| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 147028 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2014 | 8 Pages |
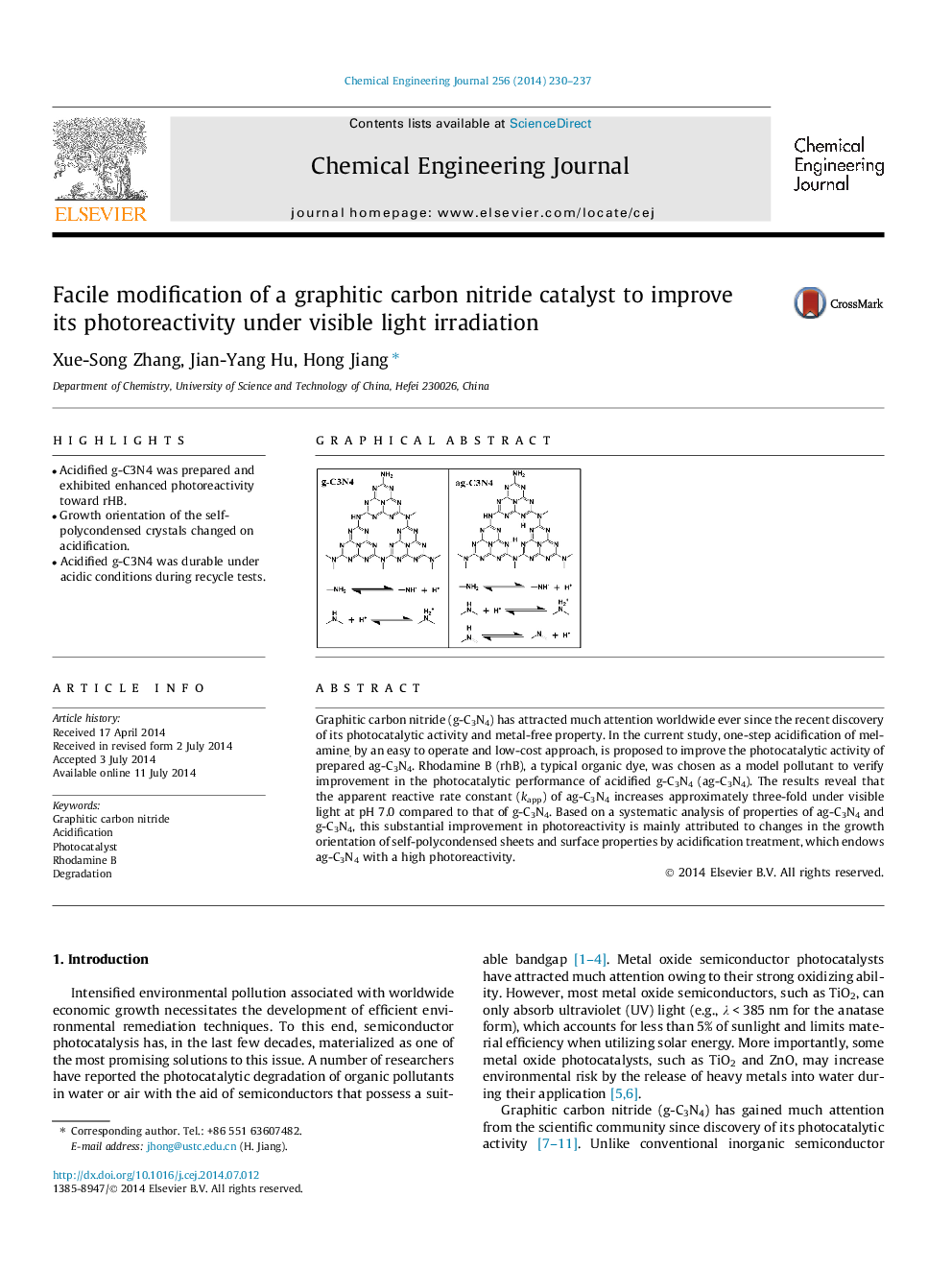
•Acidified g-C3N4 was prepared and exhibited enhanced photoreactivity toward rHB.•Growth orientation of the self-polycondensed crystals changed on acidification.•Acidified g-C3N4 was durable under acidic conditions during recycle tests.
Graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) has attracted much attention worldwide ever since the recent discovery of its photocatalytic activity and metal-free property. In the current study, one-step acidification of melamine, by an easy to operate and low-cost approach, is proposed to improve the photocatalytic activity of prepared ag-C3N4. Rhodamine B (rhB), a typical organic dye, was chosen as a model pollutant to verify improvement in the photocatalytic performance of acidified g-C3N4 (ag-C3N4). The results reveal that the apparent reactive rate constant (kapp) of ag-C3N4 increases approximately three-fold under visible light at pH 7.0 compared to that of g-C3N4. Based on a systematic analysis of properties of ag-C3N4 and g-C3N4, this substantial improvement in photoreactivity is mainly attributed to changes in the growth orientation of self-polycondensed sheets and surface properties by acidification treatment, which endows ag-C3N4 with a high photoreactivity.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide