| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 147872 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2014 | 7 Pages |
•High nitrogen loading rate in a controlled activated sludge for partial nitritation.•Nitrogen loading rate of 5.0 or 9.3 g N L−1 d−1 for reject or synthetic water.•The new control system allows a suitable and stable effluent for anammox treatment.•Effluent with total nitritation was achieved only modifying the ammonium setpoint.
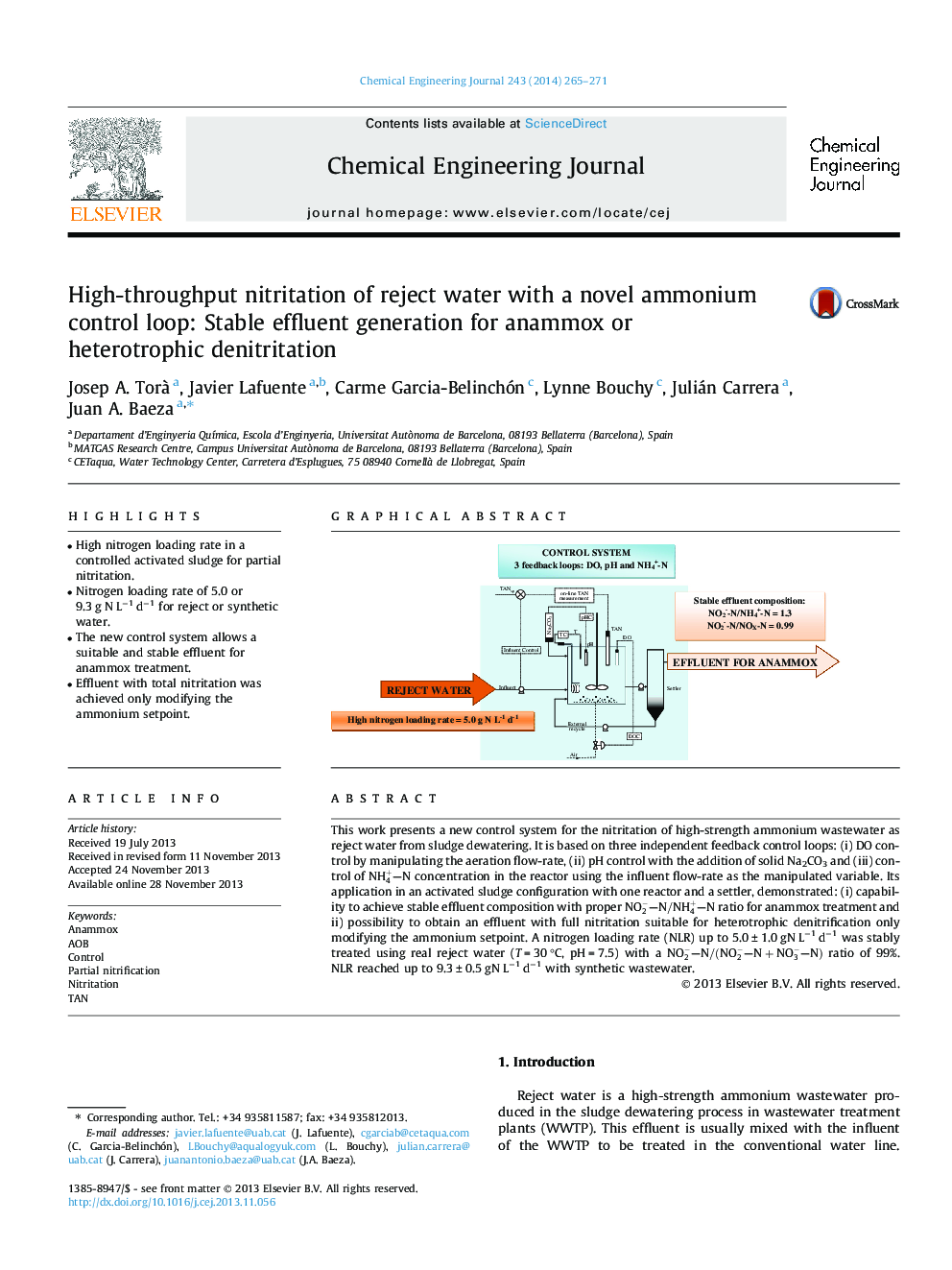
This work presents a new control system for the nitritation of high-strength ammonium wastewater as reject water from sludge dewatering. It is based on three independent feedback control loops: (i) DO control by manipulating the aeration flow-rate, (ii) pH control with the addition of solid Na2CO3 and (iii) control of NH4+–N concentration in the reactor using the influent flow-rate as the manipulated variable. Its application in an activated sludge configuration with one reactor and a settler, demonstrated: (i) capability to achieve stable effluent composition with proper NO2-–N/NH4+–N ratio for anammox treatment and ii) possibility to obtain an effluent with full nitritation suitable for heterotrophic denitrification only modifying the ammonium setpoint. A nitrogen loading rate (NLR) up to 5.0 ± 1.0 gN L−1 d−1 was stably treated using real reject water (T = 30 °C, pH = 7.5) with a NO2-–N/(NO2-–N+NO3-–N) ratio of 99%. NLR reached up to 9.3 ± 0.5 gN L−1 d−1 with synthetic wastewater.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide