| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 147913 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2014 | 8 Pages |
•A core@shell structured NiFe2O4@TiO2 magnetic nanoparticle was prepared.•The significant enhancement in photoactivity was attributed to synergism between NiFe2O4 and TiO2.•Hydrogen gases were more produced over the core@shell structured NiFe2O4@TiO2 nanocatalyst.•The remarkable magnetic property of core@shell structured NiFe2O4@TiO2 enabled more convenient photocatalyst separation.
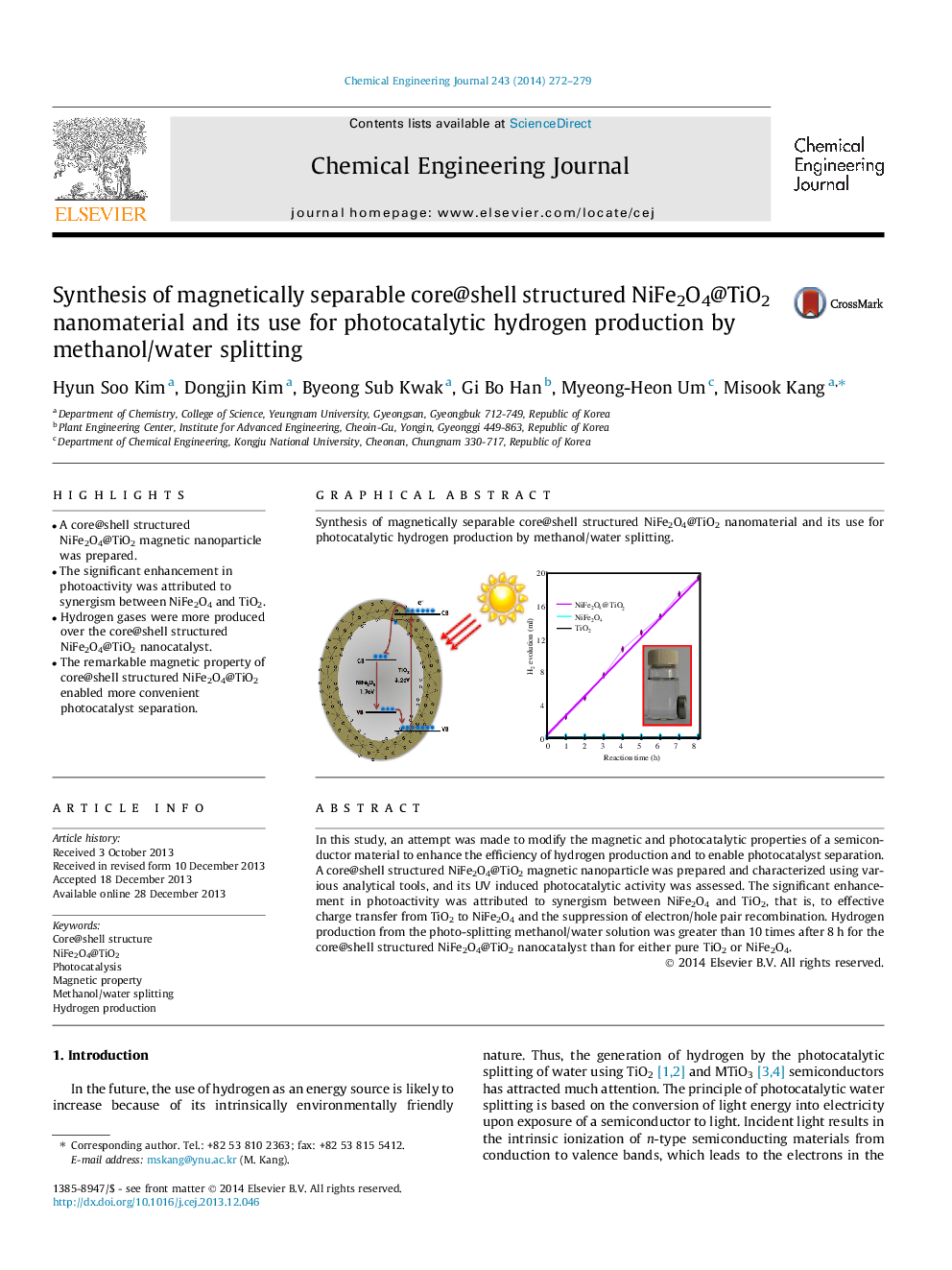
In this study, an attempt was made to modify the magnetic and photocatalytic properties of a semiconductor material to enhance the efficiency of hydrogen production and to enable photocatalyst separation. A core@shell structured NiFe2O4@TiO2 magnetic nanoparticle was prepared and characterized using various analytical tools, and its UV induced photocatalytic activity was assessed. The significant enhancement in photoactivity was attributed to synergism between NiFe2O4 and TiO2, that is, to effective charge transfer from TiO2 to NiFe2O4 and the suppression of electron/hole pair recombination. Hydrogen production from the photo-splitting methanol/water solution was greater than 10 times after 8 h for the core@shell structured NiFe2O4@TiO2 nanocatalyst than for either pure TiO2 or NiFe2O4.
Graphical abstractSynthesis of magnetically separable core@shell structured NiFe2O4@TiO2 nanomaterial and its use for photocatalytic hydrogen production by methanol/water splitting.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide