| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 147384 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2014 | 5 Pages |
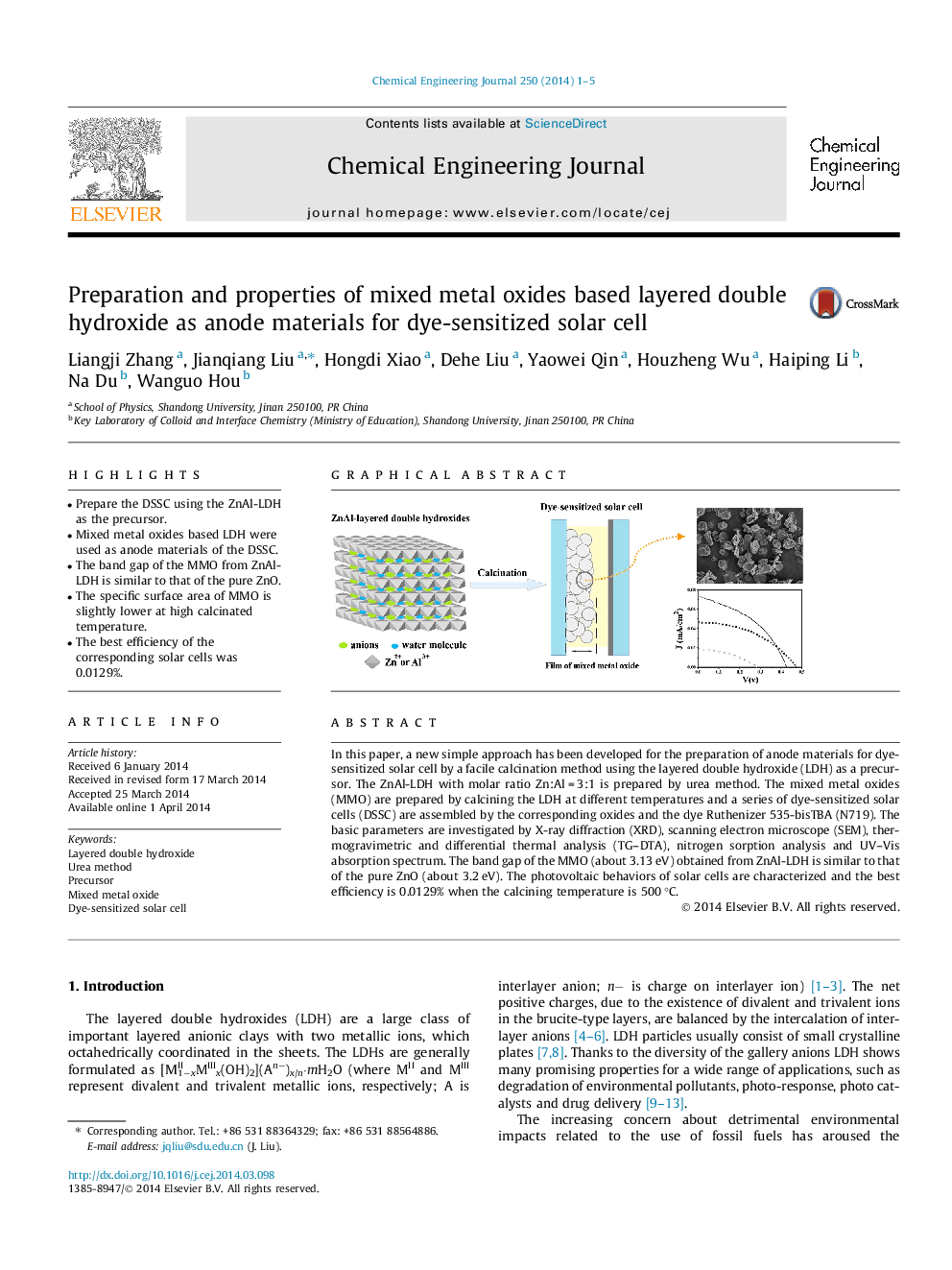
•Prepare the DSSC using the ZnAl-LDH as the precursor.•Mixed metal oxides based LDH were used as anode materials of the DSSC.•The band gap of the MMO from ZnAl-LDH is similar to that of the pure ZnO.•The specific surface area of MMO is slightly lower at high calcinated temperature.•The best efficiency of the corresponding solar cells was 0.0129%.
In this paper, a new simple approach has been developed for the preparation of anode materials for dye-sensitized solar cell by a facile calcination method using the layered double hydroxide (LDH) as a precursor. The ZnAl-LDH with molar ratio Zn:Al = 3:1 is prepared by urea method. The mixed metal oxides (MMO) are prepared by calcining the LDH at different temperatures and a series of dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSC) are assembled by the corresponding oxides and the dye Ruthenizer 535-bisTBA (N719). The basic parameters are investigated by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscope (SEM), thermogravimetric and differential thermal analysis (TG–DTA), nitrogen sorption analysis and UV–Vis absorption spectrum. The band gap of the MMO (about 3.13 eV) obtained from ZnAl-LDH is similar to that of the pure ZnO (about 3.2 eV). The photovoltaic behaviors of solar cells are characterized and the best efficiency is 0.0129% when the calcining temperature is 500 °C.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide