| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 148078 | Chemical Engineering Journal | 2013 | 9 Pages |
•A novel cationic flocculant P(AM–DAC–BA) was synthesized and characterized.•P(AM–DAC–BA) was synthesized through ultraviolet (UV) initiation.•P(AM–DAC–BA) prepared in quartz reactor was porous structure.•Comparison between quartz reactor and glass reactor was well studied.•P(AM–DAC–BA) was efficient in the dewatering of the textile sewage sludge.
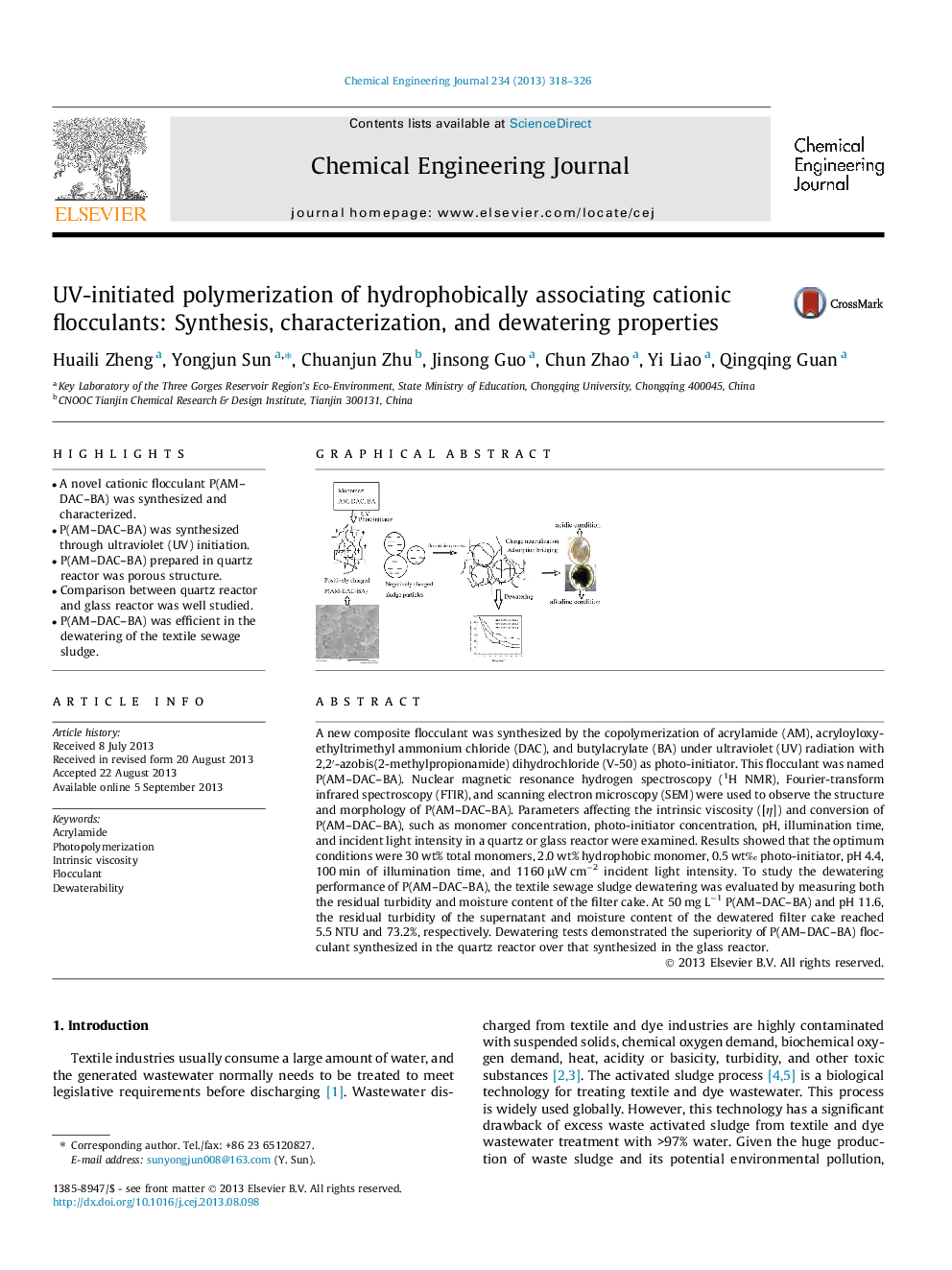
A new composite flocculant was synthesized by the copolymerization of acrylamide (AM), acryloyloxyethyltrimethyl ammonium chloride (DAC), and butylacrylate (BA) under ultraviolet (UV) radiation with 2,2′-azobis(2-methylpropionamide) dihydrochloride (V-50) as photo-initiator. This flocculant was named P(AM–DAC–BA). Nuclear magnetic resonance hydrogen spectroscopy (1H NMR), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) were used to observe the structure and morphology of P(AM–DAC–BA). Parameters affecting the intrinsic viscosity ([η]) and conversion of P(AM–DAC–BA), such as monomer concentration, photo-initiator concentration, pH, illumination time, and incident light intensity in a quartz or glass reactor were examined. Results showed that the optimum conditions were 30 wt% total monomers, 2.0 wt% hydrophobic monomer, 0.5 wt‰ photo-initiator, pH 4.4, 100 min of illumination time, and 1160 μW cm−2 incident light intensity. To study the dewatering performance of P(AM–DAC–BA), the textile sewage sludge dewatering was evaluated by measuring both the residual turbidity and moisture content of the filter cake. At 50 mg L−1 P(AM–DAC–BA) and pH 11.6, the residual turbidity of the supernatant and moisture content of the dewatered filter cake reached 5.5 NTU and 73.2%, respectively. Dewatering tests demonstrated the superiority of P(AM–DAC–BA) flocculant synthesized in the quartz reactor over that synthesized in the glass reactor.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide