| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 148024 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2014 | 9 Pages |
•Nanoporosity governs the adsorption inspite the different origin of the activated carbons.•Oxidation products have different effect on desulfurization efficiency.•4,6-DMDBT oxidation products were found that govern the desulfurization process.•π–π Interactions contribute to the adsorption process.
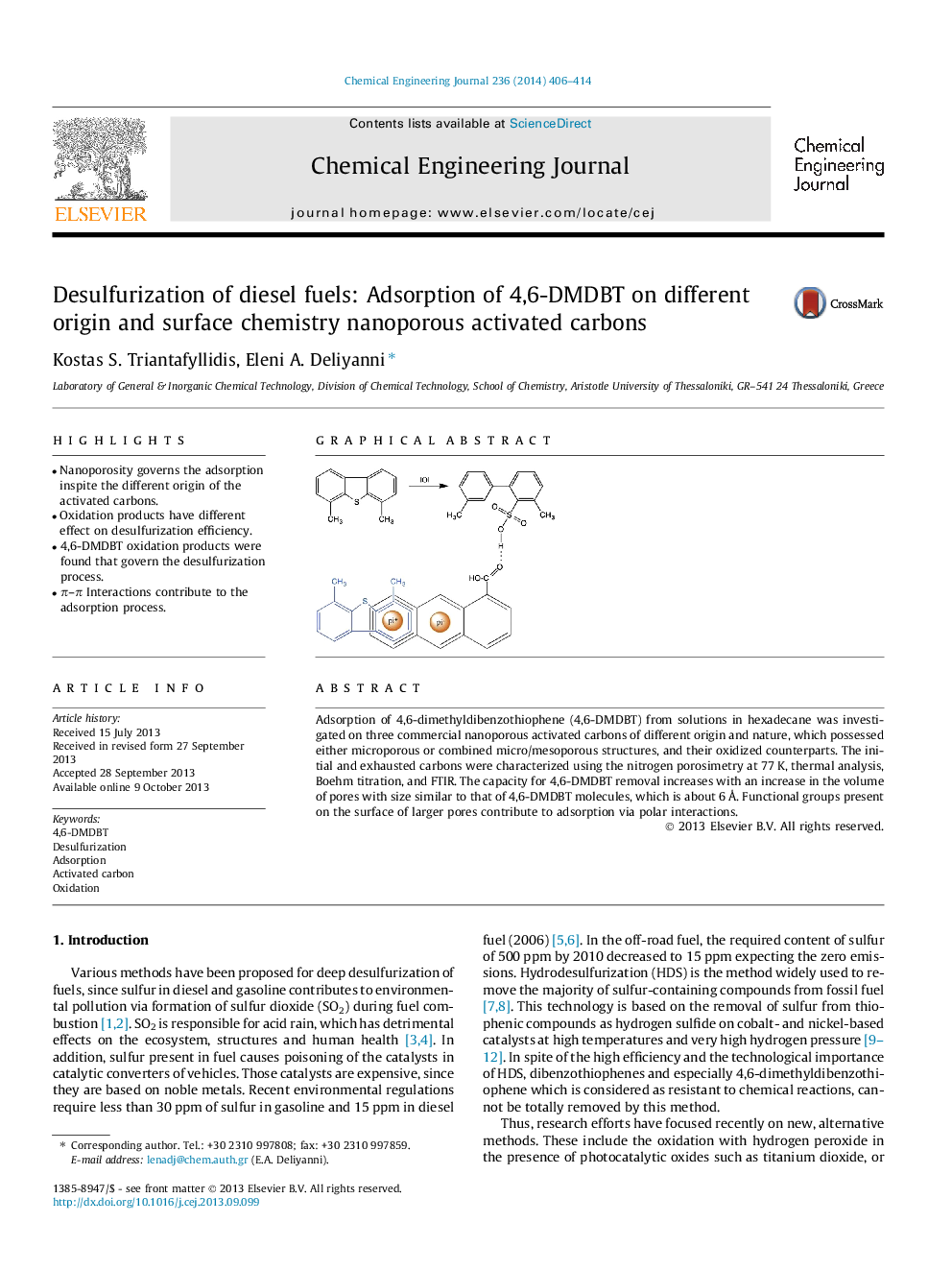
Adsorption of 4,6-dimethyldibenzothiophene (4,6-DMDBT) from solutions in hexadecane was investigated on three commercial nanoporous activated carbons of different origin and nature, which possessed either microporous or combined micro/mesoporous structures, and their oxidized counterparts. The initial and exhausted carbons were characterized using the nitrogen porosimetry at 77 K, thermal analysis, Boehm titration, and FTIR. The capacity for 4,6-DMDBT removal increases with an increase in the volume of pores with size similar to that of 4,6-DMDBT molecules, which is about 6 Å. Functional groups present on the surface of larger pores contribute to adsorption via polar interactions.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide