| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 147037 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2014 | 5 Pages |
•A nanofibrous membrane composed of two layers was fabricated for DCMD.•The membrane was composed of PVDF-co-HFP nanofibers and PAN micro/nanofibers.•The PVDF-co-HFP nanofibers showed a superhydrophobic property and high porosity.•A high flux performance was obtained for the dual-layer nanofibrous membrane.•The present dual-layer nanofibrous membrane showed good potential for DCMD.
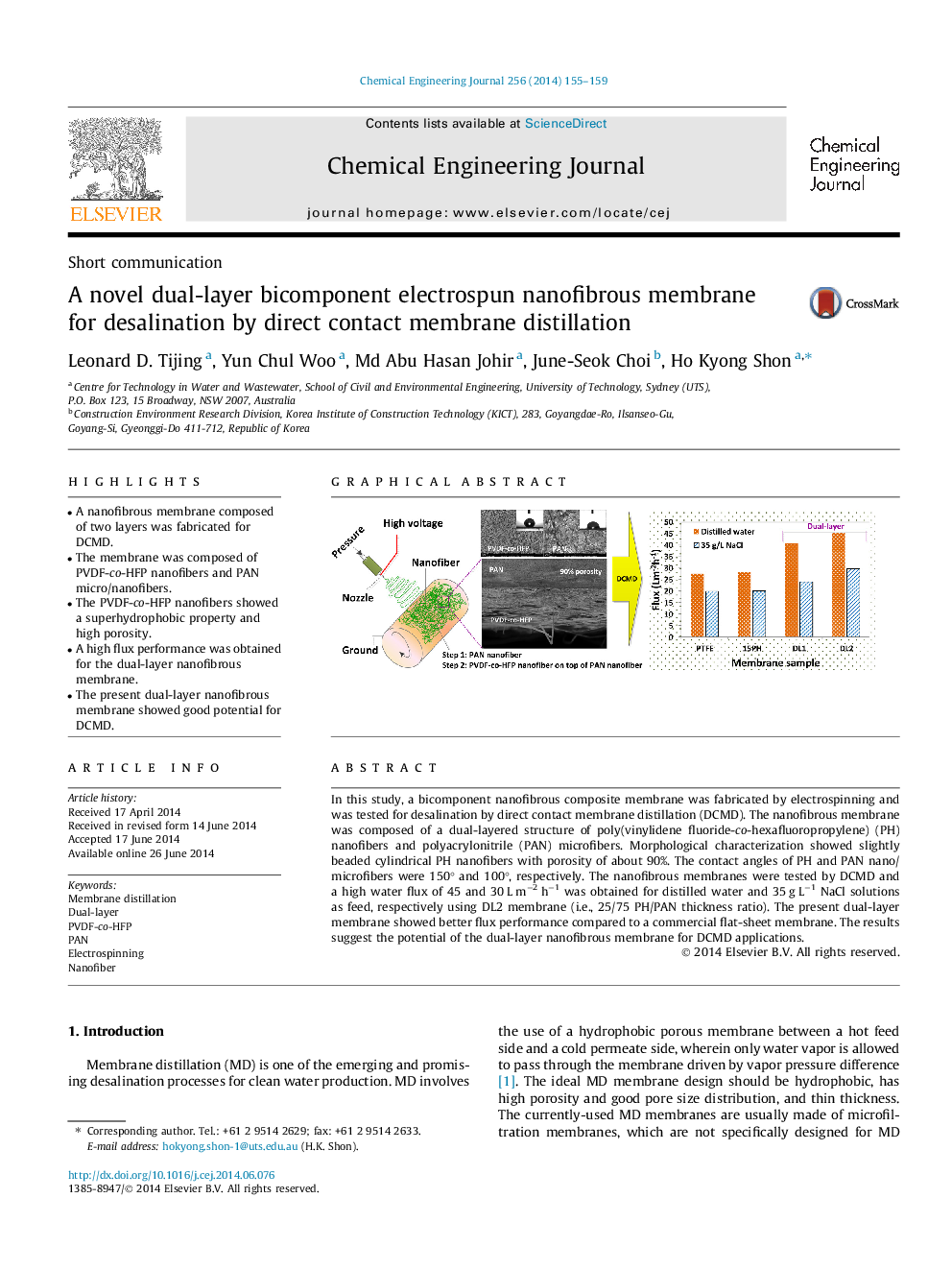
In this study, a bicomponent nanofibrous composite membrane was fabricated by electrospinning and was tested for desalination by direct contact membrane distillation (DCMD). The nanofibrous membrane was composed of a dual-layered structure of poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) (PH) nanofibers and polyacrylonitrile (PAN) microfibers. Morphological characterization showed slightly beaded cylindrical PH nanofibers with porosity of about 90%. The contact angles of PH and PAN nano/microfibers were 150° and 100°, respectively. The nanofibrous membranes were tested by DCMD and a high water flux of 45 and 30 L m−2 h−1 was obtained for distilled water and 35 g L−1 NaCl solutions as feed, respectively using DL2 membrane (i.e., 25/75 PH/PAN thickness ratio). The present dual-layer membrane showed better flux performance compared to a commercial flat-sheet membrane. The results suggest the potential of the dual-layer nanofibrous membrane for DCMD applications.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide