| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 147685 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2014 | 7 Pages |
•The Co3O4 nanocrystals on GO is a synergistic catalyst for activation of PMS.•The highest catalytic activity was achieved when the Co3O4 loading was about 50%.•The Co–OH complexes can efficiently activate PMS during the reaction.•The formation of Co–OH complexes on the surface of GO is easier than other supports.
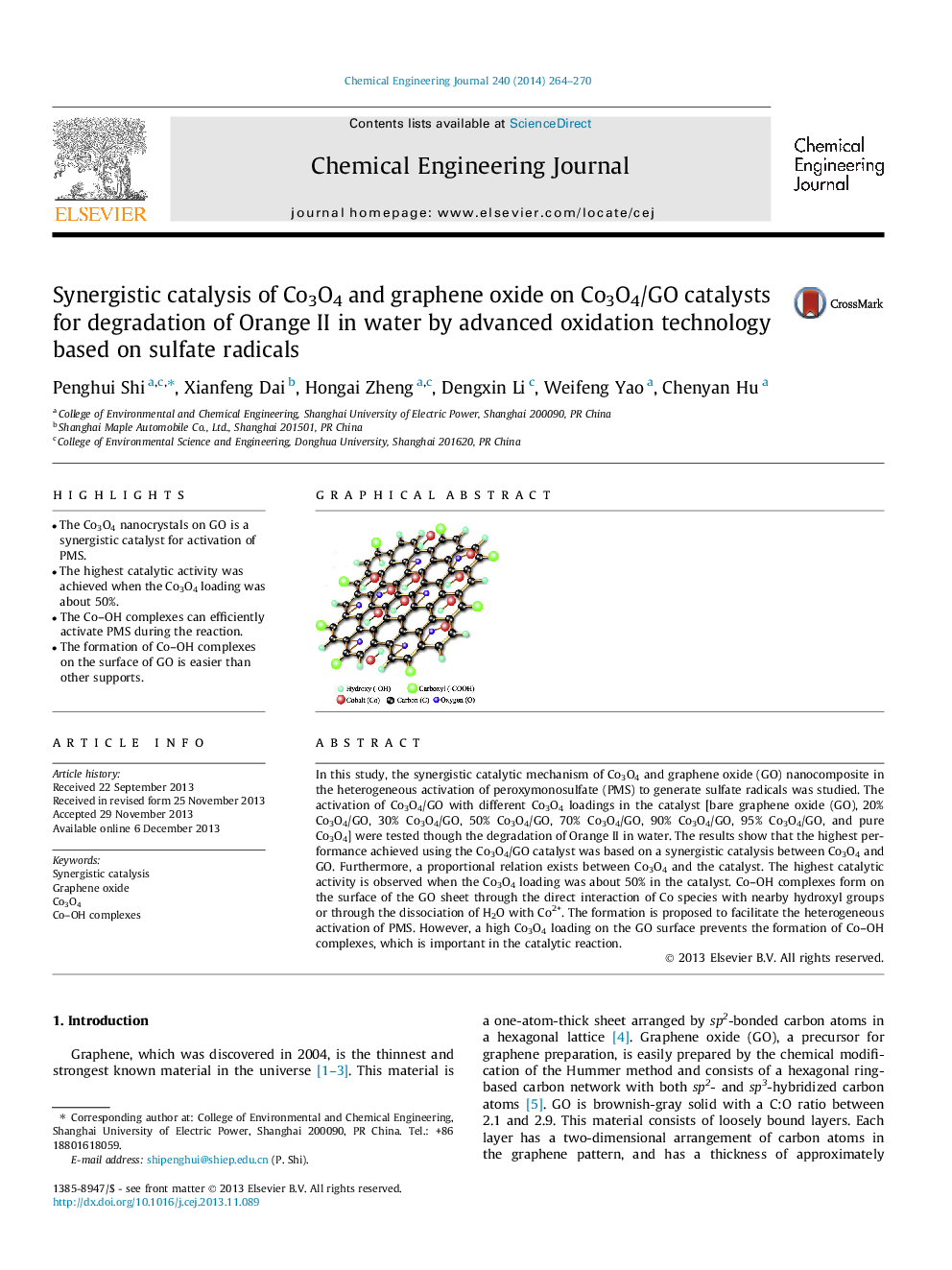
In this study, the synergistic catalytic mechanism of Co3O4 and graphene oxide (GO) nanocomposite in the heterogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate (PMS) to generate sulfate radicals was studied. The activation of Co3O4/GO with different Co3O4 loadings in the catalyst [bare graphene oxide (GO), 20% Co3O4/GO, 30% Co3O4/GO, 50% Co3O4/GO, 70% Co3O4/GO, 90% Co3O4/GO, 95% Co3O4/GO, and pure Co3O4] were tested though the degradation of Orange II in water. The results show that the highest performance achieved using the Co3O4/GO catalyst was based on a synergistic catalysis between Co3O4 and GO. Furthermore, a proportional relation exists between Co3O4 and the catalyst. The highest catalytic activity is observed when the Co3O4 loading was about 50% in the catalyst. Co–OH complexes form on the surface of the GO sheet through the direct interaction of Co species with nearby hydroxyl groups or through the dissociation of H2O with Co2+. The formation is proposed to facilitate the heterogeneous activation of PMS. However, a high Co3O4 loading on the GO surface prevents the formation of Co–OH complexes, which is important in the catalytic reaction.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide