| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 147993 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2014 | 9 Pages |
•CNTs have offered higher hydrophilicity to PES/f-MWCNTs nanocomposite membranes.•PES/f-MWCNTs membranes showed good rejection capability.•Rejection efficiency has improved without compromising the permeability.
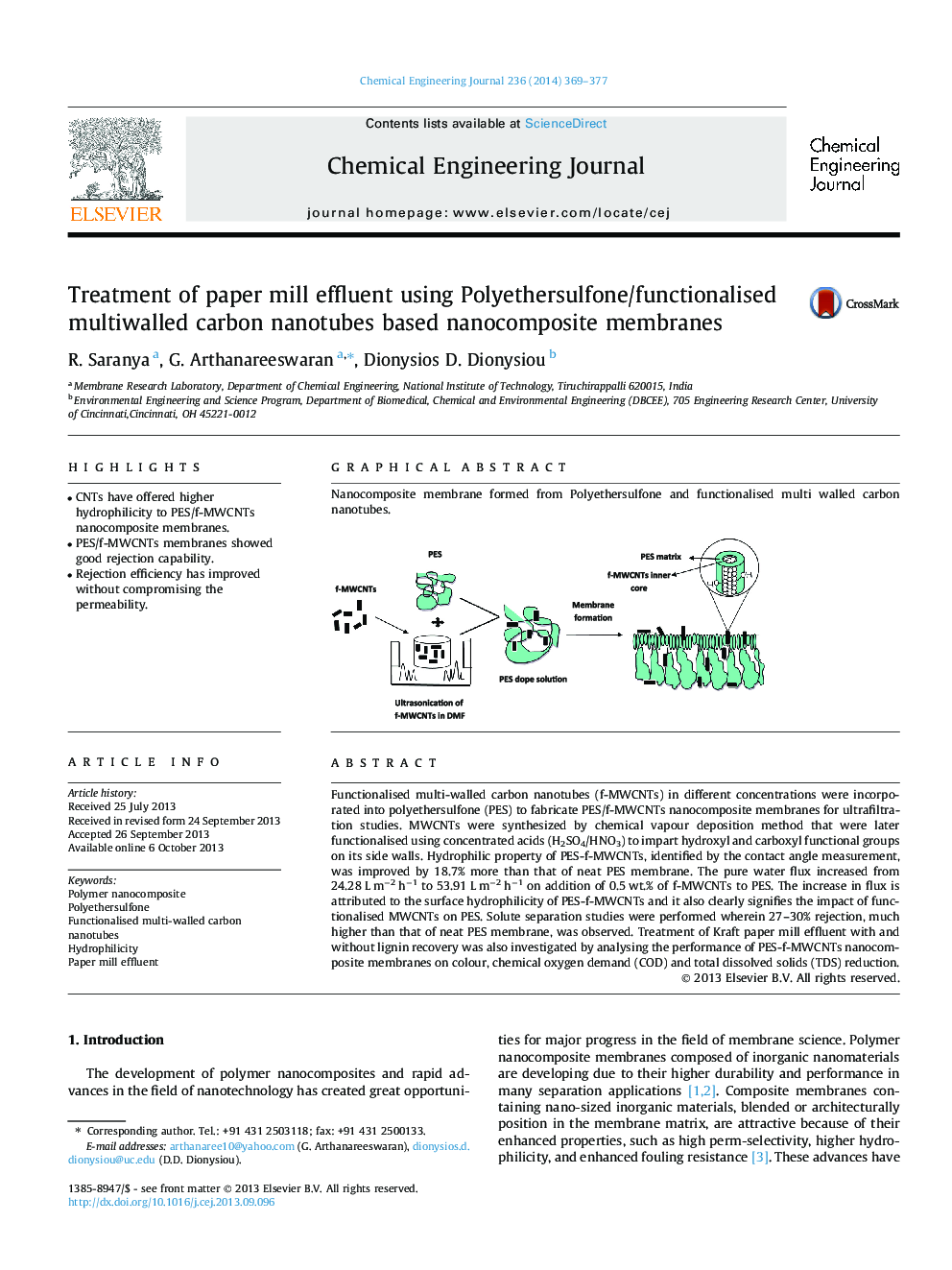
Functionalised multi-walled carbon nanotubes (f-MWCNTs) in different concentrations were incorporated into polyethersulfone (PES) to fabricate PES/f-MWCNTs nanocomposite membranes for ultrafiltration studies. MWCNTs were synthesized by chemical vapour deposition method that were later functionalised using concentrated acids (H2SO4/HNO3) to impart hydroxyl and carboxyl functional groups on its side walls. Hydrophilic property of PES-f-MWCNTs, identified by the contact angle measurement, was improved by 18.7% more than that of neat PES membrane. The pure water flux increased from 24.28 L m−2 h−1 to 53.91 L m−2 h−1 on addition of 0.5 wt.% of f-MWCNTs to PES. The increase in flux is attributed to the surface hydrophilicity of PES-f-MWCNTs and it also clearly signifies the impact of functionalised MWCNTs on PES. Solute separation studies were performed wherein 27–30% rejection, much higher than that of neat PES membrane, was observed. Treatment of Kraft paper mill effluent with and without lignin recovery was also investigated by analysing the performance of PES-f-MWCNTs nanocomposite membranes on colour, chemical oxygen demand (COD) and total dissolved solids (TDS) reduction.
Graphical abstractNanocomposite membrane formed from Polyethersulfone and functionalised multi walled carbon nanotubes..Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide