| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 147274 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2014 | 9 Pages |
•A new composite containing chitosan and iron(III) hydroxide has been manufactured.•SEM-EDX analysis revealed a homogenous distribution of Fe(OH)3 in whole material.•An adsorption column system was used for boron recovery from seawater.•Adsorption–desorption cycles were performed and desorption uptake remained >40%.•Elution was efficiently eluted with water at pH 12.
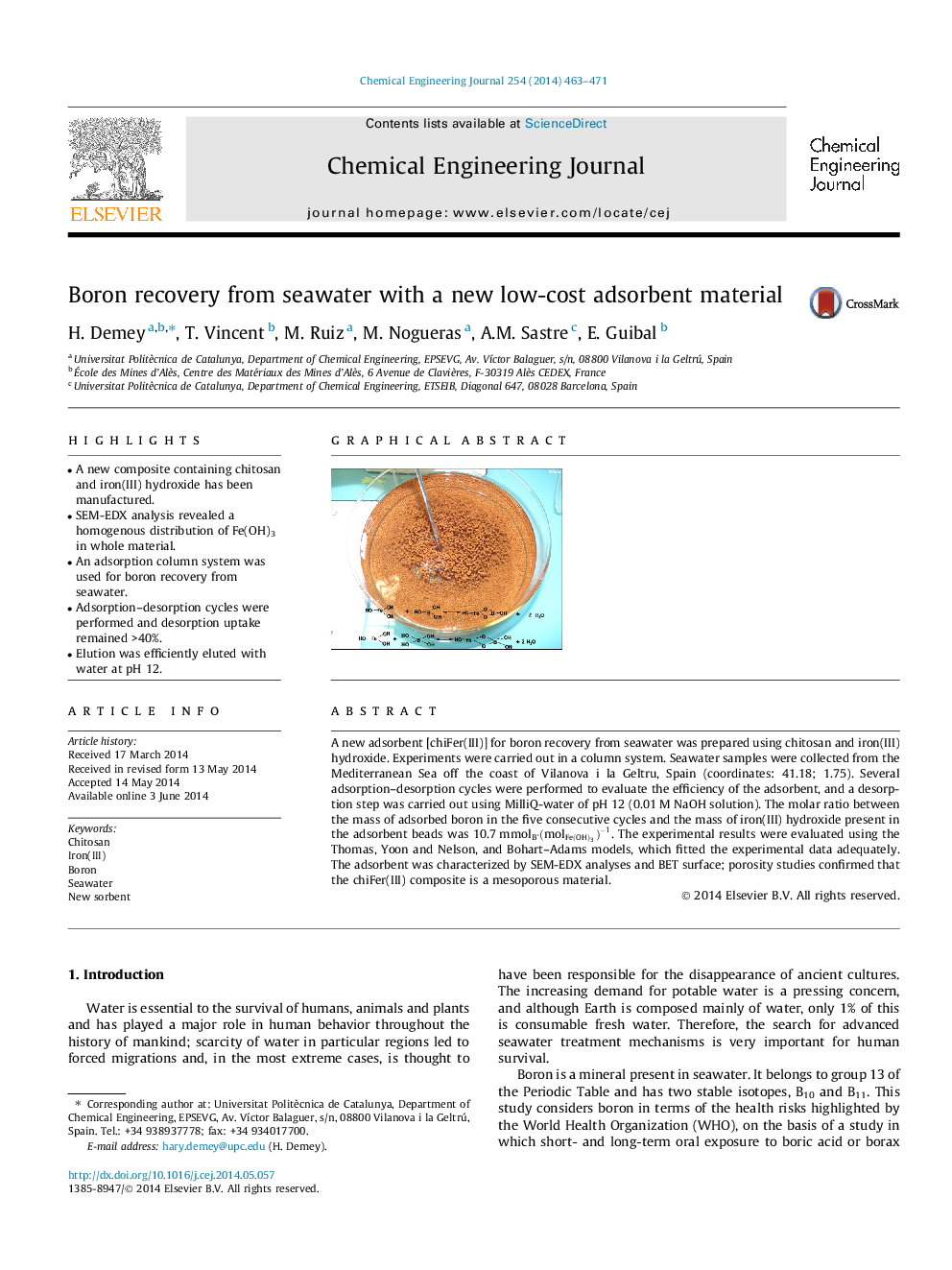
A new adsorbent [chiFer(III)] for boron recovery from seawater was prepared using chitosan and iron(III) hydroxide. Experiments were carried out in a column system. Seawater samples were collected from the Mediterranean Sea off the coast of Vilanova i la Geltru, Spain (coordinates: 41.18; 1.75). Several adsorption–desorption cycles were performed to evaluate the efficiency of the adsorbent, and a desorption step was carried out using MilliQ-water of pH 12 (0.01 M NaOH solution). The molar ratio between the mass of adsorbed boron in the five consecutive cycles and the mass of iron(III) hydroxide present in the adsorbent beads was 10.7 mmolB·(molFe(OH)3)-1(molFe(OH)3)-1. The experimental results were evaluated using the Thomas, Yoon and Nelson, and Bohart–Adams models, which fitted the experimental data adequately. The adsorbent was characterized by SEM-EDX analyses and BET surface; porosity studies confirmed that the chiFer(III) composite is a mesoporous material.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide