| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 147766 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2014 | 11 Pages |
•Hierarchically porous S–Fe2−xTixO3 was prepared by critic acid templated method.•Cooperative effect of titanium and sulfate created lots of Lewis acid sites.•Fe–Ti bimetallic solid superacid widened the pH range to 10.0 in Fenton reaction.•Light with wavelength 450–595 nm had significant effect on activity of S–Fe2−xTixO3.•Favorable synergetic effect of acid sites and photo improved catalytic activity.
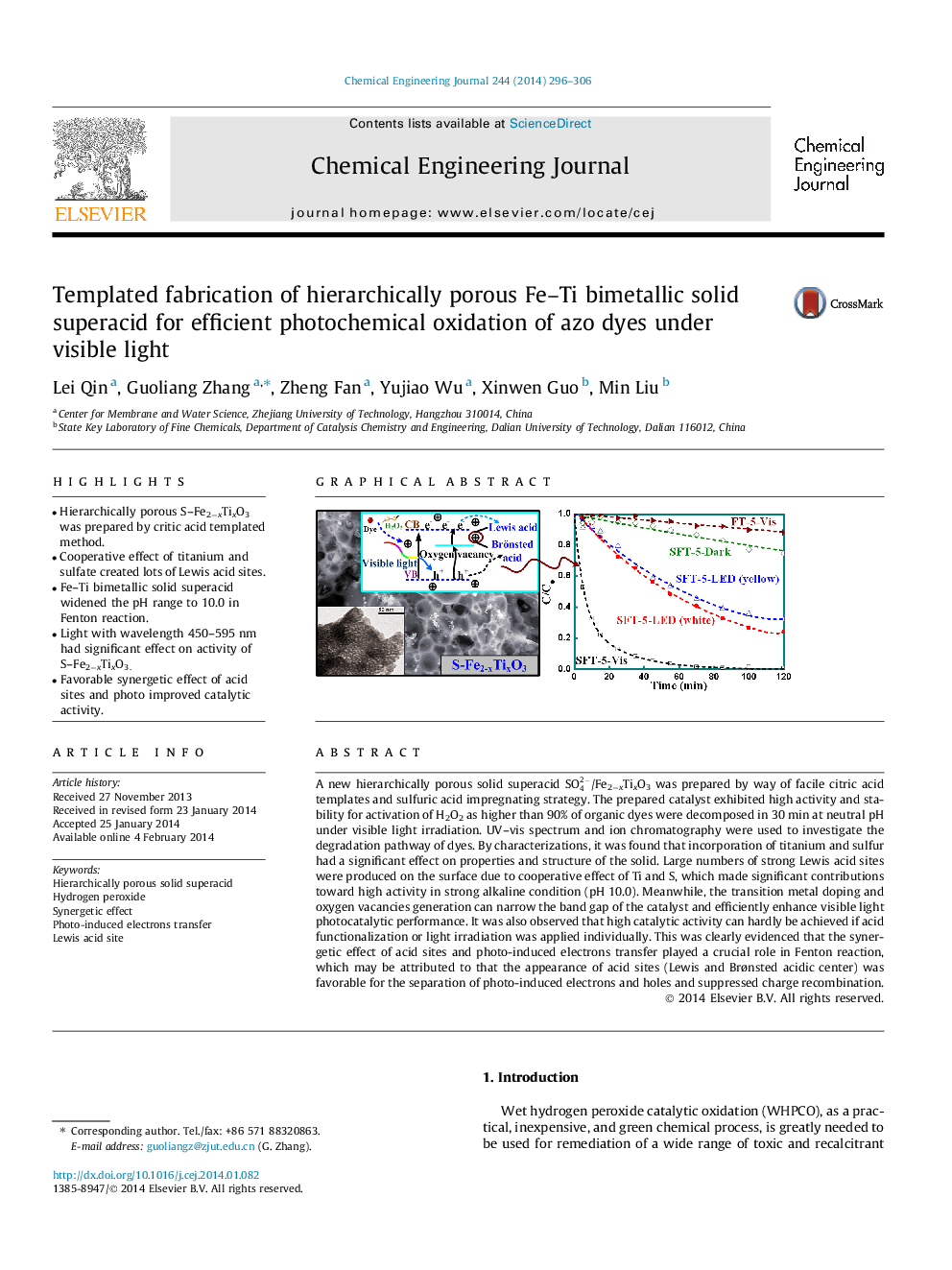
A new hierarchically porous solid superacid SO42-/Fe2−xTixO3 was prepared by way of facile citric acid templates and sulfuric acid impregnating strategy. The prepared catalyst exhibited high activity and stability for activation of H2O2 as higher than 90% of organic dyes were decomposed in 30 min at neutral pH under visible light irradiation. UV–vis spectrum and ion chromatography were used to investigate the degradation pathway of dyes. By characterizations, it was found that incorporation of titanium and sulfur had a significant effect on properties and structure of the solid. Large numbers of strong Lewis acid sites were produced on the surface due to cooperative effect of Ti and S, which made significant contributions toward high activity in strong alkaline condition (pH 10.0). Meanwhile, the transition metal doping and oxygen vacancies generation can narrow the band gap of the catalyst and efficiently enhance visible light photocatalytic performance. It was also observed that high catalytic activity can hardly be achieved if acid functionalization or light irradiation was applied individually. This was clearly evidenced that the synergetic effect of acid sites and photo-induced electrons transfer played a crucial role in Fenton reaction, which may be attributed to that the appearance of acid sites (Lewis and Brønsted acidic center) was favorable for the separation of photo-induced electrons and holes and suppressed charge recombination.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide