow rate of 300 ml/min. It was deduced that both He permeation and CO2 absorption flux were governed by the HFM surface porosity. The long-term stability test revealed the reduction of 25% in CO2 flux during the first 55 h of operation for the PSf membrane prepared at 15 cm air-gap. This study indicated that the surface modified HFMs prepared using an appropriate air-gap could be a promising option to increase membrane performance in MC systems.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide