| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 146876 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2015 | 9 Pages |
•KCl was doped into V2O5–WO3/TiO2 catalysts by impregnation method.•V2O5–WO3/TiO2 SCR catalysts were deactivated seriously with addition of KCl.•The KCl-poisoning mechanism model of V2O5–WO3/TiO2 SCR catalysts was proposed.•The synergy poisoning mechanism model of KCl and Hgel over V2O5–WO3/TiO2 SCR catalysts was proposed.
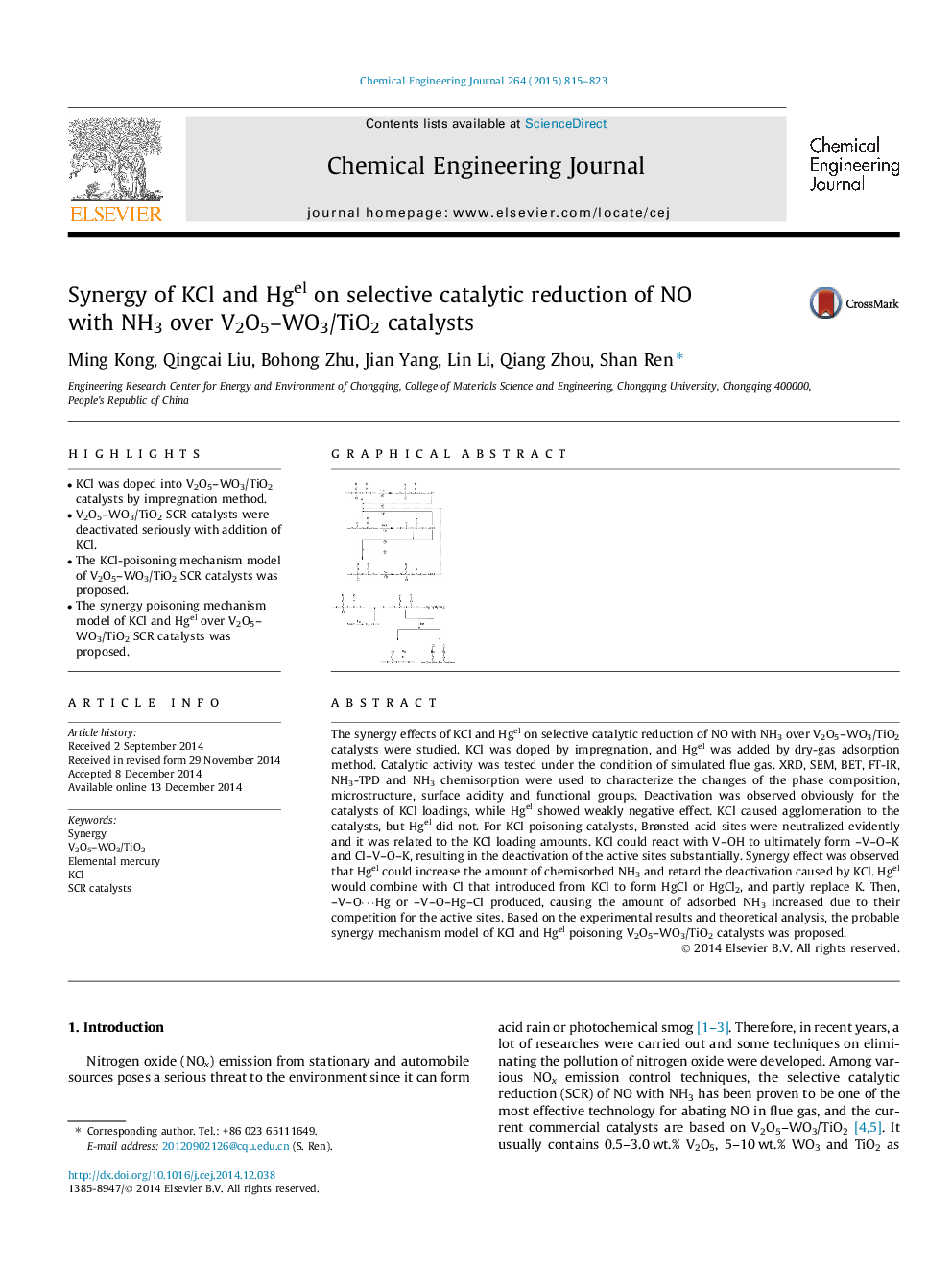
The synergy effects of KCl and Hgel on selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3 over V2O5–WO3/TiO2 catalysts were studied. KCl was doped by impregnation, and Hgel was added by dry-gas adsorption method. Catalytic activity was tested under the condition of simulated flue gas. XRD, SEM, BET, FT-IR, NH3-TPD and NH3 chemisorption were used to characterize the changes of the phase composition, microstructure, surface acidity and functional groups. Deactivation was observed obviously for the catalysts of KCl loadings, while Hgel showed weakly negative effect. KCl caused agglomeration to the catalysts, but Hgel did not. For KCl poisoning catalysts, Brønsted acid sites were neutralized evidently and it was related to the KCl loading amounts. KCl could react with V–OH to ultimately form –V–O–K and Cl–V–O–K, resulting in the deactivation of the active sites substantially. Synergy effect was observed that Hgel could increase the amount of chemisorbed NH3 and retard the deactivation caused by KCl. Hgel would combine with Cl that introduced from KCl to form HgCl or HgCl2, and partly replace K. Then, –V–O⋯Hg or –V–O–Hg–Cl produced, causing the amount of adsorbed NH3 increased due to their competition for the active sites. Based on the experimental results and theoretical analysis, the probable synergy mechanism model of KCl and Hgel poisoning V2O5–WO3/TiO2 catalysts was proposed.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide