| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 147897 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2014 | 9 Pages |
•ZnCl2 nanoparticles (∼10 nm) are strongly attached on the CMS support.•The catalysts possess strong Lewis acidity and high surface area (∼700 m2/g).•The catalysts show synergistic effect in hydroamination of cyclohexene.•The catalysts has better performance than common homo- and heterogeneous catalysts.•The catalyst can be easily separated after reaction and is recyclable.
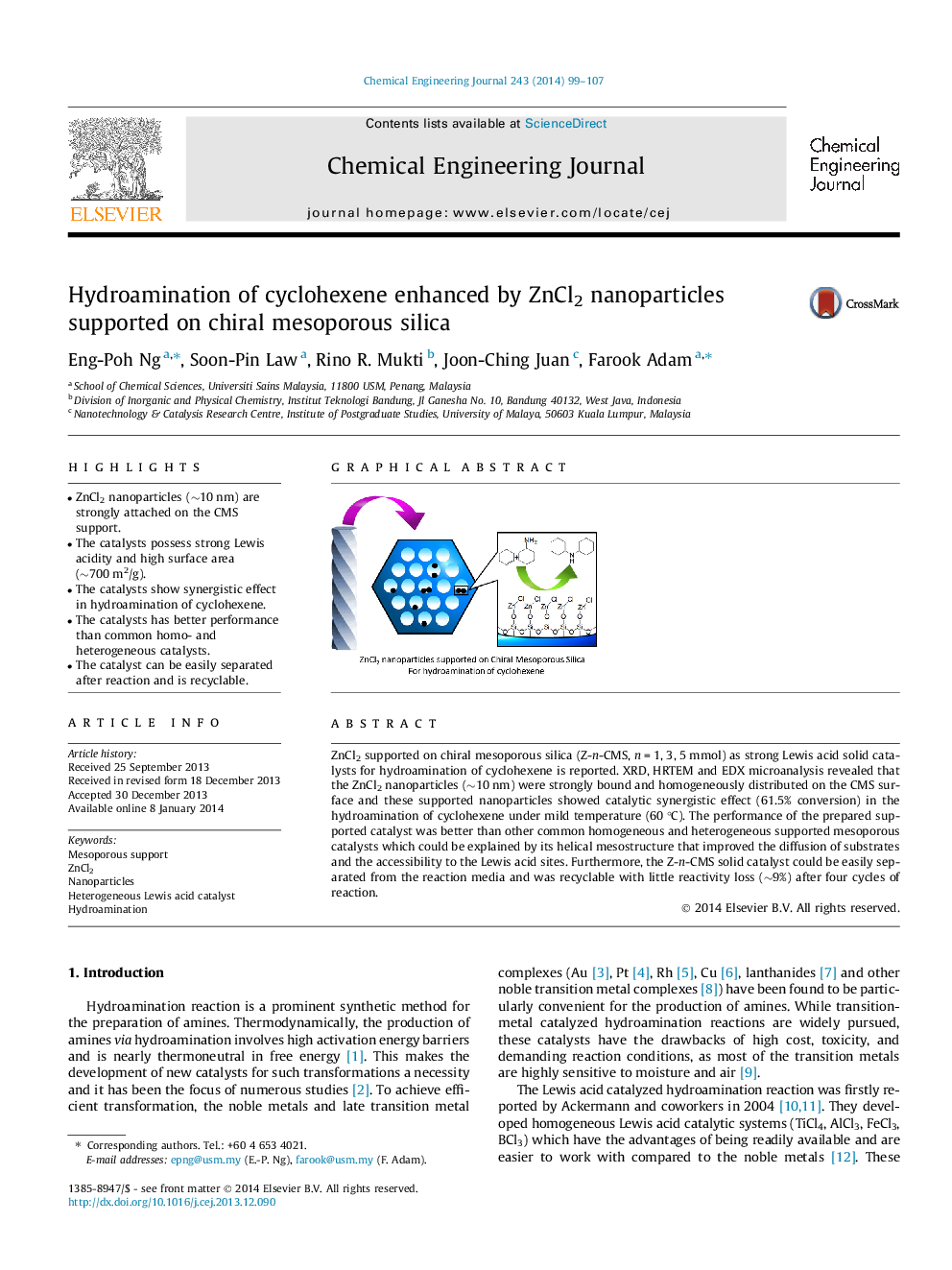
ZnCl2 supported on chiral mesoporous silica (Z-n-CMS, n = 1, 3, 5 mmol) as strong Lewis acid solid catalysts for hydroamination of cyclohexene is reported. XRD, HRTEM and EDX microanalysis revealed that the ZnCl2 nanoparticles (∼10 nm) were strongly bound and homogeneously distributed on the CMS surface and these supported nanoparticles showed catalytic synergistic effect (61.5% conversion) in the hydroamination of cyclohexene under mild temperature (60 °C). The performance of the prepared supported catalyst was better than other common homogeneous and heterogeneous supported mesoporous catalysts which could be explained by its helical mesostructure that improved the diffusion of substrates and the accessibility to the Lewis acid sites. Furthermore, the Z-n-CMS solid catalyst could be easily separated from the reaction media and was recyclable with little reactivity loss (∼9%) after four cycles of reaction.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide